Proof-of-concept exploits have already surfaced on-line for a high-severity flaw in GNU C Library’s dynamic loader, permitting native attackers to achieve root privileges on main Linux distributions.
Dubbed ‘Looney Tunables’ and tracked as CVE-2023-4911, this safety vulnerability is because of a buffer overflow weak point, and it impacts default installations of Debian 12 and 13, Ubuntu 22.04 and 23.04, and Fedora 37 and 38.
Attackers can set off it utilizing a maliciously crafted GLIBC_TUNABLES setting variable processed by the ld.so dynamic loader to achieve arbitrary code execution with root privileges when launching binaries with SUID permission.
Since Qualys’ Menace Analysis Unit disclosed it on Tuesday, a number of safety researchers have already revealed proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code that works for some system configurations.
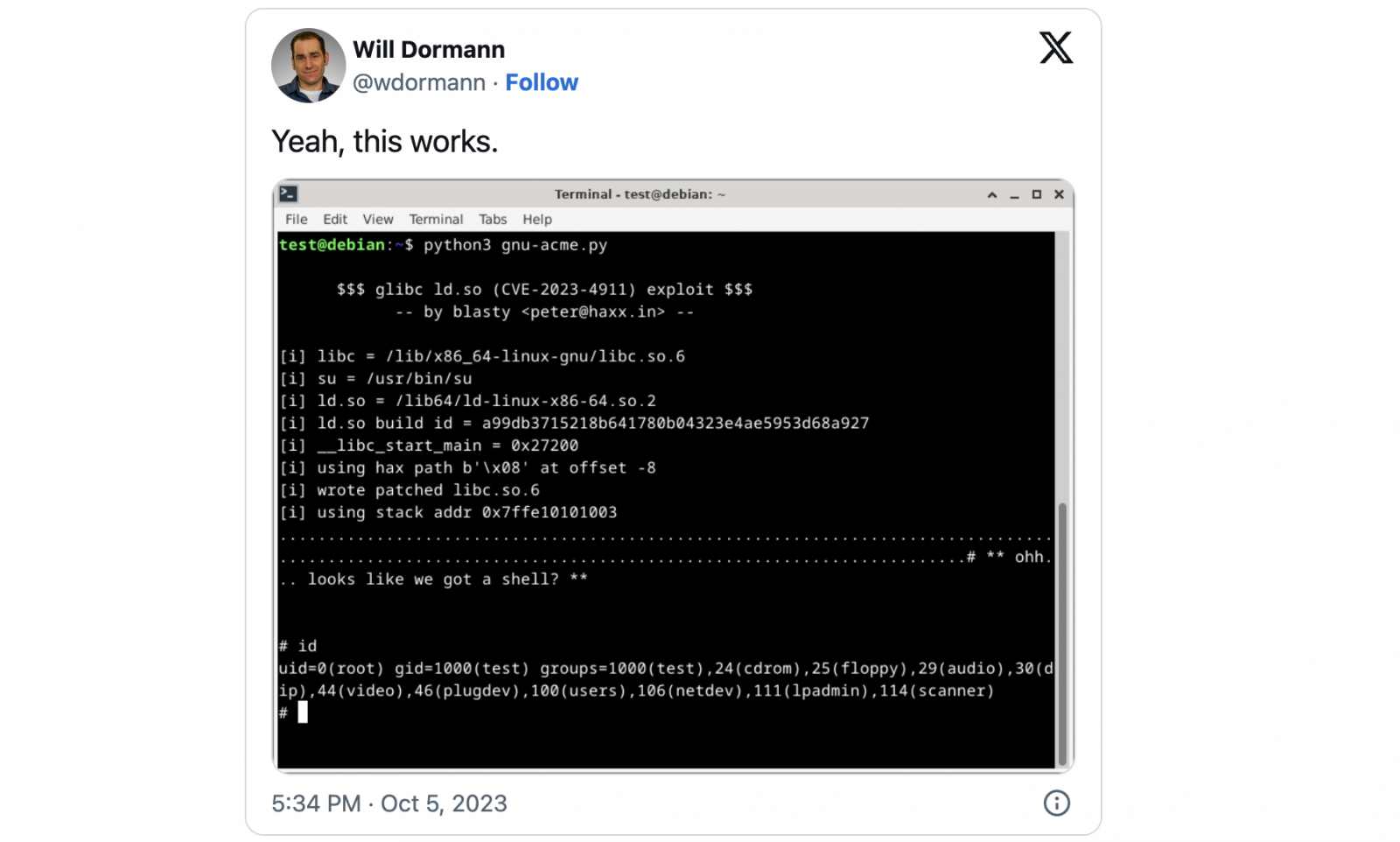
One among these PoC exploits, confirmed as working by vulnerability and exploit skilled Will Dormann, was launched by impartial safety researcher Peter Geissler (blasty) earlier immediately.
Whereas his exploit can be utilized in opposition to a restricted variety of targets, the PoC additionally consists of directions on including further ones by figuring out workable offset for every system’s ld.so dynamic loader.
Different researchers are additionally growing and quickly releasing their very own CVE-2023-4911 exploits on GitHub and elsewhere, though BleepingComputer has but to substantiate they’re working.
Directors should act promptly as a result of vital menace posed by this safety flaw, which grants full root entry to techniques working the newest releases of extensively used Linux platforms, together with Fedora, Ubuntu, and Debian.
Whereas Alpine Linux admins, a distro unaffected by this vulnerability, do not have to fret about patching their techniques, these on different affected techniques should prioritize patching to safeguard their techniques’ integrity and safety.
“Our profitable exploitation, resulting in full root privileges on main distributions like Fedora, Ubuntu, and Debian, highlights this vulnerability’s severity and widespread nature,” mentioned Saeed Abbasi, Product Supervisor at Qualys’ Menace Analysis Unit, on Tuesday.
“Though we’re withholding our exploit code for now, the convenience with which the buffer overflow could be reworked right into a data-only assault implies that different analysis groups may quickly produce and launch exploits. This might put numerous techniques in danger, particularly given the intensive use of glibc throughout Linux distributions.”
Qualys researchers have discovered and disclosed different extreme Linux safety bugs lately, together with a flaw in Polkit’s pkexec part (dubbed PwnKit), one within the Kernel’s filesystem layer (dubbed Sequoia), and one other within the Sudo Unix program (aka Baron Samedit).