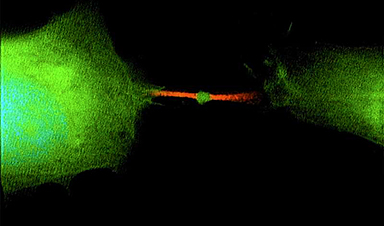
As soon as regarded as the trash can of the cell, just a little bubble of mobile stuff referred to as the midbody remnant is definitely packing working genetic materials with the ability to vary the destiny of different cells—together with turning them into most cancers.
“One cell divides into three issues: two cells and one midbody remnant, a brand new signaling organelle,” says Skop. “What shocked us is that the midbody is stuffed with genetic info, RNA, that doesn’t have a lot to do with cell division in any respect, however doubtless features in cell communication.”
In a research revealed in the present day within the journal Developmental Cell, Skop’s lab and collaborators from the Pasteur Institute in Paris, Harvard Medical Faculty, Boston College and the College of Utah analyzed the contents of midbodies—which type between the daughter cells throughout division—and tracked the interactions of the midbody remnants let loose after cell division. Their outcomes level to the midbody as a automobile for the unfold of most cancers all through the physique.
“Individuals thought the midbody was a spot the place issues died or have been recycled after cell division,” Skop says. “However one particular person’s trash is one other particular person’s treasure. A midbody is just a little packet of knowledge cells use to speak.”
The midbody’s involvement in cell signaling and stimulating cell proliferation has been investigated earlier than, however Skop and her collaborators needed to look contained in the midbody remnants to be taught extra.
What the researchers discovered inside midbodies was RNA—which is a sort of working copy of DNA used to provide the proteins that make issues occur in cells—and the mobile equipment obligatory to show that RNA into proteins. The RNA in midbodies tends to be blueprints not for the cell division course of however for proteins concerned in actions that steer a cell’s function, together with pluripotency (the flexibility to turn into any of the physique’s many several types of cells) and oncogenesis (the formation of cancerous tumors).
“A midbody remnant may be very small. It’s a micron in measurement, a millionth of a meter,” Skop says. “But it surely’s like just a little lunar lander. It’s obtained the whole lot it must maintain that working info from the dividing cell. And it might probably drift away from the positioning of mitosis, get into your bloodstream and land on one other cell far-off.”
Many midbody remnants are reabsorbed by one of many daughter cells that shed them, however people who contact down on a distant floor, like a lunar lander, could as an alternative be absorbed by a 3rd cell. If that cell swallows the midbody, it might mistakenly start utilizing the enclosed RNA as if it have been its personal blueprints.
Earlier analysis confirmed that most cancers cells are extra doubtless than stem cells to have ingested a midbody and its probably fate-altering cargo. Stem cells, which give rise to new cells and are useful for his or her pluripotency, spit lots of midbodies again out, maybe to keep up their pluripotency.
Future analysis could possibly harness the ability of midbody RNA to ship medicine to most cancers cells or to maintain them from dividing.
“We predict our findings characterize an enormous goal for most cancers detection and therapeutics,” says Skop, whose work is supported by the Nationwide Institutes of Well being.
The researchers recognized a gene, referred to as Arc, that’s key to loading the midbody and midbody remnant with RNA. Taken up way back from an historic virus, Arc additionally performs a job in the best way mind cells make reminiscences.
“Lack of Arc results in the lack of RNA within the midbody and a lack of the RNA info from attending to recipient cells,” Skop says. “We imagine this reminiscence gene is vital for all cells to speak RNA info.”
Sungjin Park, a senior scientist in Skop’s lab, is the lead creator of the brand new research. Skop and collaborators even have a patent pending on two new strategies that make it simpler to isolate midbody buildings from cell media or blood serum, bettering most cancers diagnostics.