Cynthia Horton’s earaches are the stuff of nightmares.
“I can get up from my sleep in horrible ache, like I’m having a root canal with no anesthesia,” she mentioned. “Once I sit up, my ear is usually weeping with an infection, even oozing blood.”
Already weakened by a lifelong battle with lupus, Horton’s immune system was devastated by rounds of radiation and chemotherapy after a 2003 surgical procedure for a cancerous tumor in her ear.
Ear infections grew to become the norm, normally eased by a spherical of antibiotics. However because the years handed, the micro organism in 61-year previous Horton’s ear grew to become immune to antibiotics, typically leaving her with little to no reduction.
“These multi-drug-resistant superbugs may cause persistent infections in people for months to years to generally many years. It’s ridiculous simply how virulent a few of these micro organism recover from time,” mentioned Dwayne Roach, assistant professor of bacteriophages, infectious illness and immunology at San Diego State College.
Final 12 months medical doctors provided to deal with Horton’s an infection with considered one of nature’s oldest predators — tiny tripod-looking viruses referred to as phages designed to search out, assault and gobble up micro organism.
Such infections are a “pressing international public well being menace,” killing 5 million folks worldwide, in line with 2019 statistics from the US Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention.
“It’s estimated that by 2050, 10 million folks per 12 months — that’s one particular person each three seconds — goes to be dying from a superbug an infection,” mentioned infectious illness epidemiologist Steffanie Strathdee, codirector of the primary devoted phage remedy heart in North America, the Heart for Modern Phage Purposes and Therapeutics, or IPATH, at UC San Diego College of Medication.
Anticipating a unique resolution to her recurrent ear infections, Horton was sport. Samples of her drug-resistant micro organism have been shipped from her physician’s workplace in Pennsylvania to UC San Diego’s IPATH with the hopes that phage hunters there may discover a match. What scientists found subsequent, nevertheless, was surprising.
The micro organism cultured from Horton’s ear have been an ideal match to a uncommon superbug present in sure manufacturers of over-the-counter eye drops that have been robbing folks of their imaginative and prescient and lives.
Abruptly, the seek for an answer to Horton’s downside took on new which means. Would the micro organism from her ear assist scientists discover phages that might deal with the attention infections as properly?
Lengthy-lasting and contagious
Extreme circumstances of antibiotic-resistant eye infections started popping up in Might 2022. By the next January, the CDC mentioned at least 50 sufferers in 11 states had developed superbug infections after utilizing preservative‐free synthetic tears. By Might 2023, the outbreak had unfold to 18 states: 4 folks died, one other 4 misplaced eyes, 14 suffered imaginative and prescient loss, and dozens extra developed infections in different components of the physique.
“Solely a fraction of sufferers really had eye infections, which made the outbreak extremely tough to unravel,” mentioned epidemiologist Dr. Maroya Walters, who led the CDC’s synthetic tears investigation.
“We noticed individuals who have been colonized by the organism develop urinary tract or respiratory tract infections months down the street, although they have been now not utilizing these drops,” Walters mentioned. “One affected person unfold the an infection to others within the well being care facility.”
The perpetrator was a uncommon pressure of drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa that had by no means been recognized in america earlier than the outbreak, the CDC mentioned.
Horton had by no means used eye drops, but the micro organism cultured from her ear have been the identical uncommon pressure. Utilizing these micro organism and different samples despatched by the CDC, scientists at IPATH instantly went to work and recognized greater than a dozen phages that efficiently attacked the lethal pathogen.
Scientists on the CDC have been intrigued by the invention, a lot in order that they talked about the supply of the phage therapy for the superbug on the CDC web site.
“It introduced up this concept of when we’ve an outbreak that’s brought on by micro organism with such restricted therapy choices, ought to we be eager about these various therapies?” Walters mentioned.
What is that this little creature that may topple micro organism able to withstanding all of the medication that fashionable science can muster? And extra importantly, may phage therapy develop into a serious participant within the battle to finish the superbug disaster?
The microscopic warfare inside us
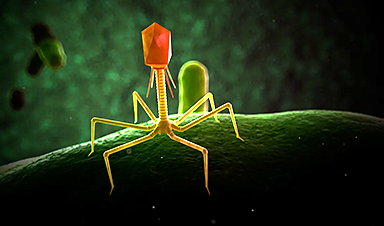
Because of evolution, the gazillions of micro organism on this planet right now have a pure enemy: tiny viruses referred to as bacteriophages genetically programmed for search-and-destroy missions. On this microscopic sport of “The Terminator,” every set of phages is uniquely designed to search out, assault and devour a selected kind of pathogen.
“Every bacterial species, and even genotypes inside it, can have an entire repertoire of phages which are attacking it, utilizing all kinds of strategies to enter and debilitate the bacterial cell,” mentioned Paul Turner, a professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at Yale College and microbiology school member at Yale College of Medication in New Haven, Connecticut.
To counter the assault, micro organism make use of varied evasive maneuvers, equivalent to shedding their outer skins to remove docking ports the phage use to enter, ravage and finally explode the pathogen into bits of bacterial goo.
That’s excellent news as a result of the newly bare micro organism could lose their resistance to antibiotics, turning into as soon as once more weak to elimination. The phage, nevertheless, is taken out of motion, now not in a position to battle.
To maximise success, specialists seek for quite a lot of phages to sort out a very nasty superbug — at occasions making a cocktail of microscopic warriors that may hopefully proceed the assault when one is neutralized.
That’s what occurred in 2016 to Strathdee’s husband, Tom Patterson, a retired professor of psychiatry at UC San Diego. As a consequence of an an infection with “Iraqibacter,” a drug-resistant bacterium discovered within the sands of Iraq, Patterson was in multi-organ failure and perilously near dying. In a race towards time, Strathdee overcame unbelievable obstacles to search out and ship a number of cocktails of purified phages to Patterson’s medical doctors.
A kind of cocktails contained a phage that “scared the micro organism a lot that it dropped its outer capsule,” mentioned Strathdee, an affiliate dean of worldwide well being sciences at UC San Diego and coauthor of “The Excellent Predator: A Scientist’s Race to Save Her Husband From a Lethal Superbug.”
“It was extra afraid of the phage, if you’ll, than the antibiotic, and that allowed the antibiotic to work once more. It was the one-two punch Tom wanted,” Strathdee mentioned. “Three days later, Tom lifted his head off the pillow out of a deep coma and kissed his daughter’s hand. It was simply miraculous.”
Phage remedy 3.0
In labs across the nation, phage scientists are taking analysis and discovery to the subsequent stage, or what Strathdee calls “phage 3.0.” Scientists in Turner’s Yale laboratory are busy mapping which phages and antibiotics are most symbiotic within the battle towards a pathogen. Roach’s San Diego State lab is investigating the physique’s immune response to phages whereas growing new phage purification methods to arrange samples for intravenous use in sufferers.
Presently, medical trials are underway to check the effectiveness of phages towards intractable urinary tract infections, persistent constipation, joint infections, diabetic foot ulcers, tonsillitis and the persistent, reoccurring infections that happen in sufferers with cystic fibrosis. The persistent infections frequent in cystic fibrosis are sometimes attributable to varied strains of drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa — the identical pathogen liable for Horton’s ear an infection and the bogus tears outbreak.
Various labs are growing libraries of phages, stockpiled with strains present in nature which are recognized to be efficient towards a specific pathogen. In Texas, a brand new facility is taking {that a} step additional — rushing up evolution by creating phages within the lab.
“Quite than simply sourcing new phages from the atmosphere, we’ve a bioreactor that in actual time creates billions upon billions of phages,” mentioned Anthony Maresso, affiliate professor at Baylor Faculty of Medication in Houston.
“Most of these phages received’t be lively towards the drug-resistant micro organism, however in some unspecified time in the future there will probably be a uncommon variant that has been skilled, so to talk, to assault the resistant micro organism, and we’ll add that to our arsenal,” Maresso mentioned. “It’s a next-generation strategy on phage libraries.”
Maresso’s lab revealed a research final 12 months on the therapy of 12 sufferers with phages custom-made to every affected person’s distinctive bacterial profile. It was a professional success: The antibiotic-resistant micro organism in 5 sufferers have been eradicated, whereas a number of extra sufferers confirmed enhancements.
“There’s a variety of approaches proper now which are occurring in parallel,” Roach mentioned. “Will we engineer phages? Will we make a phage cocktail, after which how large is the cocktail? Is it two phages or 12 phages? Ought to phages be inhaled, utilized topically or injected intravenously? There’s a variety of work underway on precisely how you can greatest do that.”
Thus far, genetic manipulation of phages has been tough due the streamlined nature of the creature: “Regular phages are optimized by evolution to be lean, imply, killing machines. There’s little or no room in there for us to get in and alter issues,” mentioned Elizabeth Villa, a professor of molecular biology at UC San Diego who research a brand new type of phage referred to as “jumbo” phages.
“Jumbo phages have very massive genomes and are available near having a nucleus that encapsulates the genetic materials, which protects them from a few of the mechanisms micro organism use towards phages to deactivate them,” mentioned Dr. Robert “Chip” Schooley, a number one infectious illness specialist at UC San Diego who’s codirector of IPATH.
“That additionally provides them room to be engineered to develop into stronger, in order that they’re very promising phages for use therapeutically,” Schooley mentioned.
Genetically engineering phages would permit scientists to focus on every particular person’s distinctive mixture of antibiotic-resistant pathogens as an alternative of looking sewage, bogs, ponds, the bilge of boats and different prime breeding grounds for micro organism to search out simply the proper phage for the job.