The research hypothesizes that ‘pre-digested’ meals contributed to the event of bigger brains.
The big, succesful human mind is a marvel of evolution, however the way it developed from a smaller primate mind into the inventive, complicated organ of right now is a thriller. Scientists can pinpoint when our evolutionary ancestors developed bigger brains, which roughly tripled in dimension as human ancestors developed from the bipedal primates referred to as Australopithecines.
However why it occurred when it did – what spurred that change – has remained elusive. Whereas some have theorized that using hearth, and the following invention of cooking, gave our ancestors sufficient nourishment for our larger-brained ancestors to grow to be dominant, a brand new principle factors to a special spark: fermentation.
The Position of Food plan in Mind Evolution
The important thing to understanding how our brains grew is most certainly rooted in what – and the way – we eat, mentioned Erin Hecht, one of many authors of the research which was just lately printed in Nature Communications Biology.
“Mind tissue is metabolically costly,” mentioned the Human Evolutionary Biology assistant professor. “It requires lots of energy to maintain it working, and in most animals, having sufficient power simply to outlive is a continuing drawback.” For larger-brained Australopiths to outlive, subsequently, one thing will need to have modified of their eating regimen. Theories put ahead have included adjustments in what these human ancestors consumed or, most popularly, that the invention of cooking allowed them to garner extra usable energy from no matter they ate.
However the issue with this principle is that the earliest proof locations using hearth at roughly 1.5 million years in the past – considerably later than the event of the hominid mind. “Our ancestors’ cranial capability started growing 2.5 million years in the past, which conservatively provides us a few 1-million-year hole within the timeline between mind dimension growing and the attainable emergence of cooking expertise,” defined Katherine L. Bryant, one of many paper’s co-authors and at present a researcher on the Institute for Language, Communication, and the Mind at Aix-Marseille Université in France. “Another dietary change will need to have been releasing metabolic constraints on mind dimension, and fermentation looks as if it may match the invoice.”
Added Hecht: “No matter modified of their diets needed to have occurred earlier than brains began getting greater.”
Fermentation: A New Perspective on Mind Development
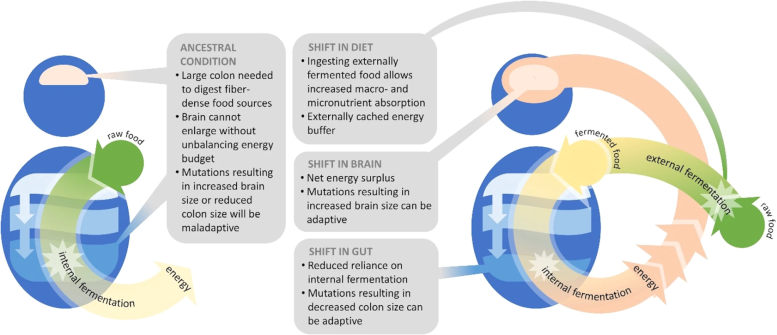
She continued, noting that in the previous couple of years, researchers have postulated different choices, such because the consumption of rotting meat. On this new paper, Hecht and her crew supply a special speculation: that cached (or saved) meals fermented, and that this “pre-digested” meals supplied a extra accessible type of nourishment, fueling that greater mind and permitting our larger-brained ancestors to outlive and thrive by way of pure choice.
The shift was in all probability a contented accident. “This was not essentially an intentional endeavor,” Hecht posited. “It could have been an unintentional facet impact of caching meals. And perhaps, over time, traditions or superstitions may have led to practices that promoted fermentation or made fermentation extra steady or extra dependable.”
This speculation is supported by the truth that the human massive gut is proportionally smaller than that of different primates, suggesting that we tailored to meals that was already damaged down by the chemical technique of fermentation. As well as, fermented meals are present in all cultures and throughout meals teams, from Europe’s wine and cheese to Asia’s soy sauce and natto, or soybeans.
Hecht instructed that a further research of mind responses to fermented and non-fermented meals may be helpful, as would possibly certainly one of olfactory and style receptors, maybe utilizing historic DNA. For the evolutionary biologist, these are all fertile areas for different researchers to choose up on. (Hecht’s focus is extra on “how mind circuits have developed to assist complicated behaviors” with analysis on each dwelling people and canine.)
As analysis progresses, Bryant sees potentialities for a variety of advantages. “This speculation additionally provides us as scientists much more causes to discover the position of fermented meals on human well being and the upkeep of a wholesome intestine microbiome,” she mentioned. “There have been various research lately linking intestine microbiome to not solely bodily however psychological well being.”
Reference: “Fermentation expertise as a driver of human mind enlargement” by Katherine L. Bryant, Christi Hansen and Erin E. Hecht, 23 November 2023, Communications Biology.
DOI: 10.1038/s42003-023-05517-3