The elevated use of language understanding in search engines like google has prioritized writing content material that’s organized by subjects and subtopics and communicates the message in a method that lacks ambiguity. Semantic HTML makes it clear to search engines like google precisely the place the content material you wish to be listed is on a webpage, which is why it ought to be thought-about for each search engine optimisation and web site accessibility.
To be clear, Semantic HTML isn’t a rating issue. It’s simply one thing that makes it simpler for search engines like google to determine the place the principle content material of a webpage is, which is an excellent factor.
Search Engines Focus On The Primary Content material
Google’s Search High quality Rater Pointers makes a distinction between three sorts of content material on a webpage:
- Primary content material
- Supplementary content material
- Promoting content material
Primary Content material
Primary content material is what the major search engines wish to index and rank.
Supplementary Content material
Supplementary content material is helpful, like website navigation nevertheless it’s not what the major search engines are fascinated by indexing.
Promoting Content material
Promoting content material can be not what search engines like google go to a webpage to crawl.
Semantic HTML Helps Webpages Obtain Their Goal
The excellence between principal content material and the opposite two sorts of content material is that the Supplementary and Promoting content material don’t assist obtain the aim of the webpage.
Solely the Primary Content material helps a webpage obtain its function and in accordance with the Search High quality Raters Pointers, these are those that obtain the next Web page High quality rating by the raters.
Whereas that’s most likely not a rating sign, creating principal content material that achieves the aim of the webpage continues to be a aim that each writer and search engine optimisation ought to work towards.
The Raters Information states on the very starting of Half 1:
“A Web page High quality (PQ) ranking activity consists of a URL and a grid to file your observations as you discover the touchdown web page and the web site related to the URL.
The aim of PQ ranking is to guage how nicely the web page achieves its function.”
The important thing to reaching the aim is within the Primary Content material. Semantic HTML is what helps the search engine crawler zero in on that principal content material.
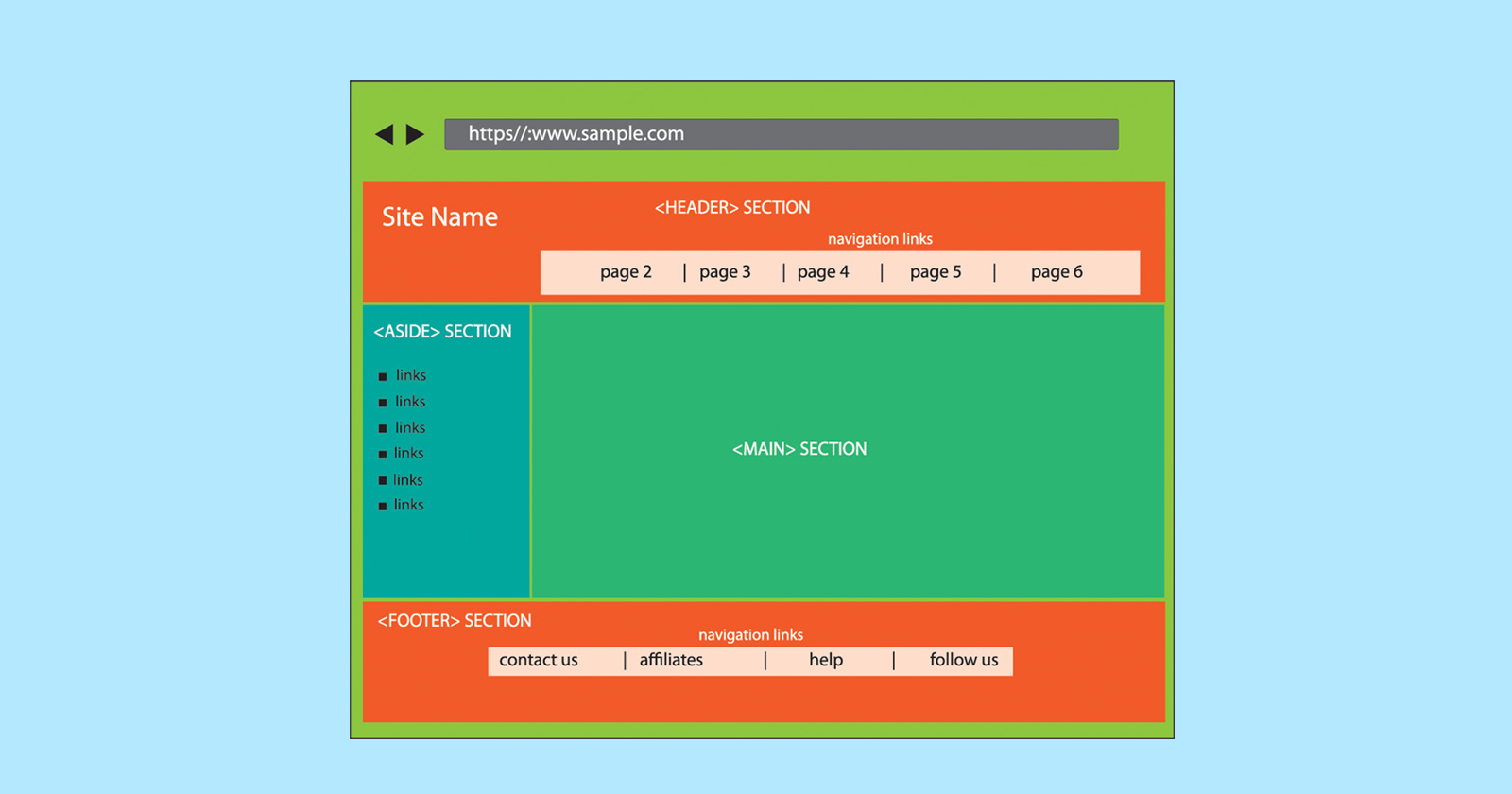
Idea of Web page Construction – Semantic HTML
Rule quantity one in every of search engine optimisation is to make webpages simple for search engines like google to know.
Semantic HTML will be essentially the most basic degree of webpage content material upon which the construction of the complete webpage will be neatly organized into the three components (principal content material, supplementary content material and promoting content material).
After we discuss Semantic HTML, we’re not speaking concerning the that means of phrases. Within the context of HTML, the phrase “semantic” is concerning the that means of a webpage, damaged down into the part components.
Identical to a physique is product of a head, torso, legs and arms, a webpage can be a group of components.
The standard construction of a webpage seems like this:
- Header (the highest half with the brand)
- Navigation
- Primary Content material
- Footer
Do you see the half that’s referred to as Primary Content material? That is the half that the major search engines are most fascinated by when indexing a webpage. It’s the half that the Search High quality Raters Pointers referred to.
When indexing a webpage, search engines like google don’t care concerning the navigation, footer, promoting, sidebars or the header sections. They care about indexing the principle content material.
Semantic HTML tells the major search engines precisely the place the principle content material exists in order that the indexer can seize it and rank it.
The <principal> HTML Ingredient
Telling a search engine what content material on a webpage to index is as simple as utilizing the <principal> HTML ingredient.
The <principal> ingredient has a gap tag (<principal>) to mark the place the principle content material begins.
And it has a closing tag (</principal>) to mark the place the principle content material ends.
A webpage can solely have one <principal> part.
Within the part the place your principal content material begins, simply drop within the <principal> ingredient. Then use the closing HTML </principal> ingredient, to indicate the place the principle part of the content material ends.
This makes it tremendous simple for the major search engines to get to the principle content material and index it.
That’s nice proper? Properly, it will get even higher.
<header> <nav> And <footer> Parts
There are just a few extra semantic HTML parts for dividing a web page into the part components.
<header>
The <header> ingredient can be utilized to indicate the realm on the high of the web page the place the brand and perhaps a search bar go. It’s the part that’s usually above the navigation space. The <header> ingredient can be used to wrap round headings (H1, H2, and so forth.) however that’s probably not obligatory.
<nav>
The <nav> ingredient is what you wrap round your navigation space. For instance, if the navigation space is inside a <div></div> you possibly can add the <nav> parts after the <div>.
Instance:
<div> <nav> principal navigation hyperlinks and stuff</nav> </div>
Technically the <div> ingredient isn’t obligatory if the <nav> ingredient is in use. They each behave as containers, precisely the identical in all fashionable browsers. The <nav> ingredient is a container like a <div> however the <nav> is a container that has a semantic that means whereas the div has no semantic that means, it’s only a container.
A <nav> ingredient will be inside a <div> ingredient however a <div> ingredient shouldn’t be inside a <nav> ingredient as a result of solely navigational parts like hyperlinks will be inside a <nav> ingredient. It may be achieved nevertheless it’s potential that this would possibly confuse a display reader .
<footer>
The <footer> ingredient, just like the <nav> ingredient, is a container like a div with the one distinction being that the <footer> ingredient has a semantic that means.
Semantic HTML For Supplementary Content material
Suppose you will have a webpage that has principal content material, nevertheless it additionally has sidebars, ads and call-out packing containers that comprise additional data that’s peripherally associated to the principle content material.
Semantic HTML has a component referred to as the <apart> HTML ingredient.
The <apart> ingredient additionally has a gap and a closing tag that denotes the start and the top of the <apart> content material.
It seems like this:
<apart></apart>
And it’s used like this:
<apart> <p>Stuff that is off subject to the principle content material however inside the principle content material space.</p> </apart> <apart><div>affiliate promoting</div></apart> <apart>Sidebar with content material that isn't part of the principle content material</apart>
The <article> Semantic HTML Ingredient
Semantic HTML permits a writer or search engine optimisation to make it clear what a part of the content material is the precise article. The <article> ingredient will be nested throughout the <principal> ingredient (however not the opposite method round). That mentioned, the only and most sensible use of the <article> ingredient is on a content material class web page the place you will have web page titles and web page excerpts for various pages.
A gap <article> and shutting </article> ingredient can wrap across the particular person title/excerpts as a result of a number of <article> parts are allowed on a web page.
There Are Many Semantic HTML Parts
There are about 100 semantic parts, however you don’t have to make use of all of them.
If you wish to be taught extra about Semantic parts try the Mozilla developer pages about Semantic HTML, it’s a helpful useful resource.
On the absolute all-time low, the least that can be utilized are the <principal> and the <apart> parts.
Even higher, use the <header>, <nav> and <footer> parts, too as a result of they’re helpful in making a overview of the complete webpage, like a format of the webpage.
Different helpful Semantic HTML parts are <button>, <kind> and <part>, which helps for accessibility causes.
Glad coding!
Featured Picture by Shutterstock/avilledorsa