In context: Diamonds are among the many most promising supplies for tech functions, reminiscent of quick telecommunications and energy conversion in electrical autos or energy vegetation. Nonetheless, diamonds aren’t simple to work with, as they have an inclination to crack when attempting to chop wafers out of them.
A brand new laser-based method developed by a workforce of Japanese scientists from Chiba College seemingly supplies a option to “effortlessly slice” diamonds alongside the optimum crystallographic airplane. The analysis was just lately printed within the journal Diamond and Associated Supplies, and it might help the semiconductor business in adopting one of many sturdiest supplies recognized to man.
Diamonds have engaging properties for semiconductor functions, the researchers mentioned, as they’ve a wider bandgap than silicon. They may theoretically be employed to create extra environment friendly semiconductors, able to working at increased voltages, frequencies, and temperatures. Nonetheless, diamonds are difficult to adapt into semiconductors as a result of there is no such thing as a environment friendly method to slice them into skinny wafers.
Professor Hirofumi Hidai and his workforce at Chiba College are proposing an answer to the issue: a laser-based slicing course of that may cleanly minimize diamonds with out breaking them. The researchers acknowledged that the brand new method prevents the propagation of undesirable cracks in the course of the laser-cutting course of by focusing quick laser pulses onto a slender cone-like quantity inside the materials.
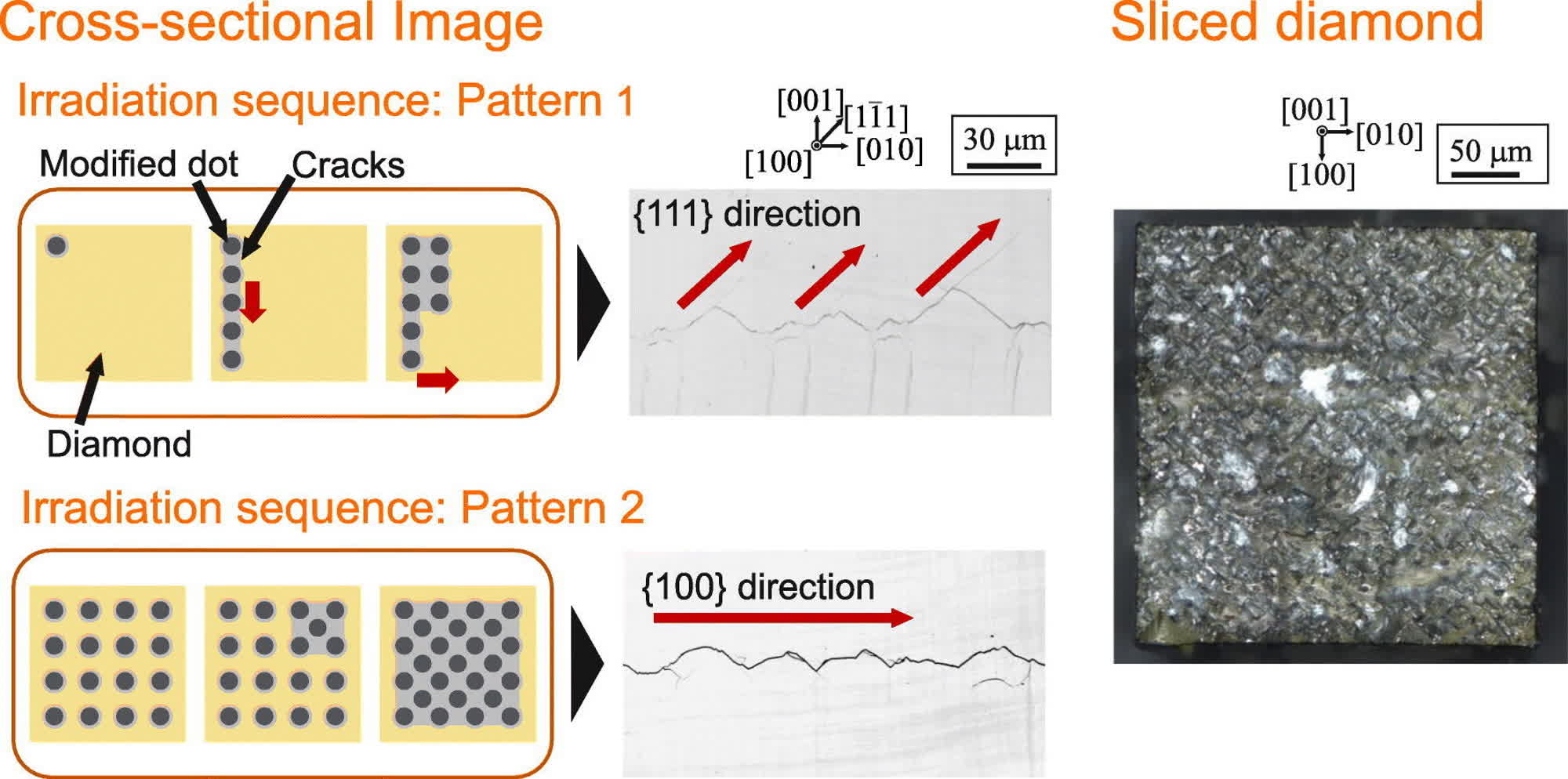
The laser pulses flip diamond into amorphous carbon with decrease density ranges. Due to this fact, the areas shot with the laser endure a discount in density and crack formation, Professor Hidai mentioned. The researchers created a grid-like sample to information the propagation of cracks alongside the designated reducing path, whereas a pointy tungsten needle was used to “simply” separate a clean wafer from the remainder of the diamond block.
Chiba College mentioned the brand new proposed method might be a pivotal step in direction of turning diamonds right into a “appropriate semiconductor materials” for future, extra environment friendly applied sciences. Professor Hidai remarked how slicing diamonds with a laser “allows the manufacturing of high-quality wafers at a low value” and is indispensable for fabricating diamond semiconductor units.
The Japanese analysis brings the business nearer to realizing diamond semiconductors for varied expertise functions, Hidai mentioned. The laser-sliced wafers might enhance the ability conversion ratio in electrical autos and trains.
Chiba College and Hidai’s workforce will not be alone of their effort to show diamonds into semiconductors. Amazon Net Providers just lately partnered with Component Six (a subsidiary of the De Beers diamond consortium) to create artificial diamonds and use them in quantum cryptography. The 2 firms try to use photon-absorbing defects in diamonds to create a world community for quantum key distribution.