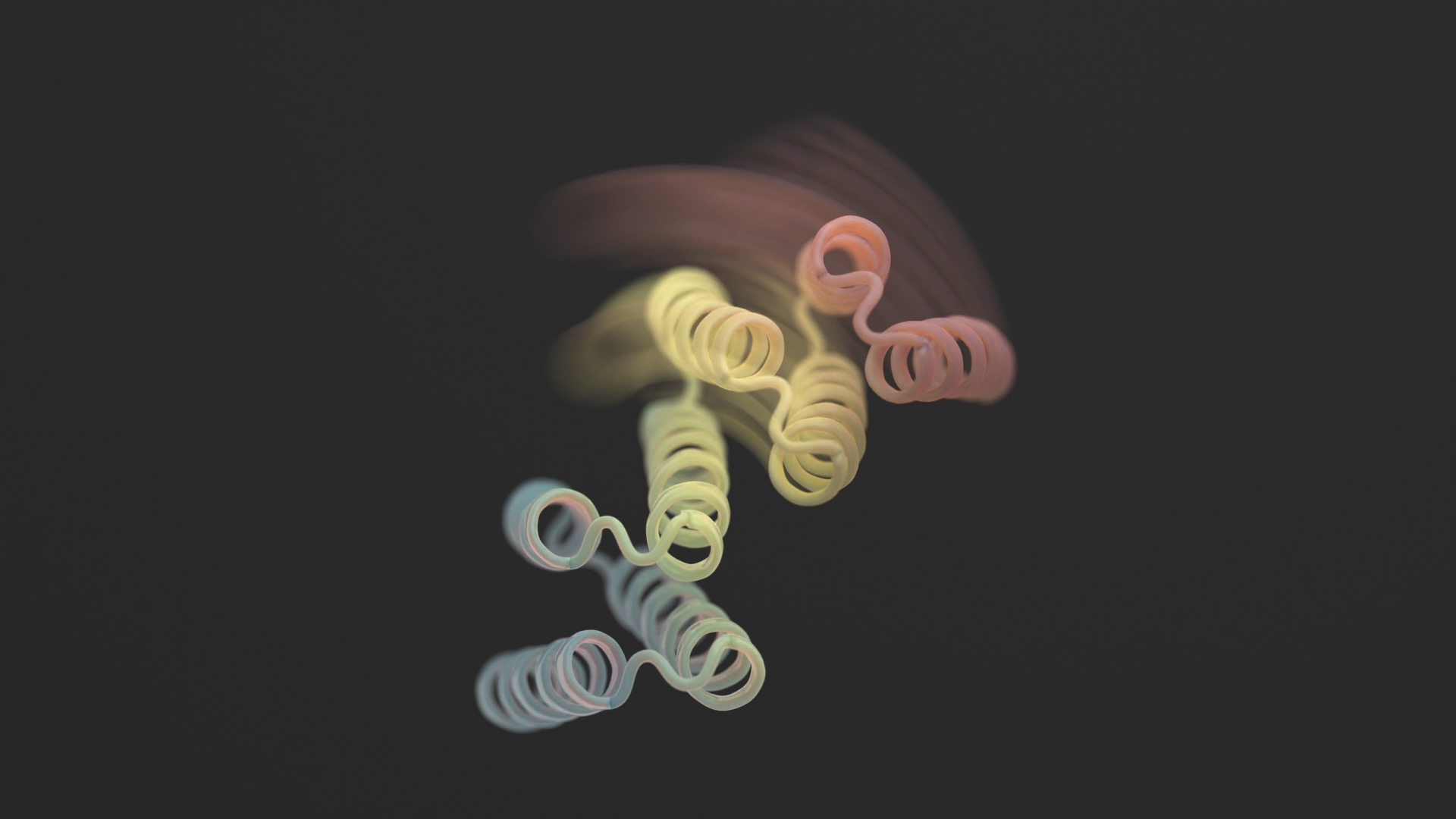We regularly consider proteins as immutable 3D sculptures.
That’s not fairly proper. Many proteins are transformers that twist and alter their shapes relying on organic wants. One configuration might propagate damaging alerts from a stroke or coronary heart assault. One other might block the ensuing molecular cascade and restrict hurt.
In a approach, proteins act like organic transistors—on-off switches on the root of the physique’s molecular “pc” figuring out the way it reacts to exterior and inside forces and suggestions. Scientists have lengthy studied these shape-shifting proteins to decipher how our our bodies operate.
However why depend on nature alone? Can we create organic “transistors,” unknown to the organic universe, from scratch?
Enter AI. A number of deep studying strategies can already precisely predict protein constructions—a breakthrough half a century within the making. Subsequent research utilizing more and more highly effective algorithms have hallucinated protein constructions untethered by the forces of evolution.
But these AI-generated constructions have a downfall: though extremely intricate, most are fully static—primarily, a form of digital protein sculpture frozen in time.
A brand new research in Science this month broke the mould by including flexibility to designer proteins. The brand new constructions aren’t contortionists with out limits. Nevertheless, the designer proteins can stabilize into two totally different varieties—assume a hinge in both an open or closed configuration—relying on an exterior organic “lock.” Every state is analogous to a pc’s “0” or “1,” which subsequently controls the cell’s output.
“Earlier than, we may solely create proteins that had one steady configuration,” mentioned research writer Dr. Florian Praetorius on the College of Washington. “Now, we will lastly create proteins that transfer, which ought to open up a unprecedented vary of functions.”
Lead writer Dr. David Baker has concepts: “From forming nanostructures that reply to chemical substances within the setting to functions in drug supply, we’re simply beginning to faucet into their potential.”
A Protein Marriage Made in AI
A fast little bit of biology 101.
Proteins construct and run our our bodies. These macromolecules start their journey from DNA. Genetic info is translated into amino acids, the constructing blocks of a protein—image beads on a string. Every string is then folded into intricate 3D shapes, with some elements sticking to others. Known as secondary constructions, some configurations appear like Twizzlers. Others weave into carpet-like sheets. These shapes additional construct on one another, forming extremely subtle protein architectures.
By understanding how proteins achieve their shapes, we will probably engineer new ones from scratch, increasing the organic universe and creating new weapons towards viral infections and different ailments.
Again in 2020, DeepMind’s AlphaFold and David Baker lab’s RoseTTAFold broke the structural biology web by precisely predicting protein constructions based mostly on their amino acid sequences alone.
Since then, the AI fashions have predicted the form of virtually each protein recognized—and unknown—to science. These highly effective instruments are already reshaping organic analysis, serving to scientists shortly nail down potential targets to fight antibiotic resistance, research the “housing” of our DNA, develop new vaccines and even make clear ailments that ravage the mind, like Parkinson’s illness.
Then got here a bombshell: generative AI fashions, corresponding to DALL-E and ChatGPT, provided a tantalizing prospect. Relatively than merely predicting protein constructions, why not have AI dream up fully novel protein constructions as a substitute? From a protein that binds hormones to manage calcium ranges to synthetic enzymes that catalyze bioluminescence, preliminary outcomes sparked enthusiasm and the potential for AI-designed proteins appeared limitless.
On the helm of those discoveries is Baker’s lab. Shortly after releasing RoseTTAFold, they additional developed the algorithm to nail down purposeful websites on a protein—the place it interacts with different proteins, medication, or antibodies—paving the best way for scientists to dream up new medicines they haven’t but imagined.
But one factor was lacking: flexibility. Numerous proteins “code shift” in form to alter their organic message. The outcome may actually be life or demise: a protein referred to as Bax, for instance, alters its form right into a conformation that triggers cell demise. Amyloid beta, a protein concerned in Alzheimer’s illness, notoriously takes a distinct form because it harms mind cells.
An AI that hallucinates comparable flip-flop proteins may edge us nearer to understanding and recapitulating these organic conundrums—resulting in new medical options.
Hinge, Line, and Sinker
Designing one protein on the atomic stage—and hoping it really works in a residing cell—is difficult. Designing one with two configurations is a nightmare.
As a free analogy, consider ice crystals in a cloud that ultimately kind into snowflakes, every one totally different in construction. The AI’s job is to make proteins that may shift between two totally different “snowflakes” utilizing the identical amino acid “ice crystals,” with every state equivalent to an “on” or “off” change. Moreover, the protein has to play good inside residing cells.
The workforce started with a number of guidelines. First, every construction ought to look vastly totally different between the 2 states—like a human profile standing or sitting. They might test this by measuring distances between atoms, defined the workforce. Second, the change must occur quick. This implies the protein can’t fully unfurl earlier than piecing itself again collectively into one other form, which takes time.
Then there are some groundskeeping tips for a purposeful protein: it must play good with bodily liquids in each states. Lastly, it has to behave as a change, altering its form relying on inputs and outputs.
Assembly all “these properties in a single protein system is difficult,” mentioned the workforce.
Utilizing a mixture of AlphaFold, Rosetta, and proteinMPNN, the ultimate design appears like a hinge. It has two inflexible elements that may transfer relative to one another, whereas one other piece stays folded. Usually the protein is closed. The set off is a small peptide—a brief chain of amino acids—that binds to the hinges and triggers its form change. These so-called “effector peptides” have been fastidiously designed for specificity, decreasing their probabilities of grabbing onto off-target elements.
The workforce first added glow-in-the-dark set off peptides to a number of hinge designs. Subsequent evaluation discovered that the set off simply grabbed onto the hinge. The protein’s configuration modified. As a sanity test, the form was one beforehand predicted utilizing AI evaluation.
Extra research utilizing crystallized constructions of the protein designs, both with or with out the effector, additional validated the outcomes. These exams additionally hunted down design ideas that made the hinge work, and parameters that tip one state to the opposite.
The take away? AI can now design proteins with two totally different states—primarily constructing organic transistors for artificial biology. For now, the system solely makes use of custom-designed effector peptides of their research, which can restrict analysis and scientific potential. However in keeping with the workforce, the technique may prolong to pure peptides, corresponding to people who bind proteins concerned in regulating blood sugar, regulate water in tissues, or affect mind exercise.
“Like transistors in digital circuits, we will couple the switches to exterior outputs and inputs to create sensing gadgets and incorporate them into bigger protein methods,” the workforce mentioned.
Examine writer Dr. Philip Leung provides: “This might revolutionize biotechnology in the identical approach transistors reworked electronics.”
Picture Credit score: Ian C Haydon/ UW Institute for Protein Design