Is there something ChatGPT can’t do? Sure, after all, however the record seems to be getting smaller and smaller. Now, researchers have used the big language mannequin to assist them design and assemble a tomato-picking robotic.
Giant language fashions (LLMs) can course of and internalize enormous quantities of textual content information, utilizing this info to reply questions. OpenAI’s ChatGPT is one such LLM.
In a brand new case research, researchers from the Delft College of Expertise within the Netherlands and the Swiss Federal Institute of Expertise (EPFL) enlisted the assistance of ChatGPT-3 to design and assemble a robotic, which could appear unusual contemplating that ChatGPT is a language mannequin.
“Although ChatGPT is a language mannequin and its code technology is text-based, it supplied important insights and instinct for bodily design, and confirmed nice potential as a sounding board to stimulate human creativity,” stated Josie Hughes, a co-author of the printed case research concerning the expertise.
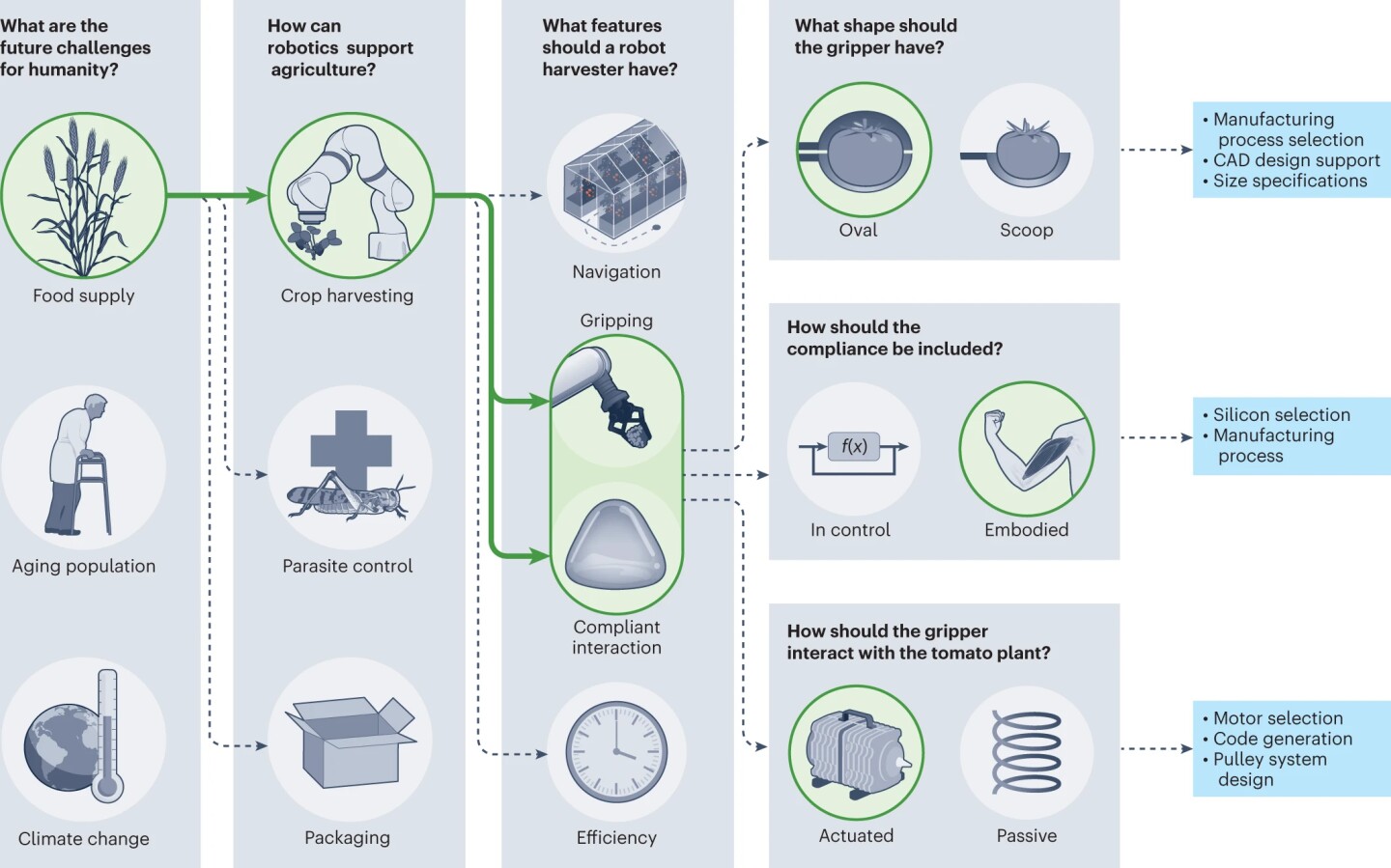
First, the researchers requested the AI mannequin, “What are the longer term challenges for humanity?” ChatGPT proposed three: meals provide, an growing old inhabitants and local weather change. The researchers selected meals provide as probably the most promising route for robotic design as a result of it was exterior their space of experience.
Utilizing the LLM’s entry to world information sourced from tutorial publications, technical manuals, books, and media, the researchers requested the AI what incorporates a robotic harvester ought to have. ChatGPT got here up with a motor-driven gripper for pulling ripe tomatoes from the vine.
As soon as this normal design was selected, the researchers may transfer on to design specifics, together with what building supplies can be used and creating laptop code that will management it. Presently, LLMs can’t generate complete computer-assisted design (CAD) fashions, consider code or robotically fabricate a robotic, so this step required the researchers to undertake a ‘technician’ position the place they assisted with these features, optimizing the code written by the LLM, finalizing the CAD and fabricating the robotic.
Stella et al./EPFL/TU Delft
“Whereas computation has been largely used to help engineers with technical implementation, for the primary time, an AI system can ideate new programs, thus automating high-level cognitive duties,” stated Francesco Stella, lead creator of the case research. “This might contain a shift of human roles to extra technical ones.”
Based mostly on the technical ideas supplied by ChatGPT-3, the researchers constructed their robotic gripper and examined it in the true world, utilizing it to select tomatoes, which it did efficiently.

Stella et al./EPFL/TU Delft
The researchers say that their case research demonstrates the potential for reworking the design course of via collaboration between people and LLMs, however they’re conscious that it opens the door to various levels of collaboration.
At one excessive, they are saying, AI would act as an ‘inventor,’ offering the whole thing of the robotic design enter with people blindly making use of it. Another can be to make use of an AI’s wide-ranging data to complement human experience. A 3rd method can be to retain the human as an inventor and use AI to refine the design course of via troubleshooting, debugging, and dealing with tedious or time-consuming processes.
The researchers increase moral and commonsense dangers that will outcome from a human-AI collaboration. They level to problems with bias, plagiarism, and mental property (IP) rights as areas of concern and query whether or not an LLM-generated design might be thought of ‘novel’ on condition that it makes use of present data.
“In our research, ChatGPT recognized tomatoes because the crop ‘most value’ pursuing for a robotic harvester,” Hughes stated. “Nonetheless, this can be biased in direction of crops which are extra lined in literature, versus these the place there may be really an actual want. When selections are made exterior the scope of data of the engineer, this will result in important moral, engineering, or factual errors.”
Regardless of these issues, the researchers consider there may be nice potential in human-AI collaboration if it’s properly managed.
“The robotics group should determine how you can leverage these highly effective instruments to speed up the development of robots in an moral, sustainable and socially empowering manner,” the researchers stated. “Wanting ahead, we strongly consider that LLMs will open up many thrilling potentialities and that, if opportunely managed, they are going to be a power for good.”
The case research was printed within the journal Nature Machine Intelligence.
Supply: EPFL

