Introduction
In as we speak’s digital age, WhatsApp has emerged as greater than only a messaging app; it is a pivotal communication instrument for companies worldwide. With over two billion lively customers, WhatsApp’s huge attain and recognition make it an indispensable platform for companies aiming to attach with their viewers successfully.
Understanding this, our goal on this weblog is to supply a complete information on leveraging WhatsApp for sending messages through it is API. This follow, a vital a part of trendy enterprise communication methods, includes reaching quite a few prospects with necessary updates, promotional content material, or different related info. We’ll discover ways to ship messages utilizing Whatsapp API in python. We’ll then delve into the intricacies of WhatsApp’s options, notably specializing in its Enterprise API, which gives superior capabilities for dealing with messaging effectively.
Furthermore, we’ll discover the combination of those messaging capabilities with workflow automation. In a enterprise panorama the place effectivity and pace are paramount, automating repetitive duties like message sending can considerably improve productiveness. Instruments like Nanonets Workflows play a vital position on this. They permit companies to streamline their operations, lowering handbook effort and focusing extra on strategic duties.
Whatsapp Enterprise Platform
The WhatsApp Enterprise Platform is designed for medium to massive companies, offering a method to have interaction with prospects on a big scale. It allows fast initiation of conversations, sending notifications about care or purchases, providing customized companies, and supporting prospects of their most popular communication channel.
This platform is constructed round three key APIs:
- Cloud API: That is hosted by Meta and gives a simple, maintenance-friendly means for companies to attach with prospects.
- On-Premises API: Companies have to host this themselves.
- Enterprise Administration API: This API is crucial for managing your WhatsApp Enterprise Account and message templates.
To speak with WhatsApp customers, companies have to make use of both the Cloud API or the On-Premises API. The Cloud API is mostly most popular because of its simplicity and decrease upkeep necessities. Nonetheless, irrespective of which API you select, the Enterprise Administration API is a should for managing your account and templates.
Introduction to Whatsapp Cloud API
WhatsApp’s Cloud API, a part of Meta’s Blueprint, permits companies to speak with prospects on a big scale with out the necessity for internet hosting their very own servers. This service is a cloud-hosted model of the WhatsApp Enterprise Platform, providing straightforward scaling and implementation.
Overview
The WhatsApp Enterprise API is designed for medium and enormous companies to interact in automated and handbook communications with prospects. It helps integration with varied backend programs like CRM and advertising and marketing platforms. Companies can select between On-Premises and Cloud API choices, with the latter usually beneficial because of its simplicity.
Default throughput is 80 messages per second (mps), upgradable to 1,000 mps.
Utilizing the API
To ship a message, a API name in python appears to be like like this:
import requests
url="https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/FROM_PHONE_NUMBER_ID/messages"
headers = {
'Authorization': 'ACCESS_TOKEN'
}
knowledge = {
'messaging_product': 'whatsapp',
'to': '1650XXXXXXX',
'textual content': {'physique': 'hello'}
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, json=knowledge)
print(response.textual content)
Getting Began
To start out with Cloud API:
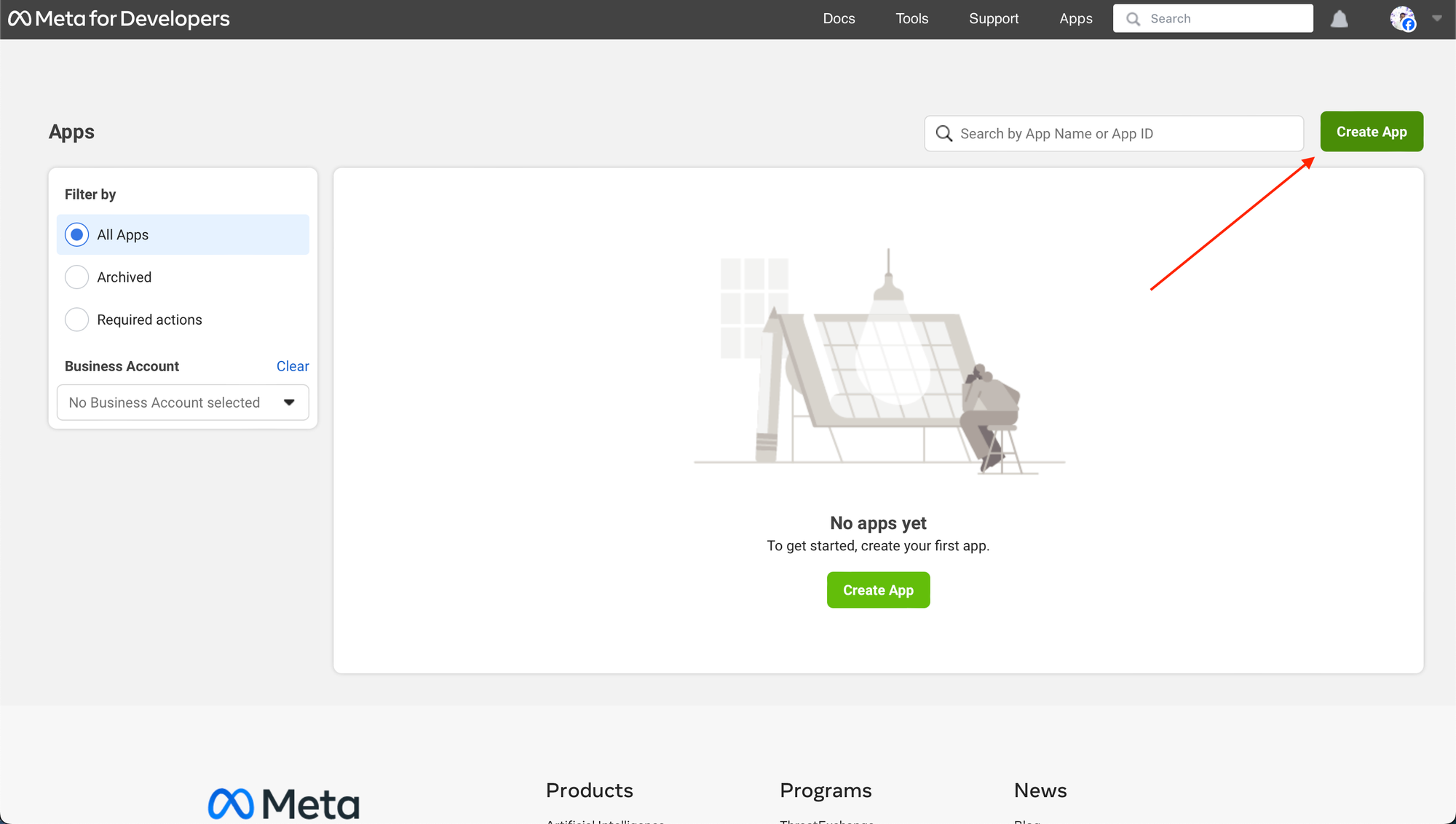
- Select “Different” within the use case part.
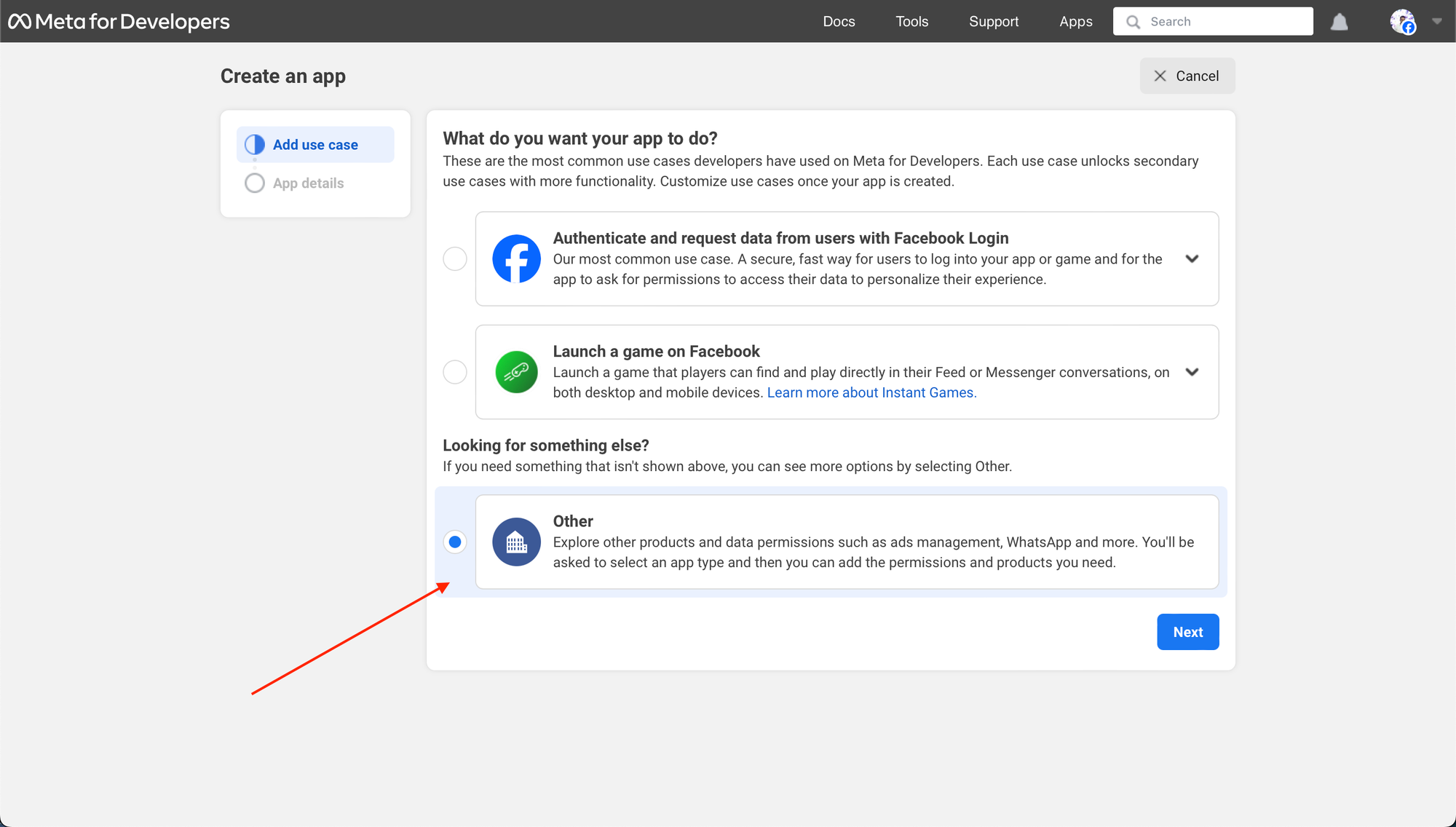
- Select “Enterprise” as App Kind.
- Add app particulars and click on on “Create App”.
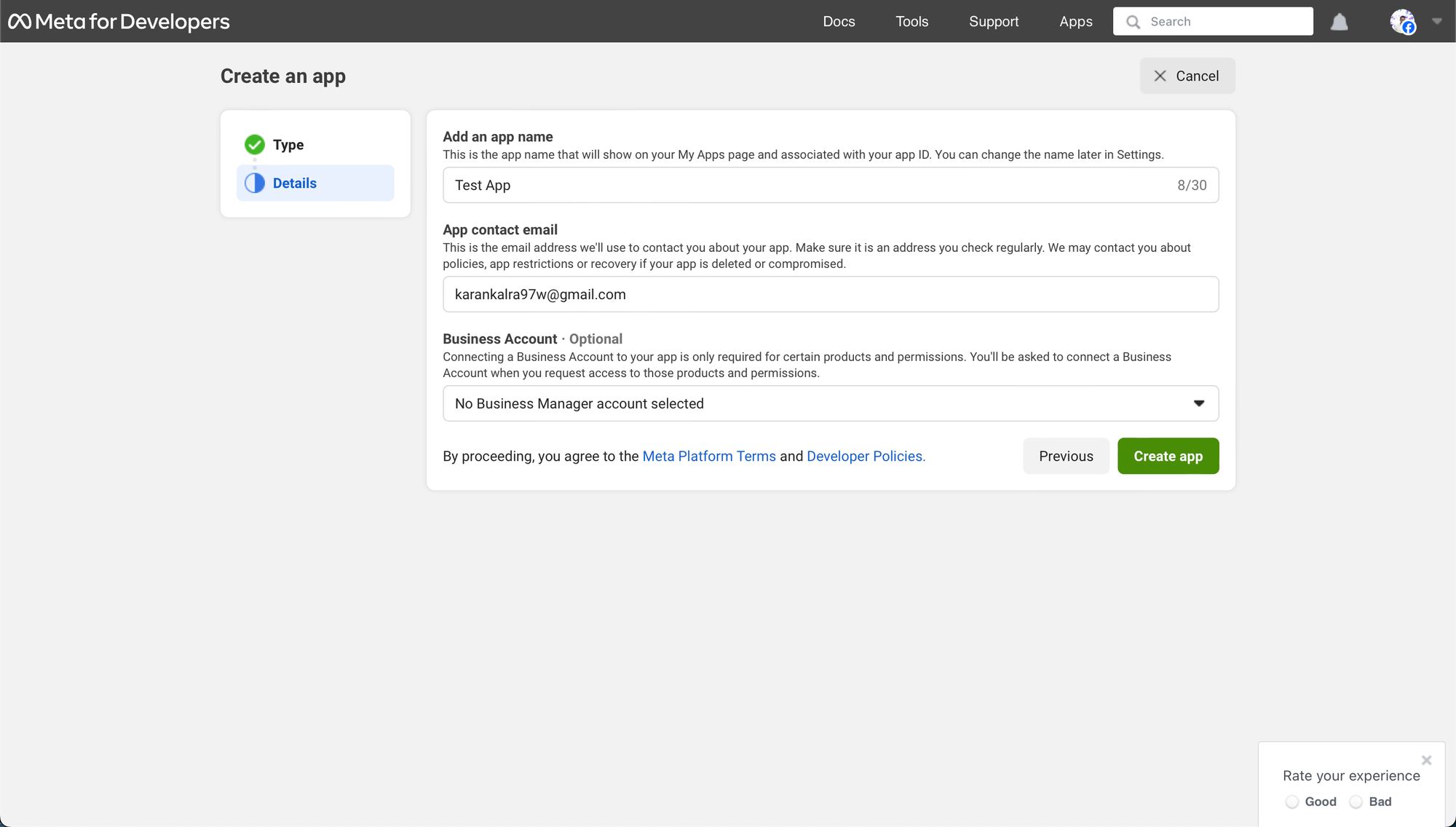
- Scroll down and Click on “Arrange” on the Whatsapp card.
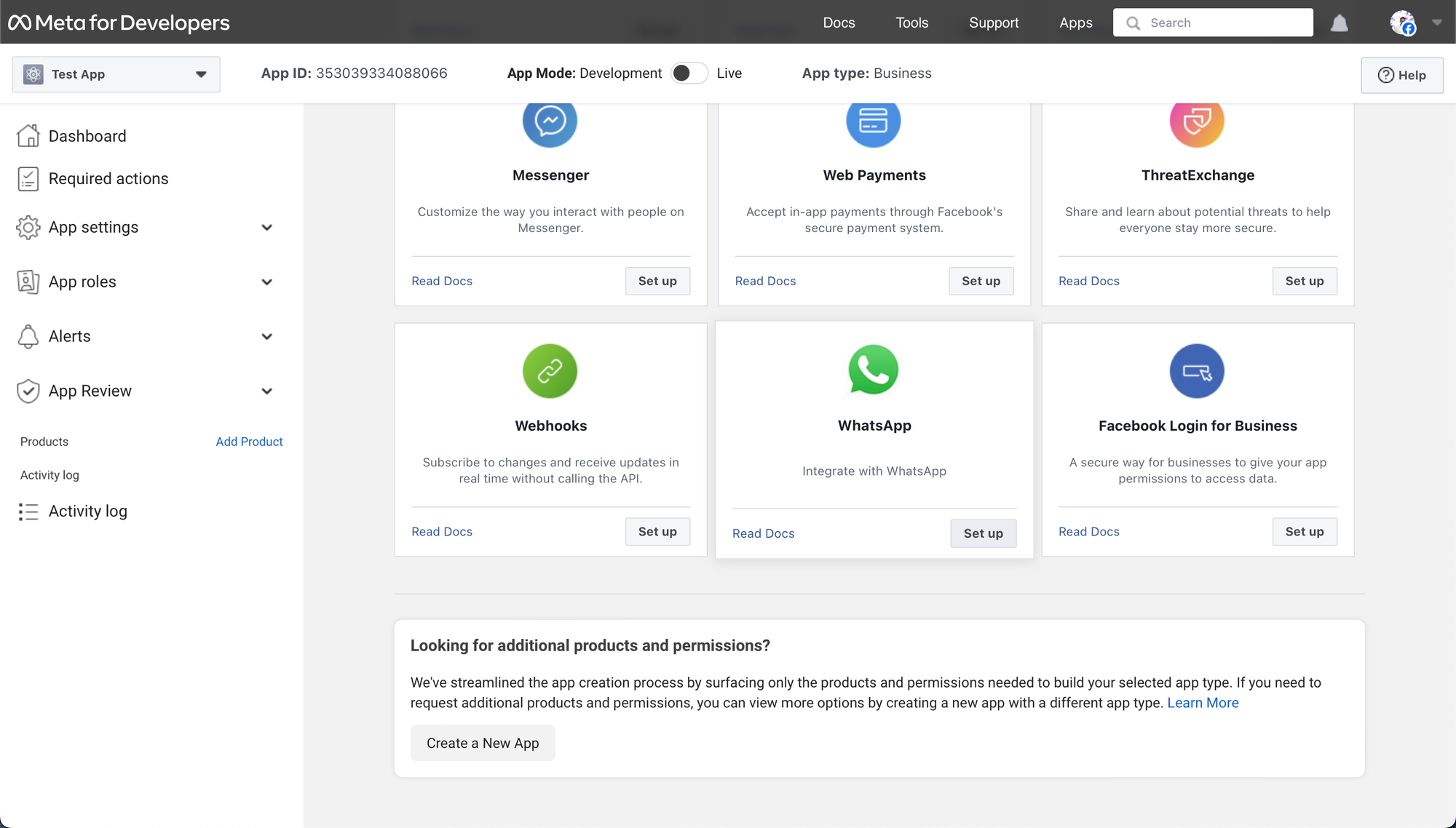
- Ought to you have got a Meta Enterprise Account (MBA), you may be requested to hyperlink it throughout this course of. If not, you may be guided to create one.
- As soon as your MBA is linked, you can be guided to a dashboard like beneath. You may start testing now.
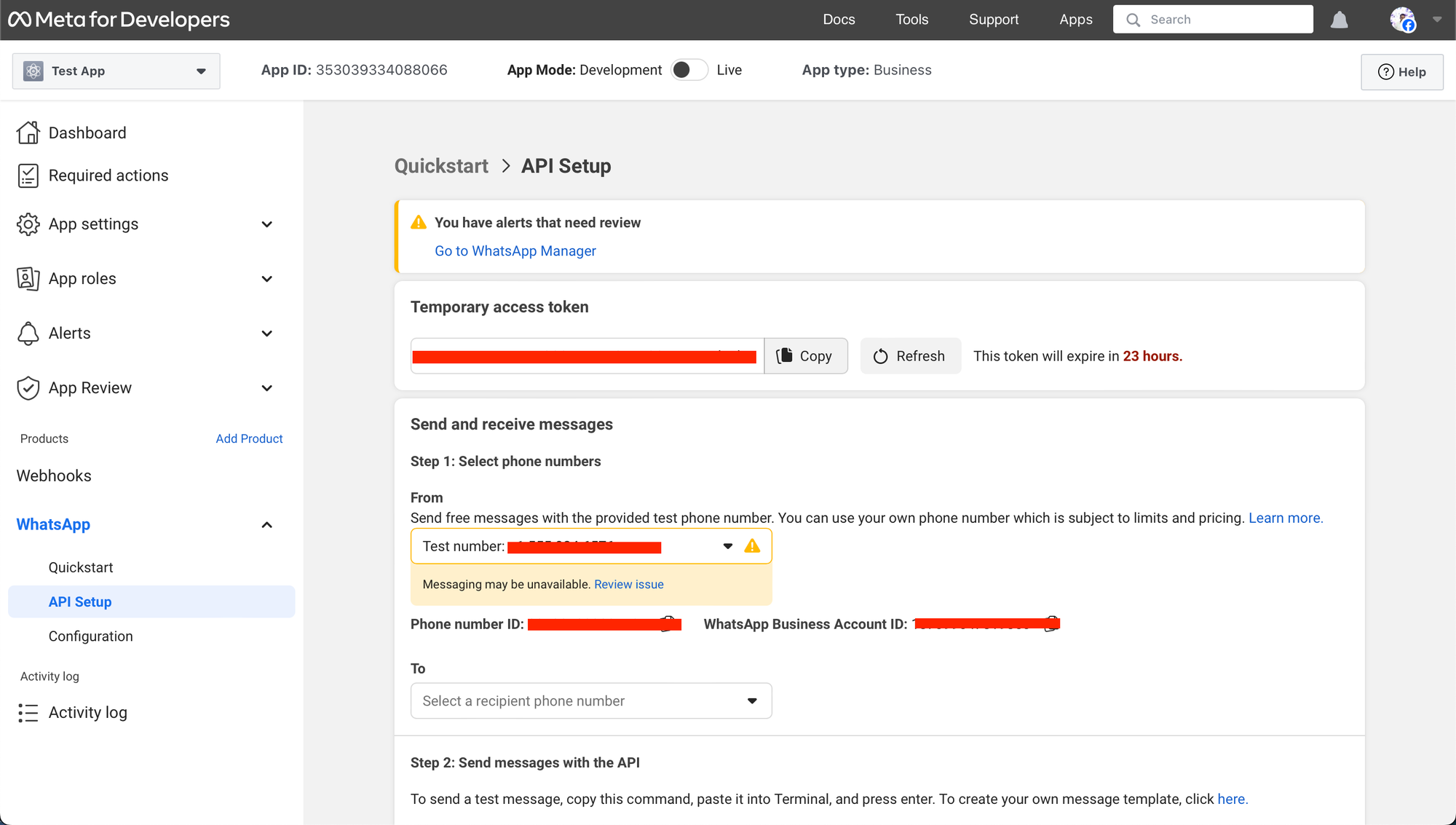
All this has ultimately allowed your app to –
- Arrange a Meta Enterprise Account, should you do not have already got one.
- Routinely generate a take a look at WhatsApp Enterprise Account, which is free for sending messages however comes with utilization limitations.
- Create a take a look at enterprise telephone quantity linked to your WhatsApp Enterprise Account, enabling you to ship free messages to as much as 5 completely different telephone numbers.
- Generate a collection of pre-approved messaging templates.
To ship take a look at messages, it is advisable add a legitimate WhatsApp quantity.
Go to the App Dashboard, navigate to WhatsApp > API Setup, and underneath the message sending part, search for the ‘To’ area to handle your telephone quantity record.
You may enter any legitimate WhatsApp quantity to obtain messages. This quantity will get a affirmation code through WhatsApp for verification.
As soon as verified, the recipient quantity will probably be prepared to be used. You may add as much as 5 numbers following this methodology.
To ship a take a look at message, use the pre-approved ‘hello_world’ template current on the dashboard.
import requests
url = "https://graph.fb.com/v17.0/206324309221106/messages"
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_TEMPORARY_ACCESS_TOKEN',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json'
}
knowledge = {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"to": "RECEPIENT_PHONE_NUMBER",
"kind": "template",
"template": {
"title": "hello_world",
"language": {
"code": "en_US"
}
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, json=knowledge)
print(response.textual content)
Within the API Setup underneath WhatsApp:
- Make sure that your take a look at enterprise quantity is within the ‘From’ area.
- Guarantee the specified recipient’s quantity is chosen within the ‘To’ area. You may ship messages to a number of numbers if added.
- Use the API panel to ship your message, or alternatively use the offered python code.
The command you may use signifies that you simply’re sending a template message, specifying the ‘hello_world’ template. A message just like the one beneath ought to seem on the recipient telephone quantity.
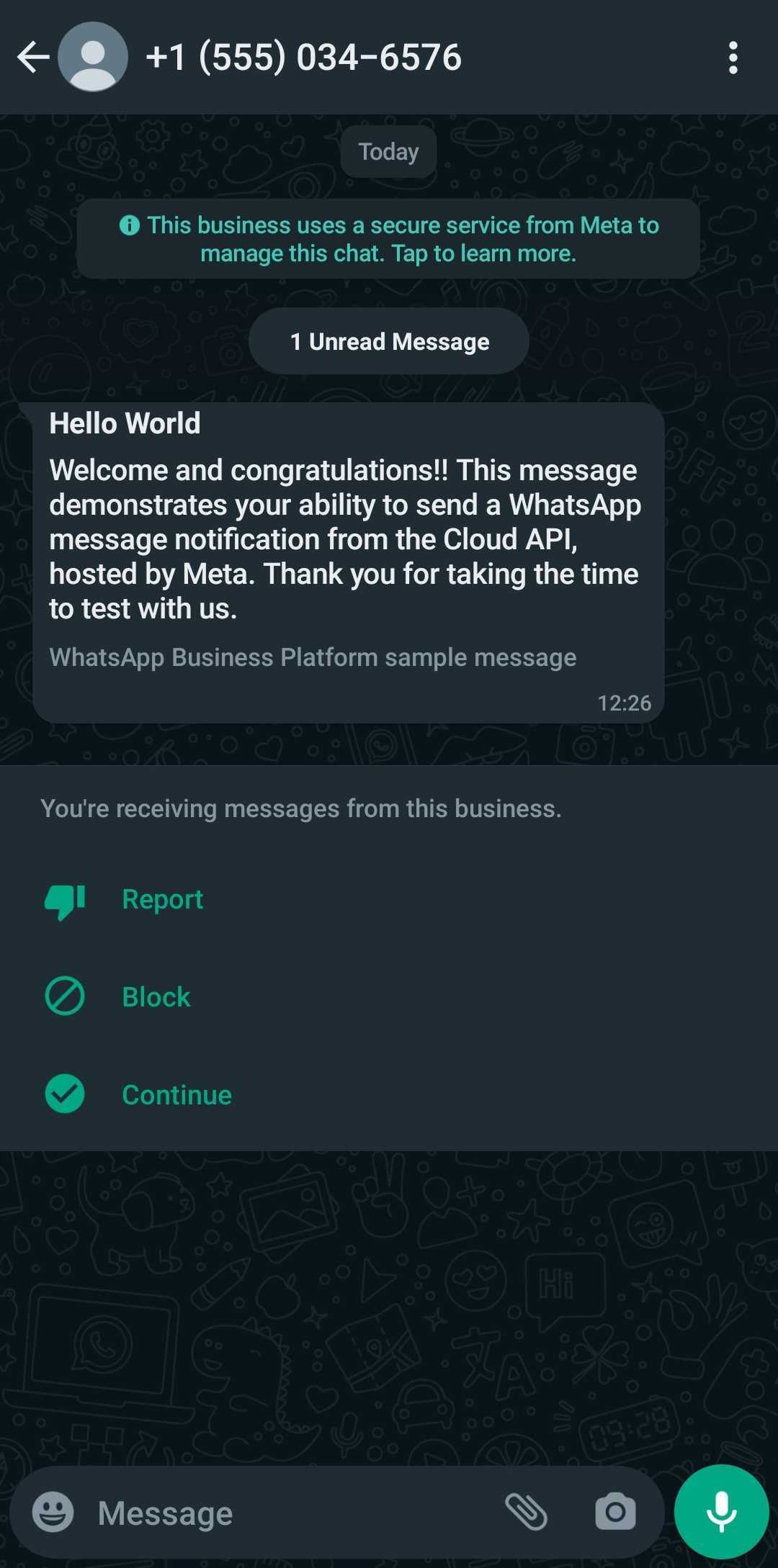
- Add a Actual Enterprise Quantity (For Later)
Whereas growing your software, you should utilize the take a look at enterprise quantity and account with none value for sending messages.
Whenever you’re prepared to interact with prospects, you possibly can add an actual enterprise telephone quantity (from which messages will probably be despatched) within the API Setup and create an official WhatsApp Enterprise Account. We’ll talk about this later.
Necessities of Whatsapp Enterprise Administration API
The Enterprise Administration API works together with the first Cloud API (which is used for sending messages and many others). It’s designed for authentication functionalities and managing WhatsApp business-related belongings like WhatsApp Enterprise Accounts and message templates.
Entry Tokens
Various kinds of entry tokens are supported:
- System Consumer Entry Tokens: These are non-expiring tokens representing your enterprise or group and are important for Resolution Companions sharing credit score strains with onboarded prospects.
- Enterprise Integration System Consumer Entry Tokens: Excellent for Tech Suppliers and Resolution Companions, these tokens are particular to onboarded buyer knowledge and help automated actions with out consumer enter or re-authentication.
- Consumer Entry Tokens: Usually used for preliminary app testing, they expire shortly and are much less appropriate for ongoing growth. This token was used within the take a look at message despatched above.
System Consumer Entry Tokens
System Consumer tokens are categorized into two sorts:
- Worker System Customers: Want entry to particular person WhatsApp Enterprise Accounts and are appropriate for restricted account entry.
- Admin System Customers: Have default full entry to all WhatsApp Enterprise Accounts and belongings, helpful for broader entry necessities.
Creating System Customers
To create a system consumer:
- Signal into the Meta Enterprise Suite.
- Find your enterprise account within the top-left dropdown menu and click on its Settings (gear) icon.
- Click on Enterprise settings.
- Navigate to Customers > System customers.
- Click on the Add button and create both an admin or worker system consumer.
Producing System Consumer Entry Tokens
To generate a System Consumer entry token after making a system consumer:
- Signal into the Meta Enterprise Suite.
- Find your enterprise account within the top-left dropdown menu and click on its Settings (gear) icon.
- Click on Enterprise settings.
- Navigate to Consumer > System customers.
- Choose the suitable system consumer from the record of system customers.
- Click on the Generate new token button.
- Choose the app that may use the token.
- Choose any permissions the app must perform correctly and generate the token.
Enterprise Integration System Consumer Entry Tokens
These tokens are generated by way of Embedded Signup and are scoped to particular person onboarded prospects. They’re essential for apps performing automated actions on buyer WhatsApp Enterprise Accounts. Be taught extra right here.
Fee Limits
The API imposes limits on the variety of calls per hour. These limits range based mostly on the kind of name and the standing of the WhatsApp Enterprise Account.
Automate Whatsapp messaging campaigns with our AI-driven workflows, designed by Nanonets for you and your groups.
Sending Messages utilizing the Whatsapp Cloud API
You may both ship free-form messages or use message templates. Allow us to discover each.
With the WhatsApp Cloud API, you possibly can ship varied kinds of free-form messages, together with:
- Textual content
- Response
- Media (pictures, movies, and many others.)
- Location
- Contacts
- Interactive messages
- Handle messages
Request Syntax for Sending Messages
To ship messages, use the POST request to the WhatsApp Enterprise Cellphone Quantity endpoint:
POST /<WHATSAPP_BUSINESS_PHONE_NUMBER>/messages
Message Payload Construction
The message payload has a typical format, with variations relying on the message kind:
{
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"recipient_type": "particular person",
"to": "<TO>",
"kind": "<TYPE>",
// Particular payload relying on message kind
}
<TO>: WhatsApp ID or telephone variety of the recipient (e.g., +16315551234).<TYPE>: Kind of message (e.g., ‘textual content’, ‘picture’, and many others.).
The response accommodates a message id which is available in helpful for sending replies/reactions, and for checking for unsuccessful requests through the standing code within the response (typical conference the place standing code 200 signifies a profitable name).
{
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"contacts": [{
"input": "<PHONE_NUMBER>",
"wa_id": "<WHATSAPP_ID>",
}],
"messages": [{
"id": "<wamid.ID>",
}]
}
Textual content Messages
To ship a textual content message:
import requests
import json
url="https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/<FROM_PHONE_NUMBER_ID>/messages"
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Bearer <ACCESS_TOKEN>',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json'
}
payload = {
'messaging_product': 'whatsapp',
'recipient_type': 'particular person',
'to': '<PHONE_NUMBER>',
'kind': 'textual content',
'textual content': {
'preview_url': False,
'physique': '<MESSAGE_CONTENT>'
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, knowledge=json.dumps(payload))
print(response.textual content)
Response Messages
For sending response messages:
import requests
import json
url="https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/<FROM_PHONE_NUMBER_ID>/messages"
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Bearer <ACCESS_TOKEN>',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json'
}
knowledge = {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"recipient_type": "particular person",
"to": "<PHONE_NUMBER>",
"kind": "response",
"response": {
"message_id": "wamid.HBgLM...",
"emoji": "uD83DuDE00"
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, knowledge=json.dumps(knowledge))
print(response.textual content)
Media Messages
Use the kindproperty to point the media asset’s kind (audio, doc, picture, sticker, or video) and both the id or hyperlink property to point its ID (which you should generate) or location in your public server.
If utilizing id, you should first add your media asset to the Whatsapp servers and seize the returned media ID. If utilizing hyperlink, your asset have to be on a publicly accessible server or the message will fail to ship.
Utilizing Hyperlink
import requests
url="https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/<FROM-PHONE-NUMBER-ID>/messages"
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Bearer <ACCESS_TOKEN>',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json',
}
knowledge = {
'messaging_product': 'whatsapp',
'recipient_type': 'particular person',
'to': '<PHONE-NUMBER>',
'kind': 'picture',
'picture': {
'hyperlink': '<IMAGE_URL>'
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, json=knowledge)
print(response.textual content)
Utilizing ID
import requests
url="https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/FROM-PHONE-NUMBER-ID/messages"
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json'
}
knowledge = {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"recipient_type": "particular person",
"to": "PHONE-NUMBER",
"kind": "picture",
"picture": {
"id": "MEDIA-OBJECT-ID"
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, json=knowledge, headers=headers)
print(response.textual content)
Location Messages
To ship location messages, make a POST name to /PHONE_NUMBER_ID/messages and fix a message object with kind=location. Then, add a location object.
import requests
url="https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/<FROM_PHONE_NUMBER_ID>/messages"
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Bearer <ACCESS_TOKEN>',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json'
}
knowledge = {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"to": "<PHONE_NUMBER>",
"kind": "location",
"location": {
"longitude": <LONG_NUMBER>,
"latitude": <LAT_NUMBER>,
"title": "<LOCATION_NAME>",
"tackle": "<LOCATION_ADDRESS>"
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, json=knowledge)
print(response.textual content)
Contacts Messages
To ship contacts messages:
import requests
import json
url="https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/FROM_PHONE_NUMBER_ID/messages"
headers = {
'Authorization': 'ACCESS_TOKEN',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json',
}
knowledge = {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"to": "PHONE_NUMBER",
"kind": "contacts",
"contacts": [{
"addresses": [{
"street": "STREET",
"city": "CITY",
"state": "STATE",
"zip": "ZIP",
"country": "COUNTRY",
"country_code": "COUNTRY_CODE",
"type": "HOME"
},
{
"street": "STREET",
"city": "CITY",
"state": "STATE",
"zip": "ZIP",
"country": "COUNTRY",
"country_code": "COUNTRY_CODE",
"type": "WORK"
}],
"birthday": "YEAR_MONTH_DAY",
"emails": [{
"email": "EMAIL",
"type": "WORK"
},
{
"email": "EMAIL",
"type": "HOME"
}],
"title": {
"formatted_name": "NAME",
"first_name": "FIRST_NAME",
"last_name": "LAST_NAME",
"middle_name": "MIDDLE_NAME",
"suffix": "SUFFIX",
"prefix": "PREFIX"
},
"org": {
"firm": "COMPANY",
"division": "DEPARTMENT",
"title": "TITLE"
},
"telephones": [{
"phone": "PHONE_NUMBER",
"type": "HOME"
},
{
"phone": "PHONE_NUMBER",
"type": "WORK",
"wa_id": "PHONE_OR_WA_ID"
}],
"urls": [{
"url": "URL",
"type": "WORK"
},
{
"url": "URL",
"type": "HOME"
}]
}]
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, knowledge=json.dumps(knowledge))
print(response.textual content)Substitute <CONTACT_PAYLOAD> with the JSON construction containing contact particulars.
Interactive Messages
Interactive messages embody record messages, reply buttons, and click-to-action URL buttons. To ship interactive messages, make a POST name to /PHONE_NUMBER_ID/messages and fix a message object with kind=interactive. Then, add an interactive object.
For record messages:
import requests
import json
url="https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/FROM_PHONE_NUMBER_ID/messages"
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json'
}
knowledge = {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"recipient_type": "particular person",
"to": "PHONE_NUMBER",
"kind": "interactive",
"interactive": {
"kind": "record",
"header": {
"kind": "textual content",
"textual content": "HEADER_TEXT"
},
"physique": {
"textual content": "BODY_TEXT"
},
"footer": {
"textual content": "FOOTER_TEXT"
},
"motion": {
"button": "BUTTON_TEXT",
"sections": [
{
"title": "SECTION_1_TITLE",
"rows": [
{
"id": "SECTION_1_ROW_1_ID",
"title": "SECTION_1_ROW_1_TITLE",
"description": "SECTION_1_ROW_1_DESCRIPTION"
},
{
"id": "SECTION_1_ROW_2_ID",
"title": "SECTION_1_ROW_2_TITLE",
"description": "SECTION_1_ROW_2_DESCRIPTION"
}
]
},
{
"title": "SECTION_2_TITLE",
"rows": [
{
"id": "SECTION_2_ROW_1_ID",
"title": "SECTION_2_ROW_1_TITLE",
"description": "SECTION_2_ROW_1_DESCRIPTION"
},
{
"id": "SECTION_2_ROW_2_ID",
"title": "SECTION_2_ROW_2_TITLE",
"description": "SECTION_2_ROW_2_DESCRIPTION"
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, knowledge=json.dumps(knowledge))
print(response.textual content)For reply buttons:
import requests
url="https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/FROM_PHONE_NUMBER_ID/messages"
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json'
}
knowledge = {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"recipient_type": "particular person",
"to": "PHONE_NUMBER",
"kind": "interactive",
"interactive": {
"kind": "button",
"physique": {
"textual content": "BUTTON_TEXT"
},
"motion": {
"buttons": [
{
"type": "reply",
"reply": {
"id": "UNIQUE_BUTTON_ID_1",
"title": "BUTTON_TITLE_1"
}
},
{
"type": "reply",
"reply": {
"id": "UNIQUE_BUTTON_ID_2",
"title": "BUTTON_TITLE_2"
}
}
]
}
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, json=knowledge)
print(response.textual content)For sending messages with CTA URL buttons:
import requests
import json
# Substitute these variables together with your precise knowledge
access_token = '<ACCESS_TOKEN>'
business_phone_number_id = '<BUSINESS_PHONE_NUMBER_ID>'
customer_phone_number="<CUSTOMER_PHONE_NUMBER>"
url = f'https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/{business_phone_number_id}/messages'
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json'
}
knowledge = {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"recipient_type": "particular person",
"to": customer_phone_number,
"kind": "interactive",
"interactive": {
"kind": "button",
"physique": {
"textual content": "BUTTON_TEXT"
},
"motion": {
"buttons": [
{
"type": "reply",
"reply": {
"id": "UNIQUE_BUTTON_ID_1",
"title": "BUTTON_TITLE_1"
}
},
{
"type": "reply",
"reply": {
"id": "UNIQUE_BUTTON_ID_2",
"title": "BUTTON_TITLE_2"
}
}
]
}
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, knowledge=json.dumps(knowledge))
print(response.textual content)Sending Replies
Sending a message as a response to an earlier message in a dialog is feasible by including the ID of the earlier message within the context object. This fashion, the recipient will get the brand new message with a contextual bubble showcasing the content material of the previous message.
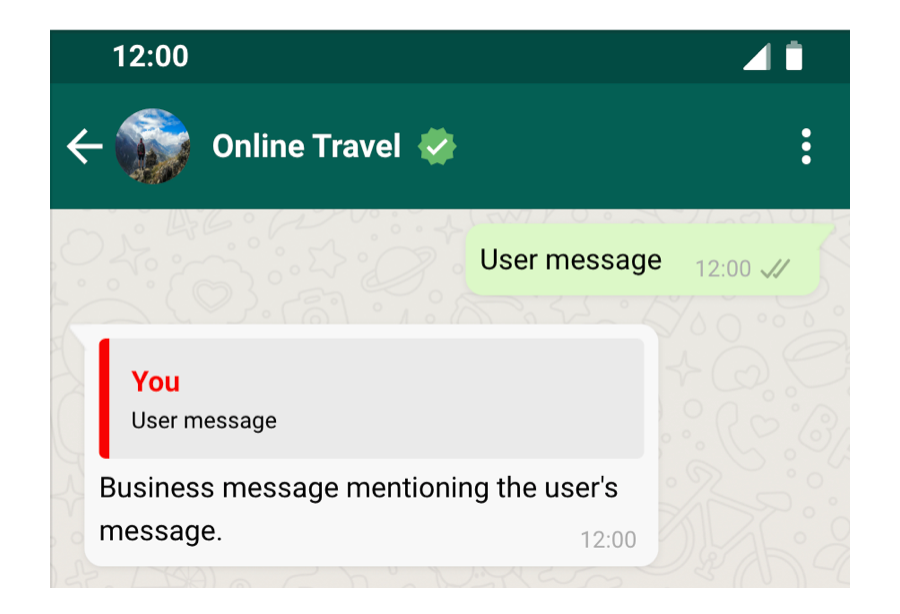
import requests
url="https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/<FROM_PHONE_NUMBER_ID>/messages"
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Bearer <ACCESS_TOKEN>',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json'
}
knowledge = {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"context": {
"message_id": "<MESSAGE_ID>"
},
"to": "<PHONE_NUMBER_OR_WA_ID>",
"kind": "textual content",
"textual content": {
"preview_url": False,
"physique": "<YOUR_TEXT_MESSAGE_CONTENT>"
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, json=knowledge)
print(response.textual content)Sending Handle Messages
Handle Message sorts are supported in India and Singapore solely. Learn Extra right here.
Sending Message Templates
WhatsApp message templates are pre-created particular message codecs that companies use to ship out notifications or buyer care messages to those who have opted in to notifications. Messages can embody appointment reminders, transport info, situation decision or cost updates.
Earlier than sending a template message, it is advisable create a template.
- Go to Enterprise Supervisor and choose your enterprise.
- Open Menu and click on on WhatsApp Supervisor.
- Click on on “Handle Message Templates”.
Now, you possibly can both use one of many pre-approved templates, or create your template with required framework and get that accredited from Meta.
Check out the pre accredited templates provided right here – https://www.fb.com/enterprise/assist/722393685250070
You can begin utilizing them straight.
For instance –
1. Sending Catalog Template Messages
This part explains learn how to ship catalog templates in a WhatsApp message, assuming you have got a list in a Meta ecommerce catalog related to your WhatsApp Enterprise Account.
Necessities
- Stock uploaded to Meta. You may create it utilizing this information.
- Ecommerce catalog related to WhatsApp Enterprise Account.
Setup
The subsequent step is to create a catalog template which will probably be used to ship the messages. Use this information to create a catalog template in minutes.
Request Syntax
Use the WhatsApp Enterprise Cellphone Quantity > Messages endpoint.
Instance Request
For instance we create a template referred to as intro_catalog_offer.
import requests
url="https://graph.fb.com/v17.0/<WHATSAPP_BUSINESS_PHONE_NUMBER_ID>/messages"
headers = {
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json',
'Authorization': 'Bearer <YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN>'
}
knowledge = {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"recipient_type": "particular person",
"to": "+16505551234",
"kind": "template",
"template": {
"title": "intro_catalog_offer",
"language": {
"code": "en_US"
},
"elements": [
{
"type": "body",
"parameters": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "100"
},
{
"type": "text",
"text": "400"
},
{
"type": "text",
"text": "3"
}
]
},
{
"kind": "button",
"sub_type": "CATALOG",
"index": 0,
"parameters": [
{
"type": "action",
"action": {
"thumbnail_product_retailer_id": "2lc20305pt"
}
}
]
}
]
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, json=knowledge, headers=headers)
print(response.json())
2. Sending Carousel Templates
This part covers the method of sending carousel templates in a WhatsApp message.
Request Syntax
Just like catalog templates, use the WhatsApp Enterprise Cellphone Quantity > Messages endpoint.
Beneath is a pattern request for dispatching a carousel template, incorporating a message bubble which wants enter for 2 distinct variables. It contains two carousel playing cards, every that includes a picture header, and necessitates enter for textual content within the physique and variables related to buttons.
Setup
The subsequent step is to create a carousal template, which will probably be used to ship messages. You may create one inside seconds utilizing this information.
Instance Request
import requests
import json
url="https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/106540352242922/messages"
headers = {
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json',
'Authorization': 'Bearer EAAJB...'
}
knowledge = {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"recipient_type": "particular person",
"to": "16505555555",
"kind": "template",
"template": {
"title": "summer_carousel_promo_2023",
"language": {
"code": "en_US"
},
"elements": [
{
"type": "BODY",
"parameters": [
{"type": "TEXT", "text": "20OFF"},
{"type": "TEXT", "text": "20%"}
]
},
{
"kind": "CAROUSEL",
"playing cards": [
{
"card_index": 0,
"components": [
{
"type": "HEADER",
"parameters": [{"type": "IMAGE", "image": {"id": "24230790383178626"}}]
},
{
"kind": "BODY",
"parameters": [
{"type": "TEXT", "text": "10OFF"},
{"type": "TEXT", "text": "10%"}
]
},
{
"kind": "BUTTON",
"sub_type": "QUICK_REPLY",
"index": "0",
"parameters": [{"type": "PAYLOAD", "payload": "59NqSd"}]
},
{
"kind": "button",
"sub_type": "URL",
"index": "1",
"parameters": [{"type": "payload", "payload": "last_chance_2023"}]
}
]
},
{
"card_index": 1,
"elements": [
{
"type": "HEADER",
"parameters": [{"type": "IMAGE", "image": {"id": "1690627074790615"}}]
},
{
"kind": "BODY",
"parameters": [
{"type": "TEXT", "text": "30OFF"},
{"type": "TEXT", "text": "30%"}
]
},
{
"kind": "BUTTON",
"sub_type": "QUICK_REPLY",
"index": "0",
"parameters": [{"type": "PAYLOAD", "payload": "7C4xhY"}]
},
{
"kind": "BUTTON",
"sub_type": "URL",
"index": "1",
"parameters": [{"type": "payload", "payload": "summer_blues_2023"}]
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
response = requests.publish(url, headers=headers, json=knowledge)
print(response.textual content)Use the beneath information to get acquainted extra with message templates – https://enterprise.fb.com/enterprise/assist/2055875911147364?id=2129163877102343
Whatsapp Messaging Workflow
On this part, we’ll take an instance of a Whatsapp advertising and marketing marketing campaign and attempt to automate it utilizing the Whatsapp API in python. We’ll delve into learn how to automate the method of extracting each day leads from HubSpot through its API after which sending automated messages to those leads by way of WhatsApp’s API. We’ll use HubSpot fields to create dynamic messages based mostly on varied attributes.
Script to Get Each day Leads from HubSpot
To start, let’s write a Python script to fetch each day leads from HubSpot. This script will use the HubSpot API to get leads based mostly on a customized area, reminiscent of Date_Created, to filter leads created within the final 24 hours.
import requests
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
# HubSpot API particulars
HUBSPOT_API_KEY = 'your_hubspot_api_key'
HUBSPOT_CONTACTS_URL = 'https://api.hubapi.com/crm/v3/objects/contacts'
# Calculate yesterday's date
yesterday = (datetime.now() - timedelta(days=1)).strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
# Question parameters for the API name
params = {
'hapikey': HUBSPOT_API_KEY,
'restrict': 100, # Modify the restrict as wanted
'properties': ['firstname', 'lastname', 'phone', 'email', 'Date_Created'],
'filters': [{
'propertyName': 'Date_Created',
'operator': 'GTE',
'value': yesterday
}]
}
# API name to get contacts
response = requests.get(HUBSPOT_CONTACTS_URL, params=params)
leads = response.json()
# Extract related info
daily_leads = [{'name': f"{lead['properties']['firstname']} {lead['properties']['lastname']}",
'telephone': lead['properties']['phone'],
'electronic mail': lead['properties']['email']}
for lead in leads['results']]
# Print the leads
print(daily_leads)
Sending Automated Messages through WhatsApp API
As soon as we have now the record of each day leads, the subsequent step is to ship them customized messages through WhatsApp. We’ll use the WhatsApp Cloud API and dynamically create messages based mostly on different HubSpot fields, like firstname, lastname, and another related knowledge.
import requests
import json
# WhatsApp API particulars
WHATSAPP_API_URL = 'https://graph.fb.com/v18.0/YOUR_PHONE_NUMBER_ID/messages'
ACCESS_TOKEN = 'your_whatsapp_access_token'
# Perform to ship message
def send_whatsapp_message(phone_number, message):
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {ACCESS_TOKEN}',
'Content material-Kind': 'software/json'
}
payload = {
'messaging_product': 'whatsapp',
'recipient_type': 'particular person',
'to': phone_number,
'kind': 'textual content',
'textual content': {'physique': message}
}
response = requests.publish(WHATSAPP_API_URL, headers=headers, json=payload)
return response.json()
# Loop by way of the leads and ship messages
for lead in daily_leads:
# Customized message based mostly on HubSpot fields
message = f"Hey {lead['name']}, we have now thrilling updates for you! Test your electronic mail at {lead['email']} for extra particulars."
# Ship message
send_response = send_whatsapp_message(lead['phone'], message)
print(f"Message despatched to {lead['name']}: {send_response}")
On this script, we first outline a perform send_whatsapp_message that takes a telephone quantity and a message as inputs and sends the message utilizing the WhatsApp API. Then, we loop by way of every lead, create a customized message, and use the perform to ship the message.
This workflow automates the method of extracting each day leads from HubSpot after which participating with them through customized WhatsApp messages. We tailor the messages in accordance with the lead’s info and preferences to make sure efficient communication.
Automate Whatsapp messaging campaigns with our AI-driven workflows, designed by Nanonets for you and your groups.
Automate the workflow with Nanonets
You may automate the above workflow inside seconds utilizing workflow automation powered by Nanonets.
We offer the necessities of our workflow as a pure language immediate, and the workflow builder spins up the workflow inside seconds.
We authenticate our Hubspot and Whatsapp accounts, after which we’re able to deploy the workflow and make it stay.
There are quite a few helpful workflows that each people and organizations may create to streamline communication, automate duties, and improve productiveness. Listed below are three sensible examples of such workflows:
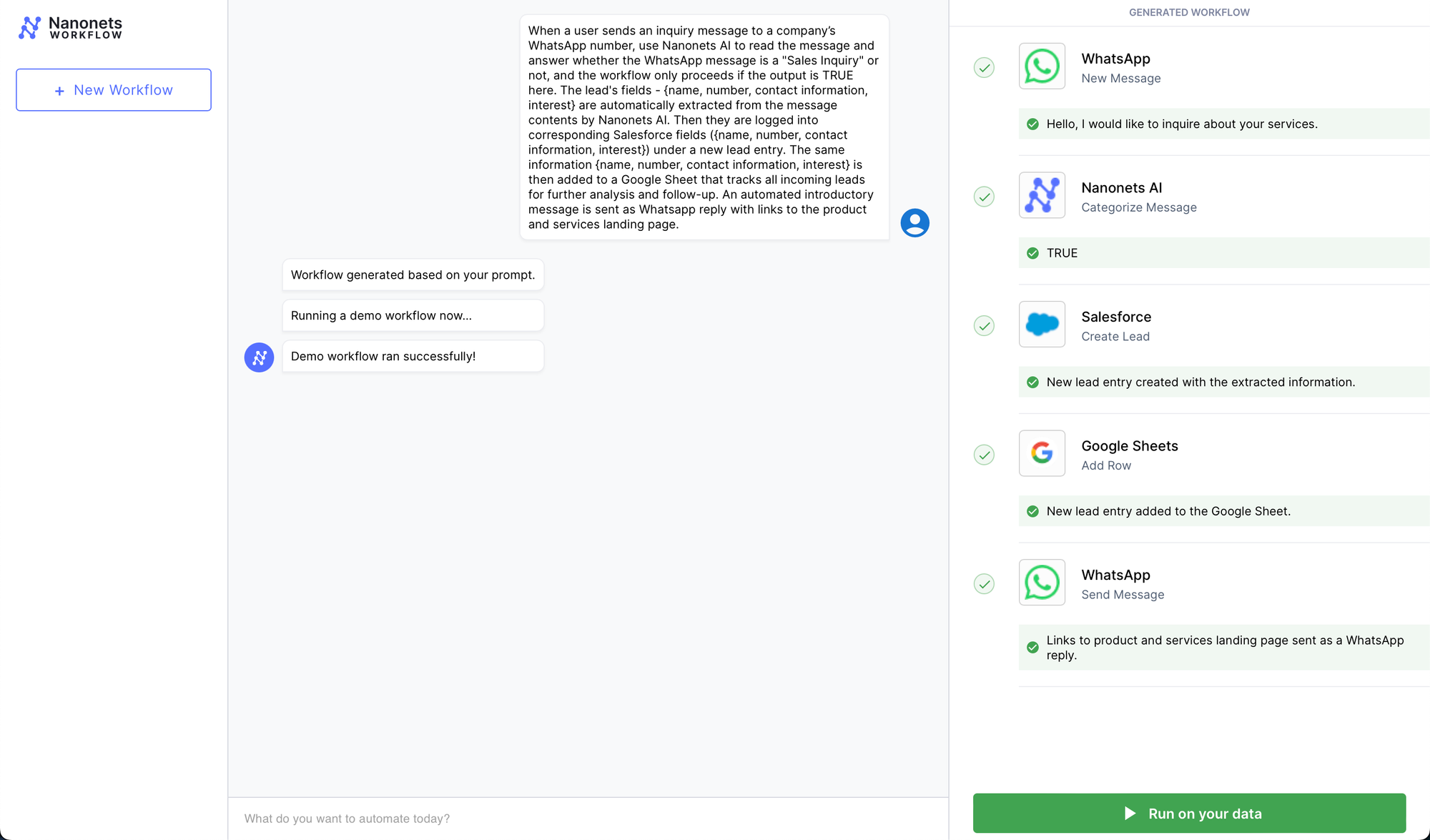
Gross sales Lead Notification Workflow
- Apps Concerned: WhatsApp, Salesforce, Google Sheets
- Workflow:
- Set off: A possible buyer sends a message to an organization’s WhatsApp quantity expressing curiosity in a services or products.
- Motion 1: The lead’s particulars (title, contact info, curiosity) are mechanically logged into Salesforce underneath a brand new lead entry.
- Motion 2: The identical info can also be added to a Google Sheet that tracks all incoming leads for additional evaluation and follow-up.
- Motion 3: An automatic introductory message created utilizing a Whatsapp Catalog Template is shipped as Whatsapp reply.
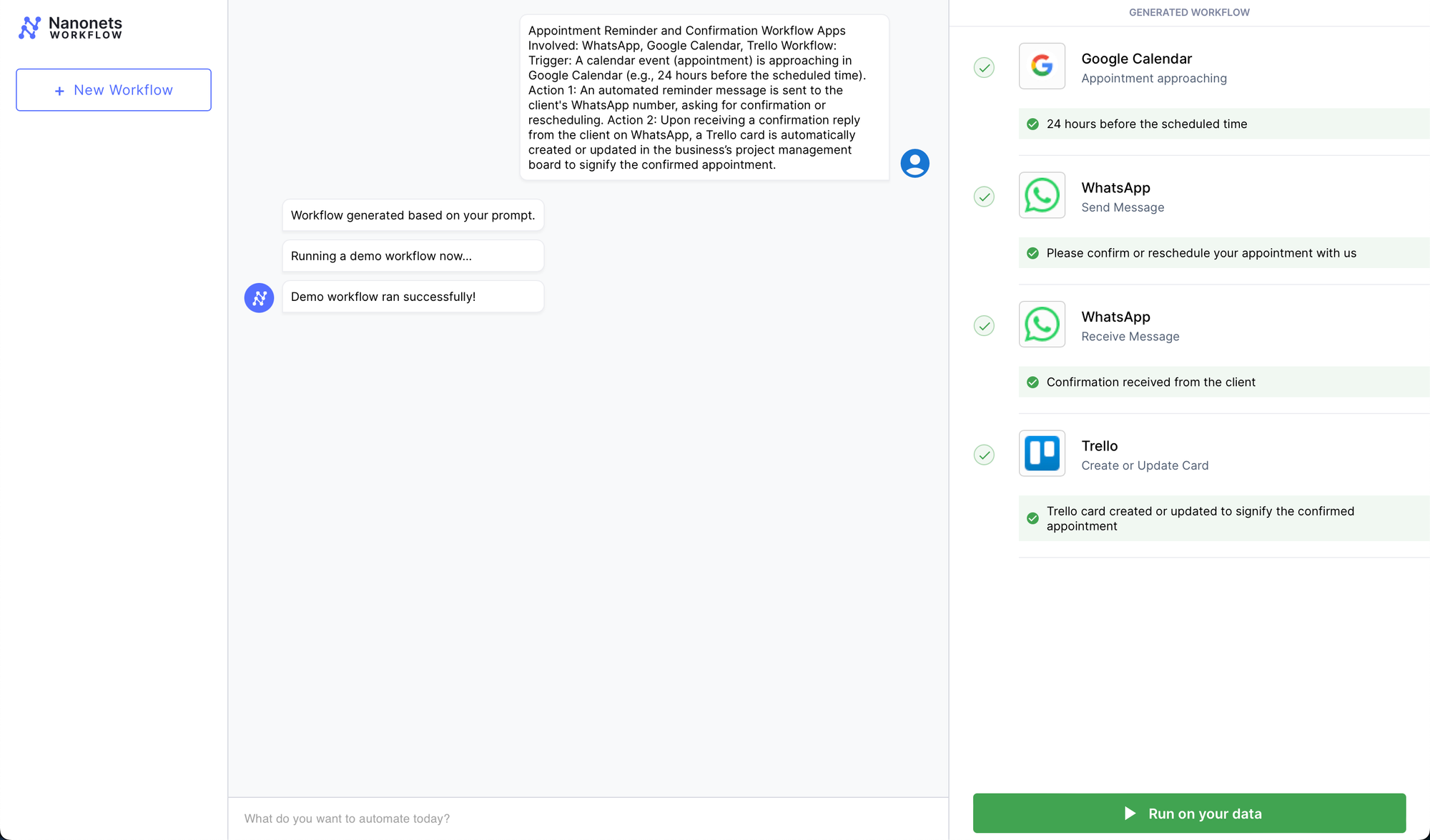
Appointment Reminder and Affirmation Workflow
- Apps Concerned: WhatsApp, Google Calendar, Trello
- Workflow:
- Set off: A calendar occasion (appointment) is approaching in Google Calendar (e.g., 24 hours earlier than the scheduled time).
- Motion 1: An automatic reminder message is shipped to the consumer’s WhatsApp quantity, asking for affirmation or rescheduling.
- Motion 2: Upon receiving a affirmation reply from the consumer on WhatsApp, a Trello card is mechanically created or up to date within the enterprise’s venture administration board to indicate the confirmed appointment.
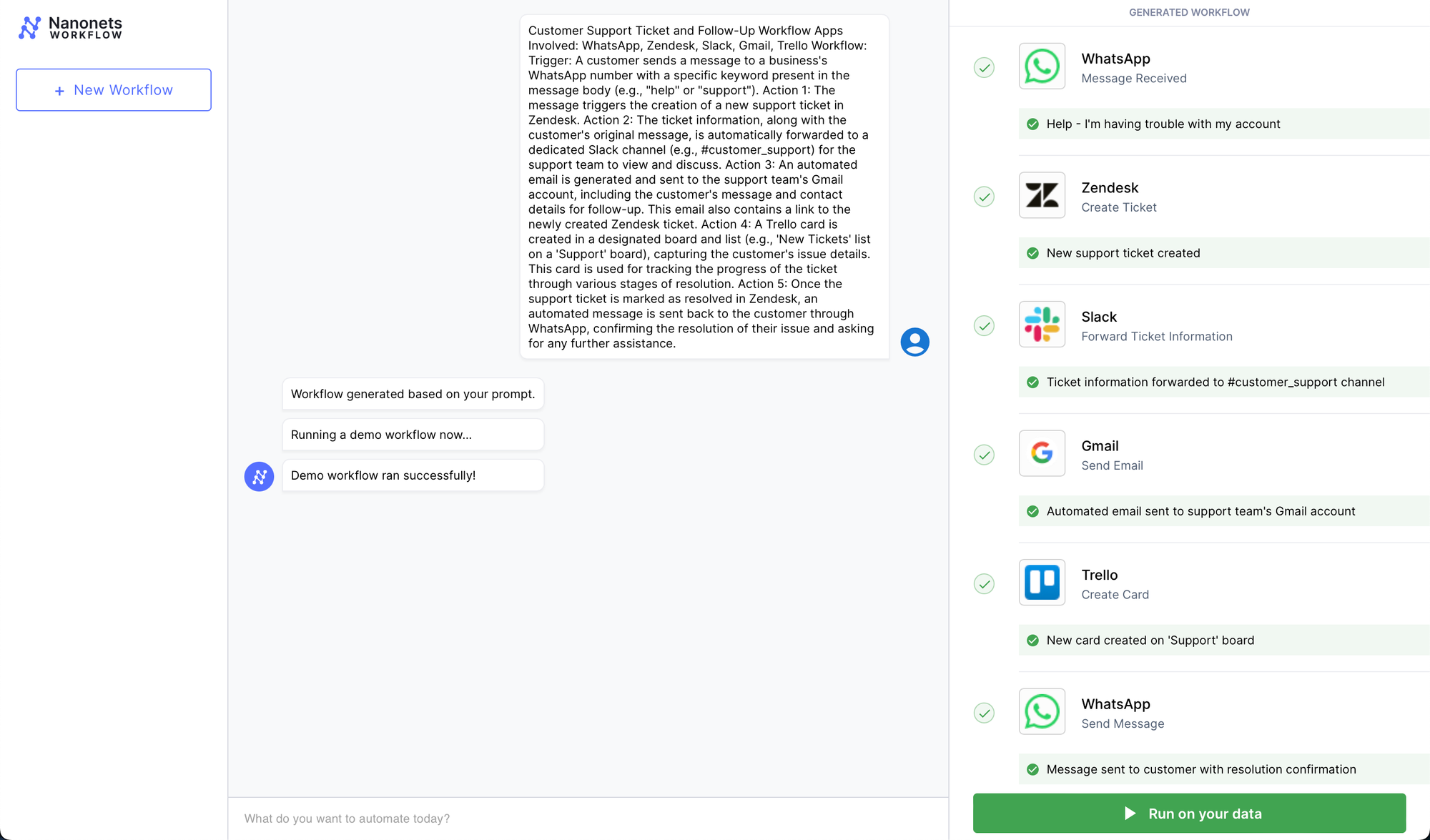
Buyer Assist Ticket and Observe-Up Workflow
- Apps Concerned: WhatsApp, Zendesk, Slack, Gmail, Trello
- Workflow:
- Set off: A buyer sends a message to a enterprise’s WhatsApp quantity with a particular key phrase current within the message physique (e.g., “assist” or “help”).
- Motion 1: The message triggers the creation of a brand new help ticket in Zendesk.
- Motion 2: The ticket info, together with the client’s unique message, is mechanically forwarded to a devoted Slack channel (e.g., #customer_support) for the help group to view and talk about.
- Motion 3: An automatic electronic mail is generated and despatched to the help group’s Gmail account, together with the client’s message and phone particulars for follow-up. This electronic mail additionally accommodates a hyperlink to the newly created Zendesk ticket.
- Motion 4: A Trello card is created in a delegated board and record (e.g., ‘New Tickets’ record on a ‘Assist’ board), capturing the client’s situation particulars. This card is used for monitoring the progress of the ticket by way of varied phases of decision.
- Motion 5: As soon as the help ticket is marked as resolved in Zendesk, an automatic message is shipped again to the client by way of WhatsApp, confirming the decision of their situation and asking for any additional help.
These workflows are designed to reinforce communication effectivity, guarantee immediate responses, and preserve observe of necessary interactions and duties throughout completely different platforms. They are often tailor-made to particular organizational wants and may considerably streamline varied enterprise processes.
Workflow Automation with Nanonets
In as we speak’s fast-paced enterprise setting, workflow automation stands out as a vital innovation, providing a aggressive edge to corporations of all sizes. The mixing of automated workflows into each day enterprise operations isn’t just a pattern; it is a strategic necessity. Along with this, the arrival of LLMs has opened much more alternatives for automation of handbook duties and processes.
Welcome to Nanonets Workflow Automation, the place AI-driven know-how empowers you and your group to automate handbook duties and assemble environment friendly workflows in minutes. Make the most of pure language to effortlessly create and handle workflows that seamlessly combine with all of your paperwork, apps, and databases.
Our platform gives not solely seamless app integrations for unified workflows but additionally the power to construct and make the most of customized Giant Language Fashions Apps for classy textual content writing and response posting inside your apps. All of the whereas guaranteeing knowledge safety stays our high precedence, with strict adherence to GDPR, SOC 2, and HIPAA compliance requirements.
To higher perceive the sensible functions of Nanonets workflow automation, let’s delve into some real-world examples.
- Automated Buyer Assist and Engagement Course of
- Ticket Creation – Zendesk: The workflow is triggered when a buyer submits a brand new help ticket in Zendesk, indicating they want help with a services or products.
- Ticket Replace – Zendesk: After the ticket is created, an automatic replace is straight away logged in Zendesk to point that the ticket has been acquired and is being processed, offering the client with a ticket quantity for reference.
- Data Retrieval – Nanonets Looking: Concurrently, the Nanonets Looking characteristic searches by way of all of the data base pages to search out related info and attainable options associated to the client’s situation.
- Buyer Historical past Entry – HubSpot: Concurrently, HubSpot is queried to retrieve the client’s earlier interplay data, buy historical past, and any previous tickets to supply context to the help group.
- Ticket Processing – Nanonets AI: With the related info and buyer historical past at hand, Nanonets AI processes the ticket, categorizing the difficulty and suggesting potential options based mostly on related previous instances.
- Notification – Slack: Lastly, the accountable help group or particular person is notified by way of Slack with a message containing the ticket particulars, buyer historical past, and instructed options, prompting a swift and knowledgeable response.
- Automated Challenge Decision Course of
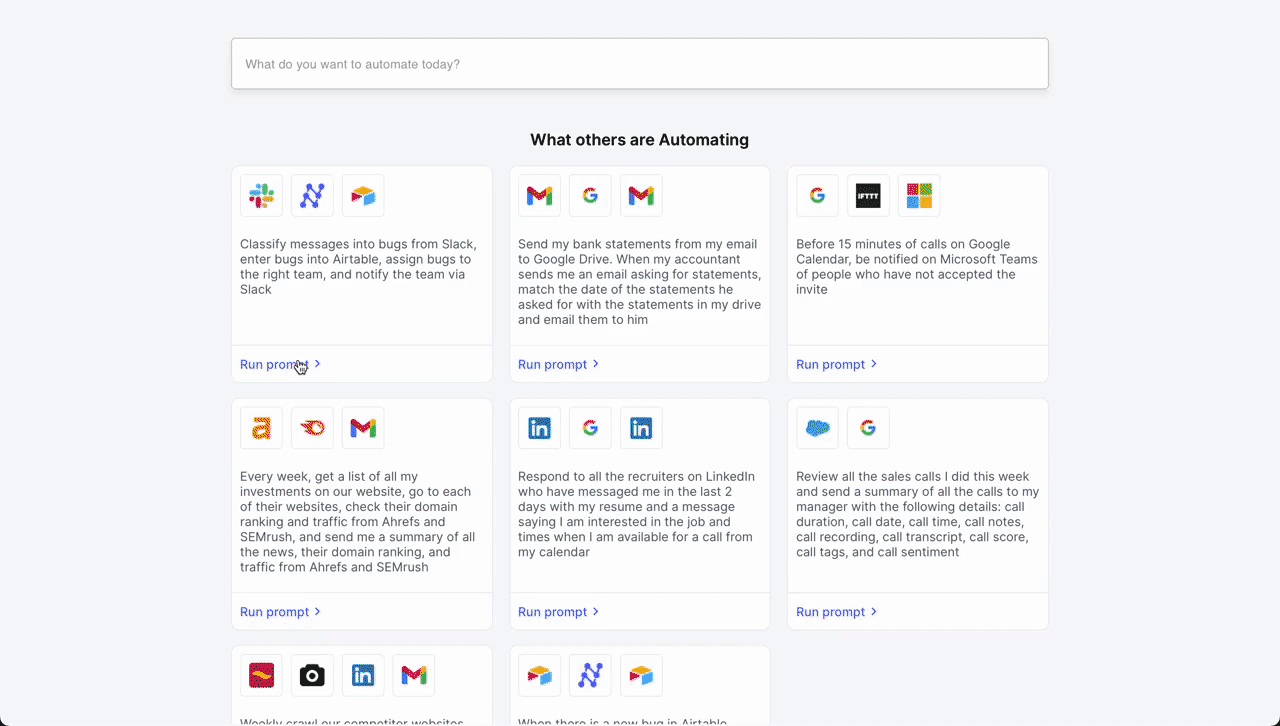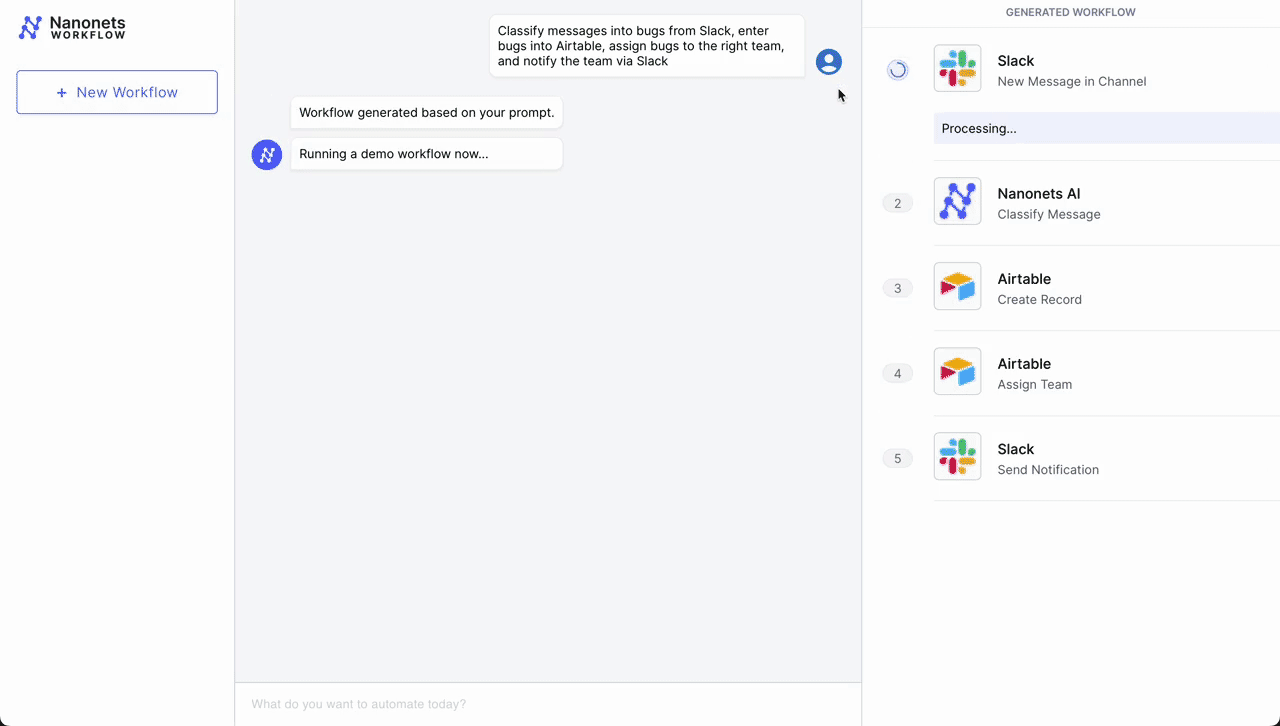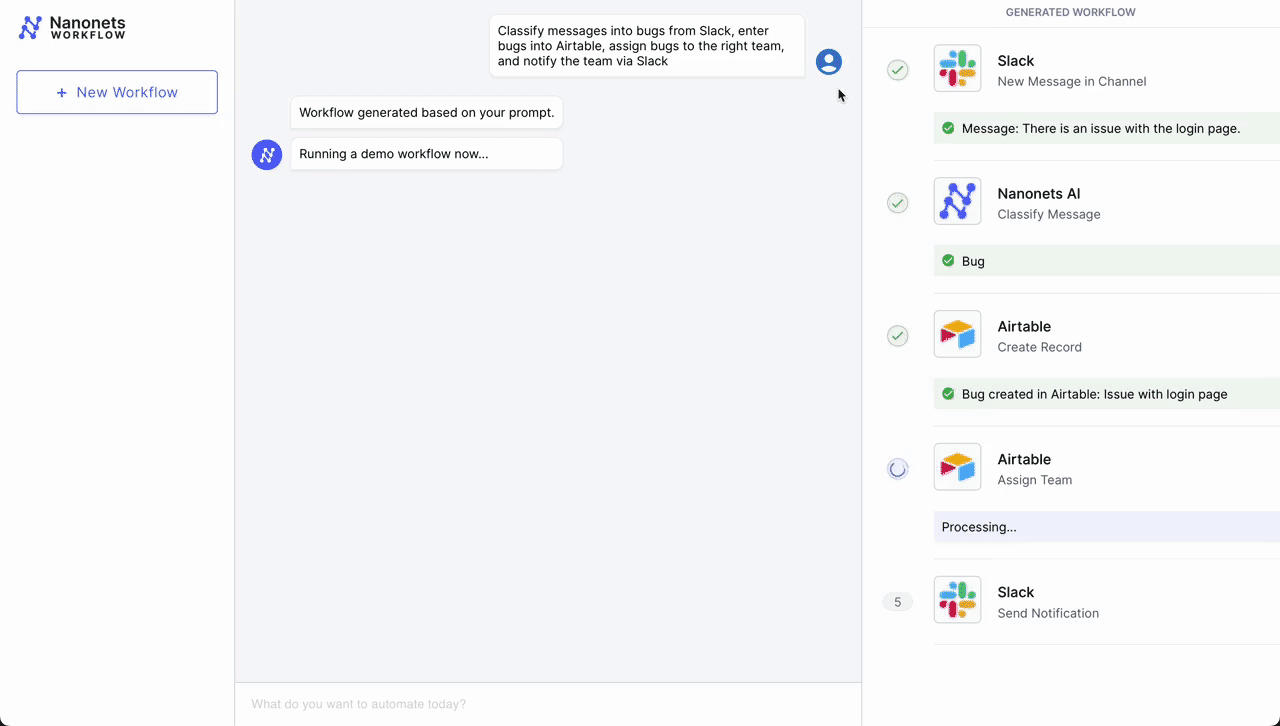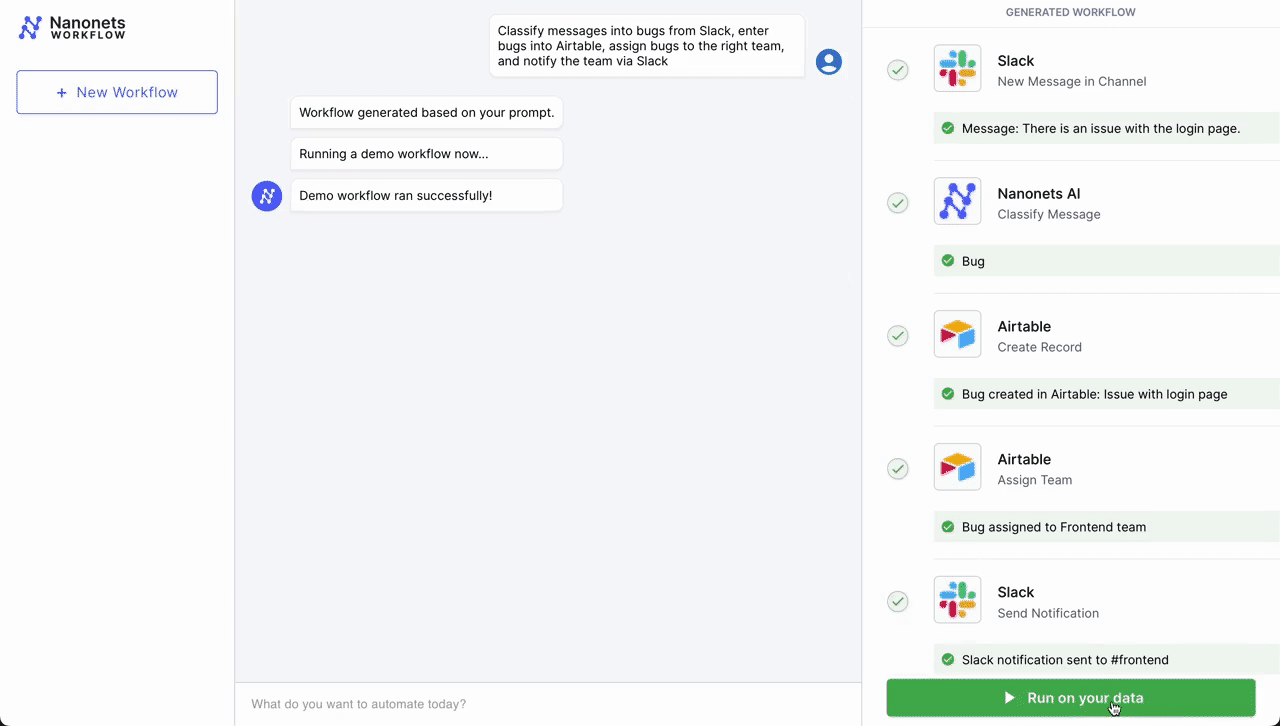
- Preliminary Set off – Slack Message: The workflow begins when a customer support consultant receives a brand new message in a devoted channel on Slack, signaling a buyer situation that must be addressed.
- Classification – Nanonets AI: As soon as the message is detected, Nanonets AI steps in to categorise the message based mostly on its content material and previous classification knowledge (from Airtable data). Utilizing LLMs, it classifies it as a bug together with figuring out urgency.
- Report Creation – Airtable: After classification, the workflow mechanically creates a brand new document in Airtable, a cloud collaboration service. This document contains all related particulars from the client’s message, reminiscent of buyer ID, situation class, and urgency degree.
- Group Task – Airtable: With the document created, the Airtable system then assigns a group to deal with the difficulty. Based mostly on the classification accomplished by Nanonets AI, the system selects probably the most acceptable group – tech help, billing, buyer success, and many others. – to take over the difficulty.
- Notification – Slack: Lastly, the assigned group is notified by way of Slack. An automatic message is shipped to the group’s channel, alerting them of the brand new situation, offering a direct hyperlink to the Airtable document, and prompting a well timed response.
- Automated Assembly Scheduling Course of
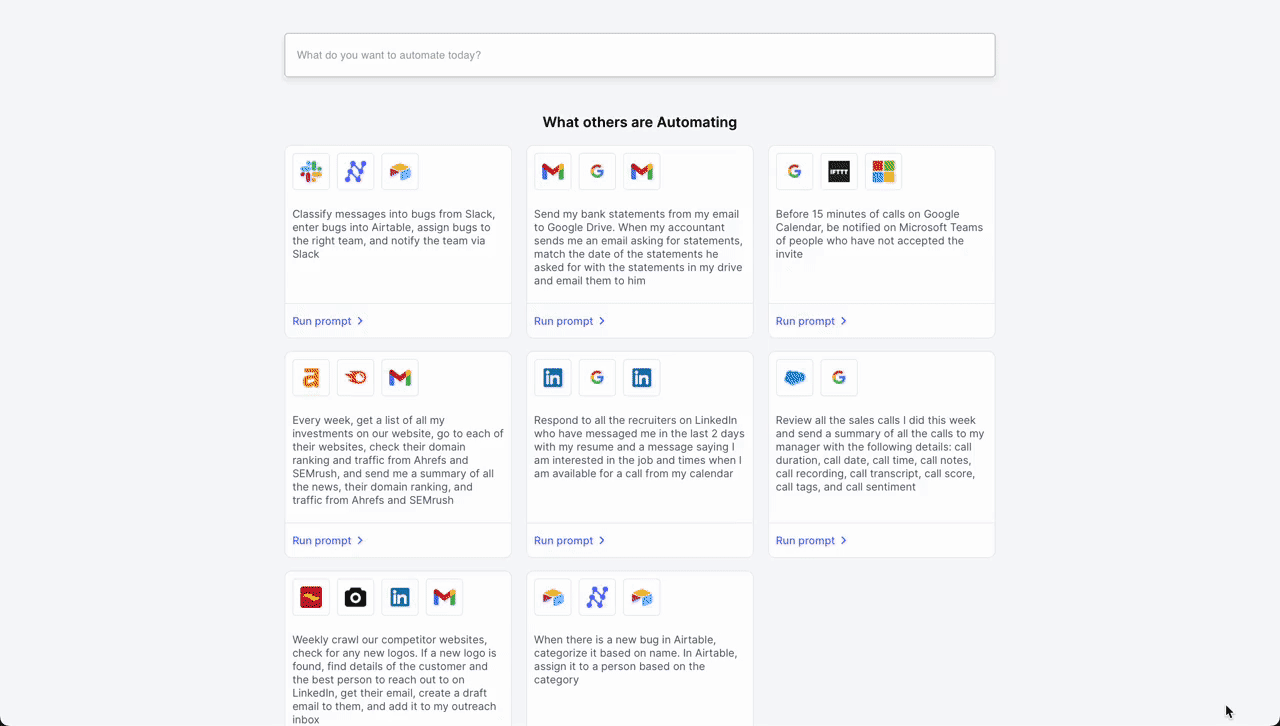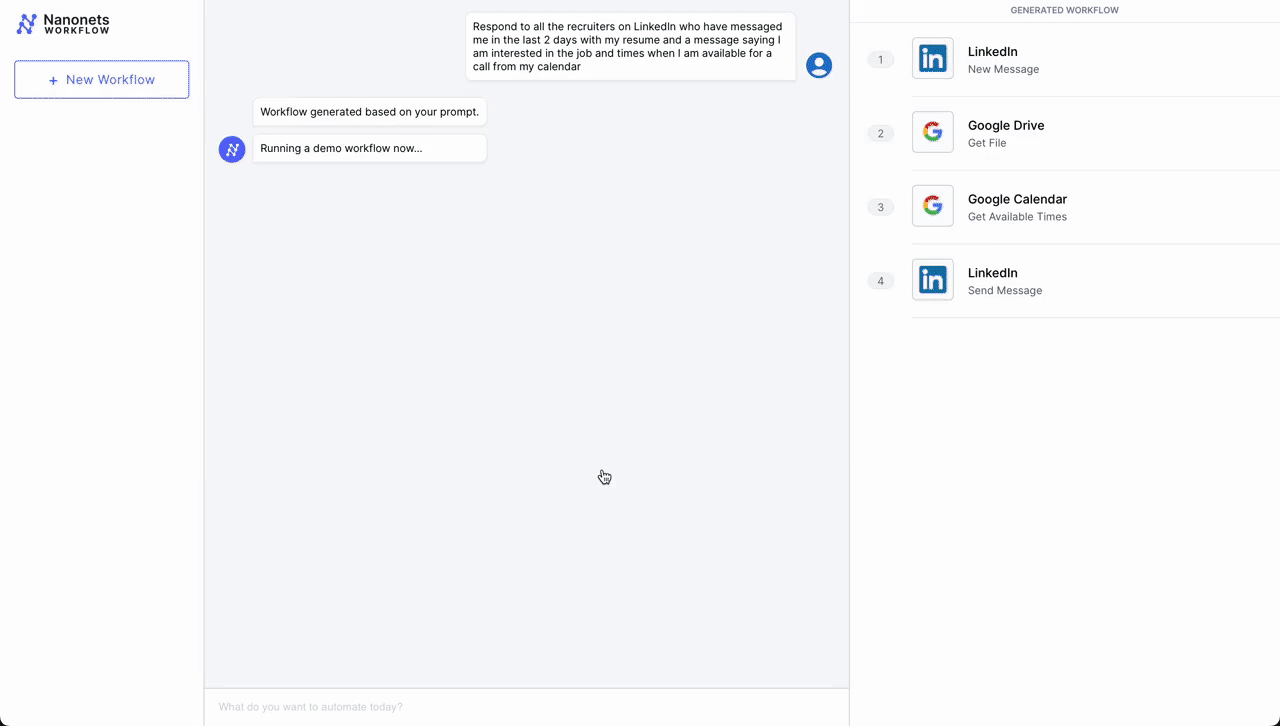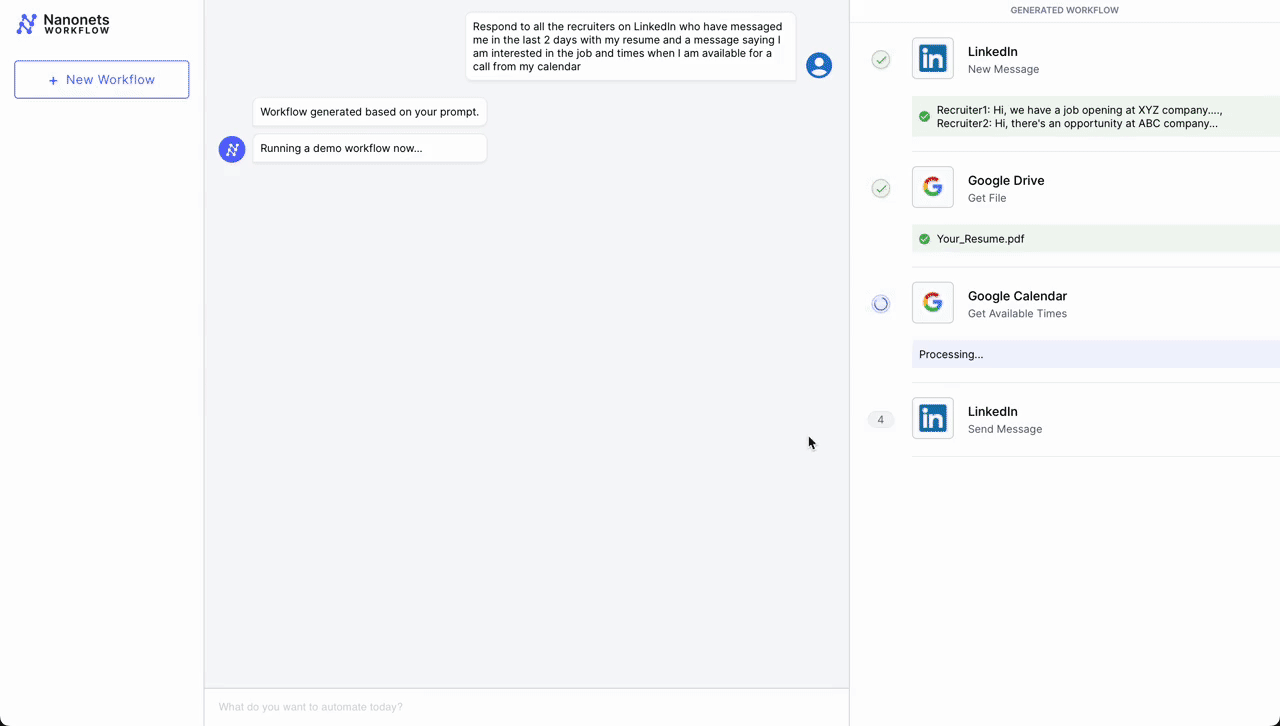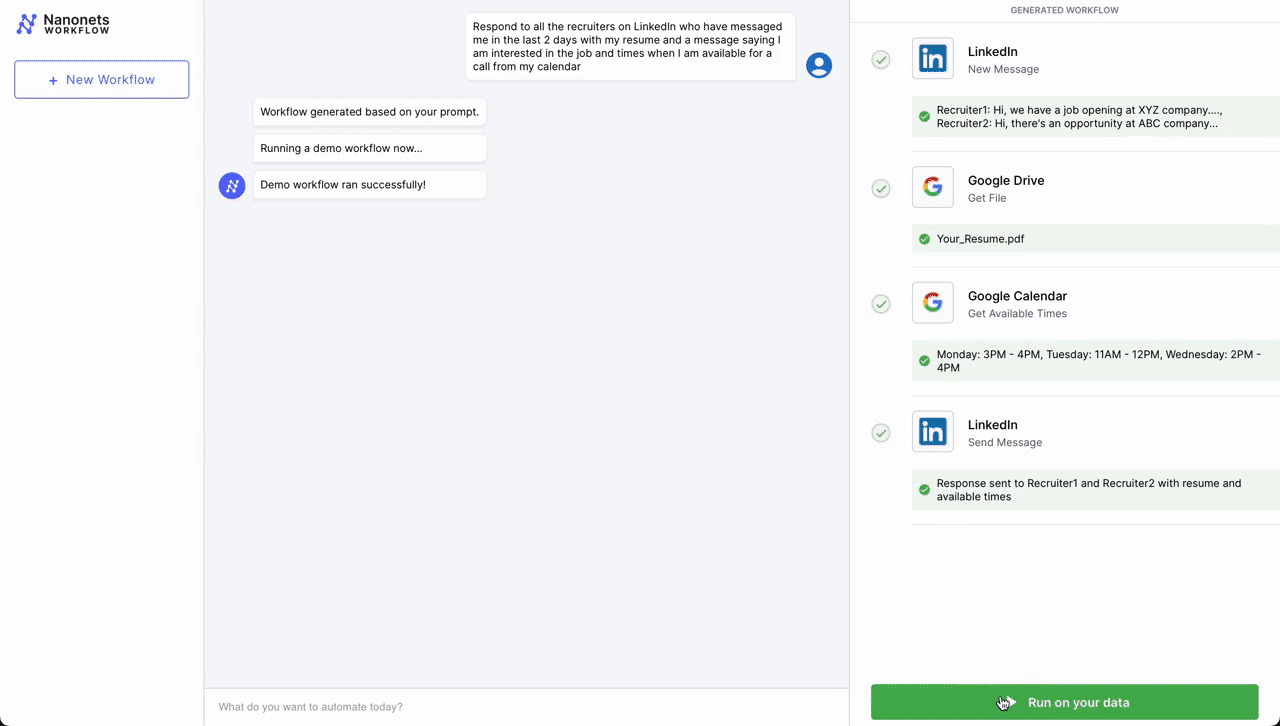
- Preliminary Contact – LinkedIn: The workflow is initiated when knowledgeable connection sends a brand new message on LinkedIn expressing curiosity in scheduling a gathering. An LLM parses incoming messages and triggers the workflow if it deems the message as a request for a gathering from a possible job candidate.
- Doc Retrieval – Google Drive: Following the preliminary contact, the workflow automation system retrieves a pre-prepared doc from Google Drive that accommodates details about the assembly agenda, firm overview, or any related briefing supplies.
- Scheduling – Google Calendar: Subsequent, the system interacts with Google Calendar to get accessible occasions for the assembly. It checks the calendar for open slots that align with enterprise hours (based mostly on the placement parsed from LinkedIn profile) and beforehand set preferences for conferences.
- Affirmation Message as Reply – LinkedIn: As soon as an appropriate time slot is discovered, the workflow automation system sends a message again by way of LinkedIn. This message contains the proposed time for the assembly, entry to the doc retrieved from Google Drive, and a request for affirmation or various options.
- Bill Processing in Accounts Payable
- Receipt of Bill – Gmail: An bill is acquired through electronic mail or uploaded to the system.
- Knowledge Extraction – Nanonets OCR: The system mechanically extracts related knowledge (like vendor particulars, quantities, due dates).
- Knowledge Verification – Quickbooks: The Nanonets workflow verifies the extracted knowledge towards buy orders and receipts.
- Approval Routing – Slack: The bill is routed to the suitable supervisor for approval based mostly on predefined thresholds and guidelines.
- Fee Processing – Brex: As soon as accredited, the system schedules the cost in accordance with the seller’s phrases and updates the finance data.
- Archiving – Quickbooks: The finished transaction is archived for future reference and audit trails.
- Inner Information Base Help

- Preliminary Inquiry – Slack: A group member, Smith, inquires within the #chat-with-data Slack channel about prospects experiencing points with QuickBooks integration.
- Automated Knowledge Aggregation – Nanonets Information Base:
- Ticket Lookup – Zendesk: The Zendesk app in Slack mechanically offers a abstract of as we speak’s tickets, indicating that there are points with exporting bill knowledge to QuickBooks for some prospects.
- Slack Search – Slack: Concurrently, the Slack app notifies the channel that group members Patrick and Rachel are actively discussing the decision of the QuickBooks export bug in one other channel, with a repair scheduled to go stay at 4 PM.
- Ticket Monitoring – JIRA: The JIRA app updates the channel a few ticket created by Emily titled “QuickBooks export failing for QB Desktop integrations,” which helps observe the standing and backbone progress of the difficulty.
- Reference Documentation – Google Drive: The Drive app mentions the existence of a runbook for fixing bugs associated to QuickBooks integrations, which may be referenced to grasp the steps for troubleshooting and backbone.
- Ongoing Communication and Decision Affirmation – Slack: Because the dialog progresses, the Slack channel serves as a real-time discussion board for discussing updates, sharing findings from the runbook, and confirming the deployment of the bug repair. Group members use the channel to collaborate, share insights, and ask follow-up questions to make sure a complete understanding of the difficulty and its decision.
- Decision Documentation and Information Sharing: After the repair is carried out, group members replace the inner documentation in Google Drive with new findings and any extra steps taken to resolve the difficulty. A abstract of the incident, decision, and any classes realized are already shared within the Slack channel. Thus, the group’s inner data base is mechanically enhanced for future use.
The Way forward for Enterprise Effectivity
Nanonets Workflows is a safe, multi-purpose workflow automation platform that automates your handbook duties and workflows. It gives an easy-to-use consumer interface, making it accessible for each people and organizations.
To get began, you possibly can schedule a name with certainly one of our AI consultants, who can present a customized demo and trial of Nanonets Workflows tailor-made to your particular use case.
As soon as arrange, you should utilize pure language to design and execute complicated functions and workflows powered by LLMs, integrating seamlessly together with your apps and knowledge.

Supercharge your groups with Nanonets Workflows permitting them to concentrate on what really issues.
Automate Whatsapp messaging campaigns with our AI-driven workflows, designed by Nanonets for you and your groups.

