Google has assigned a brand new CVE ID (CVE-2023-5129) to a libwebp safety vulnerability exploited as a zero-day in assaults and patched two weeks in the past.
The corporate initially disclosed the flaw as a Chrome weak point, tracked as CVE-2023-4863, reasonably than assigning it to the open-source libwebp library used to encode and decode pictures in WebP format.
This zero-day bug was collectively reported by Apple Safety Engineering and Structure (SEAR) and the Citizen Lab at The College of Toronto’s Munk Faculty on Wednesday, September 6, and stuck by Google lower than every week later.
Safety researchers at Citizen Lab have a longtime monitor document of detecting and revealing zero-days which have been abused in focused spyware and adware campaigns, typically linked to state-sponsored risk actors primarily focusing on high-risk people reminiscent of journalists and opposition politicians.
The choice to tag it as a Chrome bug induced confusion throughout the cybersecurity group, prompting questions concerning Google’s option to categorize it as a Google Chrome challenge reasonably than figuring out it as a flaw in libwebp.
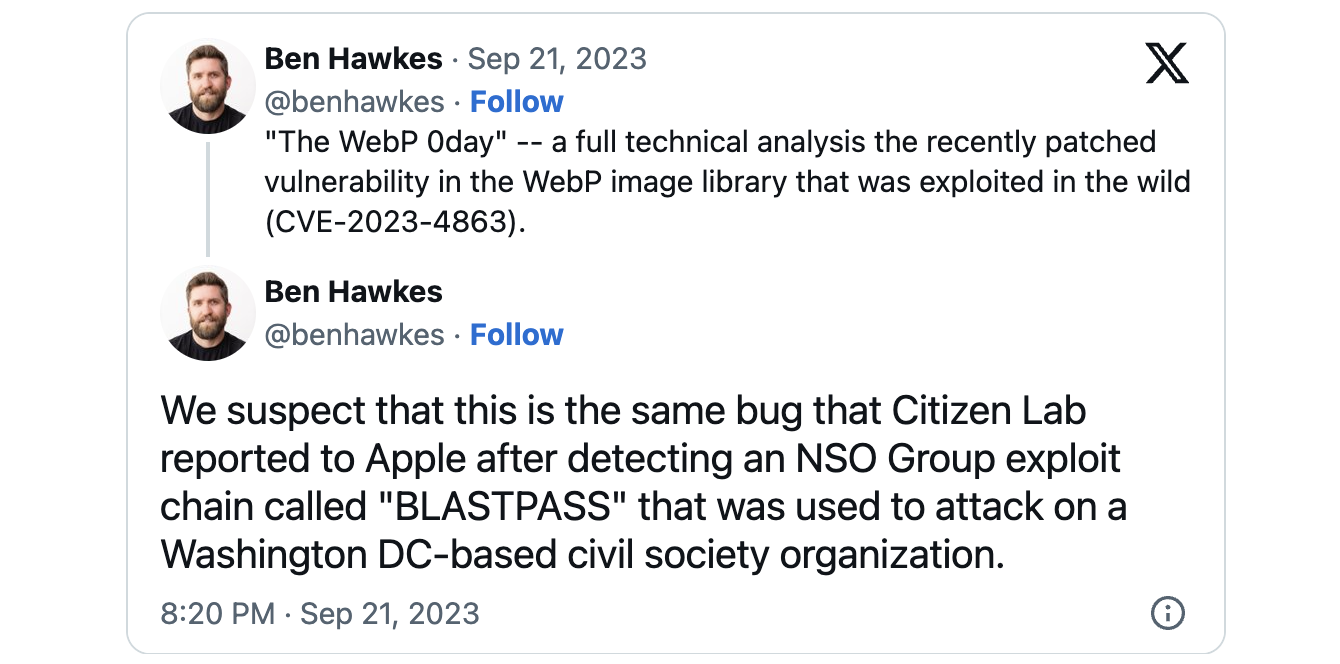
Safety consulting agency founder Ben Hawkes (who beforehand led Google’s Mission Zero workforce) additionally linked CVE-2023-4863 to the CVE-2023-41064 vulnerability addressed by Apple on September 7 and abused as a part of a zero-click iMessage exploit chain (dubbed BLASTPASS) to contaminate totally patched iPhones with NSO Group’s Pegasus industrial spyware and adware.
New most severity CVE
Nonetheless, it has now assigned one other CVE ID, CVE-2023-5129, marking it as a crucial challenge in libwebp with a most 10/10 severity ranking. This alteration has vital implications for different initiatives utilizing the libwebp open-source library.
Now formally acknowledged as a libwebp flaw, it entails a heap buffer overflow in WebP, impacting Google Chrome variations previous 116.0.5845.187.
This vulnerability resides throughout the Huffman coding algorithm utilized by libwebp for lossless compression and it allows attackers to execute out-of-bounds reminiscence writes utilizing maliciously crafted HTML pages.
This sort of exploit can have extreme penalties, from crashes to arbitrary code execution and unauthorized entry to delicate info.
The reclassification of CVE-2023-5129 as a libwebp vulnerability holds specific significance because of it initially going unnoticed as a possible safety risk for quite a few initiatives utilizing libwebp, together with 1Password, Sign, Safari, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Opera, and the native Android internet browsers.
The revised crucial ranking underscores the significance of promptly addressing the safety vulnerability (now tracked underneath a number of CVE IDs with completely different severity rankings) throughout these platforms to make sure customers’ information safety.
A Google spokesperson was not instantly accessible for remark when contacted by BleepingComputer earlier immediately.