Utilizing a 3D-printed materials delicate to electrical fields, researchers have created a novel sensor that may precisely acknowledge and distinguish objects as much as 10 centimeters – about 4 inches – away while not having to the touch them bodily. The touchless contact sensor might present a brand new stage of sensitivity to human-like robotics.
The previous few years have seen vital progress in producing electronics that may bend, twist, and fold, leading to a variety of practical wearable units. Understandably, integrating next-level contact sensors into digital human pores and skin has grow to be a key consideration, with the potential to be used throughout robotics, well being, and tech.
Digital pores and skin with built-in touchless sensing know-how may benefit many. Having the ability to wave a finger or gesture to launch software program, for instance, could be very handy – particularly for individuals who can’t bodily maintain a tool. Or, folks with visible disabilities would be capable of navigate round obstacles safely. This performance might prolong, after all, to any system related to the Web of Issues (IoT).
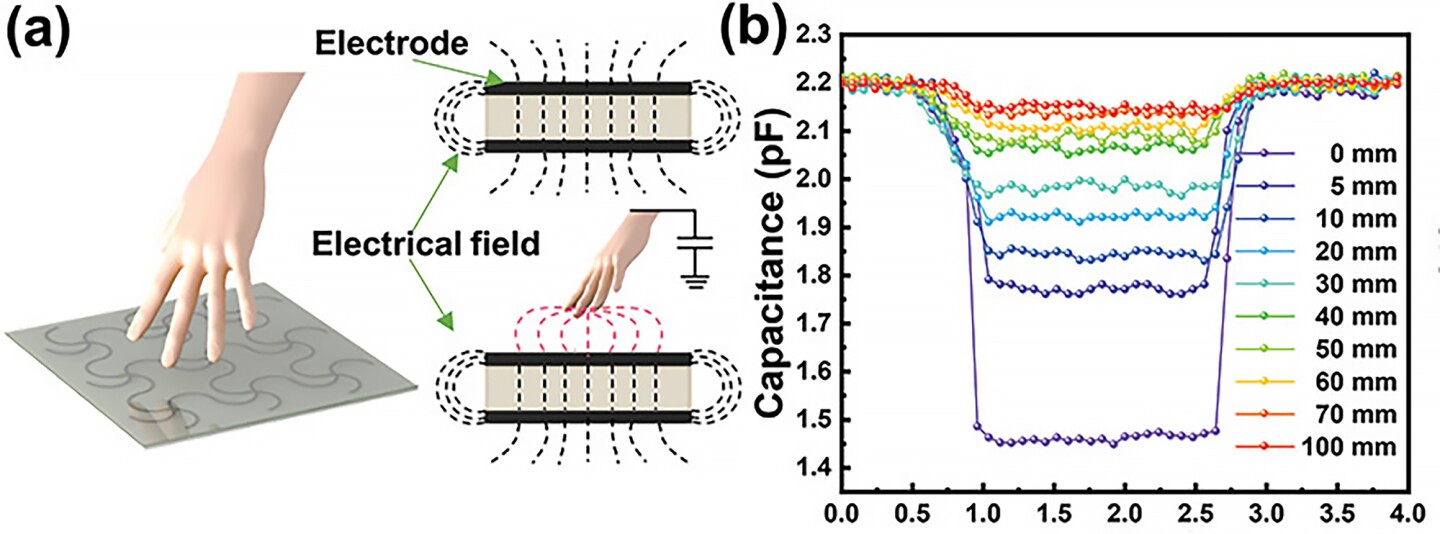
Most present contact sensors depend on touching an object on to create a measurable bodily deformation and corresponding power within the sensor. Nonetheless, with a brand new research by researchers from Qingdao College, China, we could have come one step nearer to contactless sensing. They’ve developed a contact sensor that’s so delicate it really works with out direct contact between it and the thing being detected.
“To convey higher sensitivity and flexibility, now we have developed new composite movies with shocking and really helpful electrical properties,” stated Xinlin Li, one of many research’s corresponding authors.
To create their composite movies, the researchers mixed small quantities of graphitic carbon nitride (GCN) with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) 3D-printed right into a grid. Surprisingly, they discovered that combining these two supplies with a excessive dielectric fixed – a measure of the flexibility to retailer electrical vitality in {an electrical} subject – resulted in a cloth with a low dielectric fixed and, due to this fact, a sensor extra delicate to electrical fields.
Bingxiang Li et al.
Testing the grid’s capabilities utilizing their very own fingers because the objects being detected, the researchers discovered that the grid sensed the fingers between 0.5 and 10 cm (0.2 to three.9 in) away and didn’t must be touched bodily, clearly figuring out the finger as a 3D object. Testing it on a round desk and a trigonal prism, the sensor might precisely acknowledge and distinguish completely different shapes and motions.
“The efficiency was excellent by way of sensitivity, pace of response and sturdy stability by way of many cycles of use,” Li stated. “This opens new potentialities within the subject of wearable objects and digital pores and skin.”
Following the profitable efficiency of their sensors, the researchers built-in them right into a printed circuit board to create a unified system able to remotely monitoring human movement. Digital pores and skin containing the novel sensors is affixed to the wrist, making certain a steady reference to a tool devoted to capturing and wirelessly transmitting the 3D form of objects to smartphones, smartwatches, and computer systems in real-time utilizing 4G know-how.
The researchers plan to refine the sensing know-how with a view to mass-producing it. They’ll additionally discover potentialities past detecting form and motion.
The research was revealed within the journal Science & Know-how of Superior Supplies.
Supply: ACN Newswire

