Mastodon, the free and open-source decentralized social networking platform, has patched 4 vulnerabilities, one in all them essential that permits hackers to create arbitrary information on the server utilizing specifically crafted media information.
Mastodon has about 8.8 million customers unfold throughout 13,000 separate servers (situations) hosted by volunteers to assist distinct but inter-connected (federated) communities.
All of the 4 points fastened had been found by unbiased auditors at Cure53, an organization that gives penetration testing for on-line providers. The auditors inspected Mastodon’s code at Mozilla’s request.
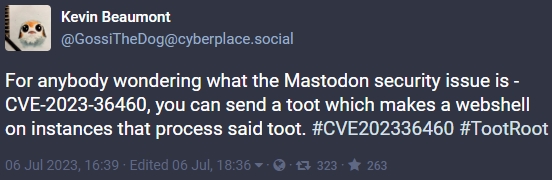
Probably the most extreme of the vulnerabilities is tracked as CVE-2023-36460 and has been named TootRoot. It provides attackers a very straightforward strategy to compromise goal servers.
CVE-2023-36460 is an issue in Mastodon’s media processing code that permits utilizing media information on toots (the equal of tweets) to trigger a spread of issues, from denial of service (DoS) to arbitrary distant code execution.
Though Mastodon’s safety bulletin is laconic, safety researcher Kevin Beaumont highlighted the dangers related to TootRoot, saying {that a} toot can be utilized to plant backdoors on the servers that ship content material to Mastodon customers.
Such a compromise would give attackers limitless management over the server and the information it hosts and manages, and extends to customers’ delicate info.
The second critical-severity flaw is CVE-2023-36459, a cross-site scripting (XSS) on oEmbed preview playing cards utilized in Mastodon that permits bypassing HTML sanitization on the goal browser.
Assaults leveraging this flaw may very well be used for account hijacking, person impersonation or accessing delicate knowledge.
The opposite two vulnerabilities that Mastodon addressed are CVE-2023-36461, a high-severity DoS flaw by means of gradual HTTP responses, and CVE-2023-36462, additionally rated with high-severity that lets an attacker format a verified profile hyperlink in a misleading method that can be utilized for phishing.
The 4 vulnerabilities impression all variations of Mastodon from 3.5.0 onward, and had been patched in variations 3.5.9, 4.0.5, and 4.1.3.
The patches are server safety updates and have to be utilized by directors to take away the danger for his or her communities.