We’re at present ready for the UK authorities to publish its semiconductor technique. As context for such a technique, my earlier two blogposts have summarised the worldwide state of the business:
Half 1: the UK’s place within the semiconductor world
Half 2: the previous and way forward for the worldwide semiconductor business
Right here I contemplate what a sensible and helpful UK semiconductor technique would possibly embrace.
To summarise the worldwide context, the important nations in superior semiconductor manufacturing are Taiwan, Korea and the USA for making the chips themselves. As well as, Japan and the Netherlands are very important for essential components of the availability chain, notably the tools wanted to make chips. China has been devoting vital useful resource to develop its personal semiconductor business – in consequence, it’s sturdy in all however essentially the most superior applied sciences for chip manufacture, however is weak to being lower off from essential components of the availability chain.
The expertise of chip manufacture is approaching maturity; the very fast charges of improve in computing energy we noticed within the Nineteen Eighties and Nineties, related to a mix of Moore’s regulation and Dennard scaling, have considerably slowed. On the expertise frontier we’re seeing diminishing returns from the ever bigger investments in capital and R&D which might be wanted to take care of advances. Additional enhancements in pc efficiency are more likely to put extra premium on customized designs for chips optimised for particular purposes.
The UK’s place in semiconductor manufacturing is marginal in a worldwide perspective, and never a relative power within the context of the general UK economic system. There may be truly a barely stronger place within the wider provide chain than in chip manufacture itself, however essentially the most vital power isn’t in manufacture, however design, with ARM having a globally vital place and newcomers like Graphcore displaying promise.
The historical past of the worldwide semiconductor business is a historical past of main authorities interventions coupled with very massive non-public sector R&D spending, the latter pushed by dramatically growing gross sales. The UK primarily opted out of the race within the 1980’s, since when Korea and Taiwan have established globally main positions, and China has develop into a quick increasing new entrant to the business.
The harder geopolitical atmosphere has led to a return of business technique on an enormous scale, led by the USA’s CHIPS Act, which appropriates greater than $50 billion over 5 years to reestablish its international management, together with $39 billion on direct subsidies for manufacturing.
How ought to the UK reply? What I’m speaking about right here is the core enterprise of producing semiconductor gadgets and the encompassing provide chain, reasonably than data and communication expertise extra broadly. First, although, let’s be clear about what the objectives of a UK semiconductor technique could possibly be.
What’s a semiconductor technique for?
A nationwide technique for semiconductors may have a number of objectives. The UK Science and Know-how Framework identifies semiconductors as one in all 5 essential applied sciences, judged towards standards together with their foundational character, market potential, in addition to their significance for different nationwide priorities, together with nationwide safety.
It could be useful to tell apart two barely completely different objectives for the semiconductor technique. The primary is the query of safety, within the broadest sense, prompted by the availability issues that emerged within the pandemic, and heightened by the rising realisation of the significance and vulnerability of Taiwan within the international semiconductor business. Right here the inquiries to ask are, what industries are in danger from additional disruptions? What are the nationwide safety points that might come up from interruptions in provide?
The federal government’s newest refresh of its built-in international and defence technique guarantees to “make sure the UK has a transparent path to assured entry for every [critical technology], a powerful voice in influencing their improvement and use internationally, a managed strategy to produce chain dangers, and a plan to guard our benefit as we construct it.” It reasserts as a mannequin launched within the earlier Built-in Evaluate the “personal, collaborate, entry” framework.
This framework is a welcome recognition of the the truth that the UK is a medium measurement nation which may’t do the whole lot, and in an effort to have entry to the expertise it wants, it should in some circumstances collaborate with pleasant nations, and in others entry expertise via open international markets. However it’s price asking what precisely is supposed by “personal”. That is outlined within the Built-in Evaluate thus: “Personal: the place the UK has management and possession of latest developments, from discovery to large-scale manufacture and commercialisation.”
In what sense does the nation ever personal a expertise? There are nonetheless a couple of circumstances the place wholly state owned organisations retain each a sensible and authorized monopoly on a selected expertise – nuclear weapons stay the obvious instance. However applied sciences are largely managed by non-public sector firms with a fancy, and infrequently international possession construction. We would suppose that the applied sciences of semiconductor built-in circuit design that ARM developed are British, as a result of the corporate relies in Cambridge. However it’s owned by a Japanese funding financial institution, who’ve an excessive amount of latitude in what they do with it.
Maybe it’s extra useful to speak about management than possession. The UK state retains a specific amount of management of applied sciences owned by firms with a considerable UK presence – it has been in a position in impact to dam the acquisition of the Newport Wafer Fab by the Chinese language owned firm Nexperia. However this new assertiveness is a really current phenomenon; till very just lately UK governments have been solely relaxed in regards to the acquisition of expertise firms by abroad firms. Certainly, in 2016 ARM’s acquisition by Softbank was welcomed by the then PM, Theresa Could, as being within the UK’s nationwide curiosity, and a vote of confidence in post-Brexit Britain. The federal government has taken new powers to dam acquisitions of firms via the Nationwide Safety and Funding Act 2021, however this will solely be accomplished on grounds of nationwide safety.
The second objective of a semiconductor technique is as a part of an effort to beat the UK’s persistent stagnation of financial productiveness, to “generate innovation-led financial progress” , within the phrases of a current Authorities response to a BEIS Choose Committee report. As I’ve written about at size, the UK’s productiveness drawback is critical and chronic, so there’s definitely a must determine and help excessive worth sectors with the potential for progress. There’s a regional dimension right here, recognised within the authorities’s aspiration for the technique to create “excessive paying jobs all through the UK”. So it could be solely applicable for a technique to help the present cluster within the Southwest round Bristol and into South Wales, in addition to to create new clusters the place there are strengths in associated business sectors
The economies of Taiwan and Korea have been remodeled by their very efficient deployment of an energetic industrial technique to make the most of an business at a time of fast technological progress and increasing markets. There are two questions for the UK now. Has the UK state (and the broader financial consensus within the nation) overcome its ideological aversion to energetic industrial technique on the East Asian mannequin to intervene on the essential scale? And, would such an intervention be well timed, given the place semiconductors are within the expertise cycle? Or, to place it extra provocatively, has the UK left it too late to seize a major share of a expertise that’s approaching maturity?
What, realistically, can the UK do about semiconductors?
What interventions are doable for the UK authorities in devising a semiconductor technique that addresses these two objectives – of accelerating the UK’s financial and army safety by lowering its vulnerability to shocks within the international semiconductor provide chain, and of bettering the UK’s financial efficiency by driving innovation-led financial progress? There’s a menu of choices, and what the federal government chooses will rely upon its urge for food for spending cash, its willingness to take belongings onto its steadiness sheet, and the way a lot it’s ready to intervene available in the market.
May the UK set up the manufacturing of forefront silicon chips? This appears implausible. That is essentially the most subtle manufacturing course of on the planet, enormously capital intensive and drawing on an enormous quantity of proprietary and tacit data. The one method it may occur is that if one of many three firms at present at or near the expertise frontier – Samsung, Intel or TSMC – could possibly be enticed to determine a producing plant within the UK. What could be in it for them? The UK doesn’t have a giant market, it has a labour market that’s excessive price, but missing within the essential abilities, so its solely probability could be to advance massive direct subsidies.
In any case, the eye of those firms is elsewhere. TSMC is constructing a brand new plant in Arizona, at a value of $40 billion, whereas Samsung’s new plant in Texas is costing $25 billion, with the US authorities utilizing among the CHIPS act cash to subsidise these investments. Regardless of Intel’s well-reported difficulties, it’s planning vital funding in Europe, supported by inducements from EU and its member states below the EU Chips act. Intel has dedicated €12 billion to increasing its operations in Eire and €17 billion for a brand new fab within the current semiconductor cluster in Saxony, Germany.
From the perspective of safety of provide, it’s not simply chips from the forefront which might be essential; for a lot of purposes, in cars, defence and industrial equipment, legacy chips produced by processes which might be not at the forefront are ample. In precept establishing manufacturing amenities for such legacy chips could be much less difficult than making an attempt to determine manufacturing at the forefront. Nevertheless, right here, the economics of building new manufacturing amenities may be very tough. The price of producing chips is dominated by the necessity to amortise the very massive capital price of organising a fab, however a brand new plant could be in competitors with long-established crops whose capital price is already totally depreciated. These legacy chips are a commodity product.
So in practise, our safety of provide can solely be assured by reliance on pleasant nations. It could have been useful if the UK had been capable of take part within the improvement of a European technique to safe semiconductor provide chains, as Hermann Hauser has argued for. However what does the UK must contribute, within the creation of extra resilient provide chains extra localised in networks of reliably pleasant nations?
The UK’s key asset is its place in chip design, with ARM because the anchor agency. However, as a agency based mostly on mental property reasonably than the massive capital investments of fabs and factories, ARM is doubtlessly footloose, and as we’ve seen, it isn’t British by possession. Reasonably it’s owned and managed by a Japanese conglomerate, which must promote it to lift cash, and can search to realize the best return from such a sale. After the proposed sale to Nvidia was blocked, the doubtless final result now could be a floatation on the US inventory market, the place the everyday valuations of tech firms are greater than they’re within the UK.
The UK state may search to take care of management over ARM by the system of a “Golden Share”, because it at present does with Rolls-Royce and BAE Techniques. I’m unsure what the mechanism for this may be – I’d think about that the one surefire method of doing this may be for the UK authorities to purchase ARM outright from Softbank in an agreed sale, after which subsequently float it itself with the golden share in place. I don’t suppose this may be low cost – the agreed worth for the thwarted Nvidia take over was $66 billion. The UK authorities would then try to recoup as a lot of the acquisition worth as doable via a subsequent floatation, however the presence of the golden share would presumably scale back the market worth of the remaining shares. Nonetheless, the UK authorities did spend £46 billion nationalising a financial institution.
What different levers does the UK must consolidate its place in chip design? Clever use of presidency buying energy is usually cited as an ingredient of a profitable industrial coverage, and right here there is a chance. The federal government made the welcome announcement within the Spring Finances that it could commit £900 m to construct an exascale pc to create a sovereign functionality in synthetic intelligence. The procurement course of for this facility needs to be designed to drive innovation within the design, by UK firms, of specialized processing models for AI with decrease vitality consumption.
A powerful public R&D base is a essential – however not ample – situation for an efficient industrial technique in any R&D intensive business. As a matter of coverage, the UK ran down its public sector analysis effort in mainstream silicon microelectronics, in response to the UK’s total weak place within the business. The Engineering and Bodily Analysis Council proclaims on its web site that: “In 2011, EPSRC determined to not help analysis geared toward miniaturisation of CMOS gadgets via gate-length discount, as massive non-UK industrial funding on this area meant such analysis would have been unlikely to have had vital nationwide affect.” I don’t suppose this was – or is – an unreasonable coverage given the realities of the UK’s international place. The UK maintains tutorial analysis power in areas such III-V semiconductors for optoelectronics, 2-d supplies similar to graphene, and natural semiconductors, to offer a couple of examples.
Given the sophistication of state-of-the-art microelectronic manufacturing expertise, for R&D to be related and translatable into business merchandise it’s important that open entry amenities can be found to permit the prototyping of analysis gadgets, and with pilot scale tools to reveal manufacturability and facilitate scale-up. The UK doesn’t have analysis centres on the size of Belgium’s IMEC, or Taiwan’s ITRI, and the difficulty is whether or not, given the self-love of the UK’s business base, there could be a buyer base for such a facility. There are a variety of college amenities targeted on supporting tutorial researchers in numerous specialisms – at Glasgow, Manchester, Sheffield and Cambridge, to offer some examples. Two centres are related to the Catapult Community – The Nationwide Printable Electronics Centre in Sedgefield, and the Compound Semiconductor Catapult in South Wales.
This current infrastructure is definitely inadequate to help an ambition to broaden the UK’s semiconductor sector. However a call to boost this analysis infrastructure will want a cautious and lifelike analysis of what niches the UK may realistically hope to construct some presence in, constructing on areas of current UK power, and understanding the size of funding elsewhere on the planet.
To summarise, the UK should recognise that, in semiconductors, it’s at present in a comparatively weak place. For safety of provide, the main focus have to be on staying near like-minded nations like our European neighbours. For the UK to develop its personal semiconductor business additional, the emphasis have to be on discovering and growing explicit niches the place the UK’s does have some current power to construct on, and there’s the prospect of quickly rising markets. And the UK ought to take care of its one real space of power, in chip design.
4 classes for industrial technique
What ought to the UK do about semiconductors? One other tempting, however unhelpful, reply is “I wouldn’t begin from right here”. The UK’s present place displays previous decisions, so to conclude, maybe it’s price drawing some extra common classes about industrial technique from the historical past of semiconductors within the UK, and globally.
1. Fundamental analysis isn’t sufficient
The historian David Edgerton has noticed that it’s a long-running behavior of the UK state to make use of analysis coverage as an alternative choice to industrial technique. Fundamental analysis is comparatively low cost, in comparison with the costly and time-consuming technique of growing and implementing new merchandise and processes. Within the 1980’s, it turned typical knowledge that governments shouldn’t become involved in utilized analysis and improvement, which needs to be left to non-public business, and, as I just lately mentioned at size, this has profoundly formed the UK’s analysis and improvement panorama. However excellence in primary analysis has not produced a aggressive semiconductor business.
The final vital act of presidency help for the semiconductor business within the UK was the Alvey programme of the Nineteen Eighties. The programme was not with out some technical successes, however it clearly failed in its strategic objective of preserving the UK semiconductor business globally aggressive. Because the official analysis of the programme concluded in 1991 [1]: “Assist for pre-competitive R&D is a essential however inadequate means for enhancing the aggressive efficiency of the IT business. The programme was not funded or outfitted to take care of the completely different phases of the innovation course of able to being addressed by authorities expertise insurance policies. If enhanced competitiveness is the objective, both the funding or scope of motion needs to be commensurate, or expectations needs to be lowered accordingly”.
However the correct R&D establishments might be helpful; the expertise of each Japan and the USA exhibits the worth of business consortia – however this solely works if there’s already a powerful, R&D intensive business base. The creation of TSMC exhibits that it’s doable to create a worldwide large from scratch, and this emphasises the function of translational analysis centres, like Taiwan’s ITRI and Belgium’s IMEC. However to be efficient in creating new companies, such centres must have a deal with course of enchancment and manufacturing, in addition to discovery science.
2. Massive is gorgeous in deep tech.
The fashionable semiconductor business is the epitome of “Deep Tech”: arduous innovation, normally within the materials or organic domains, demanding long run R&D efforts and enormous capital investments. For all of the romance of garage-based start-ups, in a enterprise that calls for up-front capital investments within the $10’s of billions and annual analysis budgets on the size of medium measurement nation states, one wants critical, massive scale organisations to succeed.
The possession and management of those organisations does matter. From a nationwide perspective, it is very important have massive corporations anchored to the territory, whether or not by possession or by vital capital funding that might be arduous to undo, so guaranteeing the permanence of such corporations is the authentic enterprise of presidency. Naturally, huge corporations usually begin as quick rising small ones, and the UK ought to make extra effort to hold on to firms as they scale up.
3. Getting the timing proper within the expertise cycle
Technological progress is uneven – at any given time, one business could also be present process very dramatic technological change, whereas different sectors are comparatively stagnant. There could also be a second when the state of expertise guarantees a interval of fast improvement, and there’s a matching market with the potential for quick progress. Corporations which have the capability to take a position and exploit such “home windows of alternative”, to make use of David Sainsbury’s phrase, will have the ability to generate and seize a excessive and rising degree of added worth.
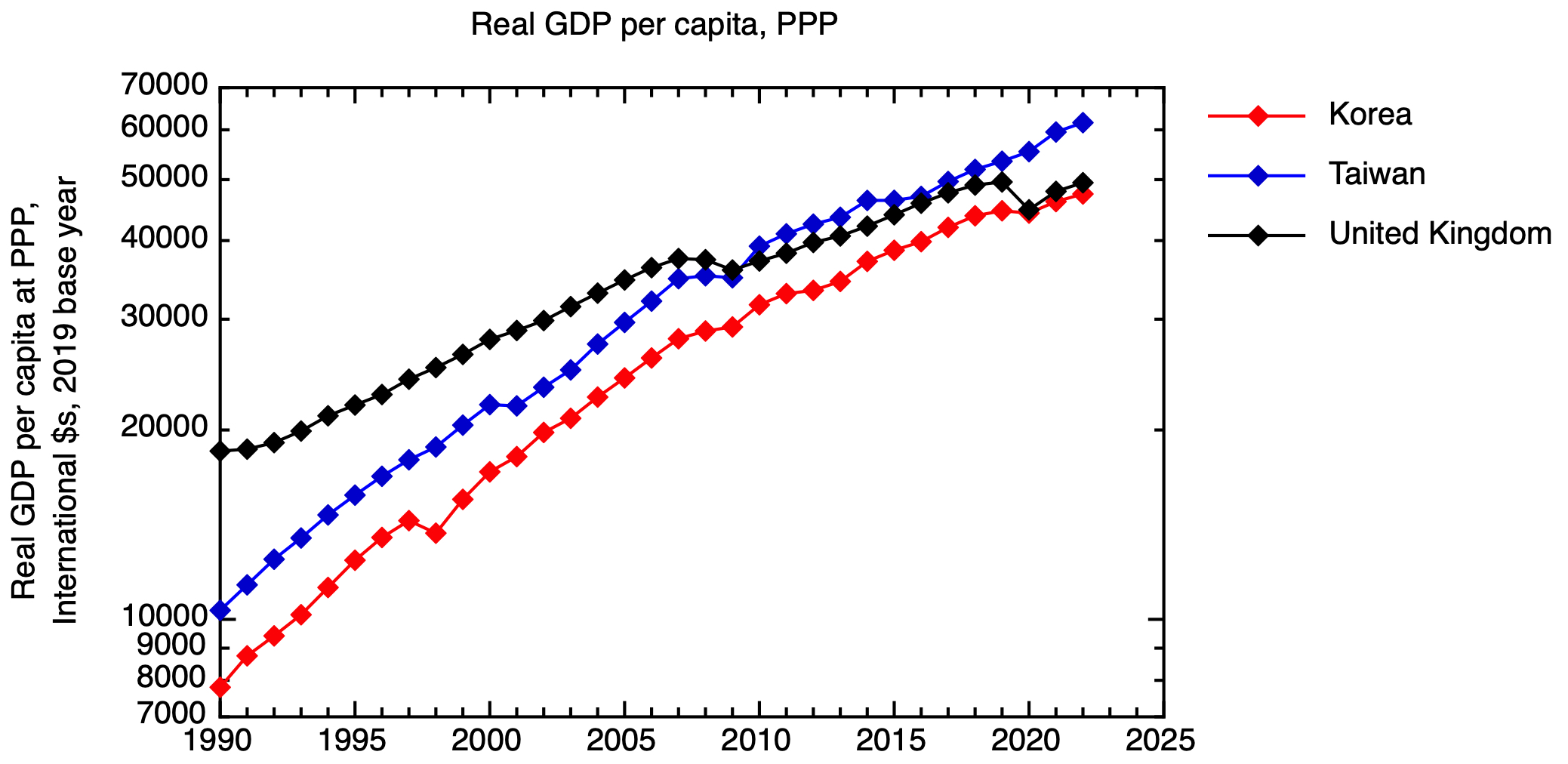
The timing of interventions to help such corporations is essential, and undoubtedly not straightforward, however historical past exhibits us that nations which might be capable of provide vital ranges of strategic help on the proper stage can see a cloth affect on their financial efficiency. The current fast financial progress of Korea and Taiwan is a working example. These nations have gone past catch-up financial progress, to equal or surpass the UK, reflecting their reaching the technological frontier in excessive worth sectors similar to semiconductors. In fact, in these nations, there was a a lot nearer entanglement between the state and corporations than UK coverage makers are comfy with.
Actual GDP per capita at buying energy parity for Taiwan, Korea and the UK. Based mostly on information from the IMF. GDP at PPP in worldwide {dollars} was taken for the bottom 12 months of 2019, and a time collection constructed utilizing IMF actual GDP progress information, & then expressed per capita.
4. In case you don’t select sectors, sectors will select you
Within the UK, so-called “vertical” industrial technique, the place express decisions are made to help particular sectors, have lengthy been out of favour. Making decisions between sectors is tough, and being perceived to have made the incorrect decisions damages the fame of people and establishments. However even within the absence of an explicitly articulated vertical industrial technique, coverage decisions can have the impact of favouring one sector over one other.
Within the Nineties and 2000s, UK selected oil and gasoline and monetary companies over semiconductors, or certainly superior manufacturing extra usually. Our present financial state of affairs displays, partly, that alternative.
[1] Analysis of the Alvey Programme for Superior Info Know-how. Ken Man, Luke Georghiou, et al. HMSO for DTI and SERC (1991)