
The U.S. authorities launched a report after analyzing easy strategies, e.g. SIM swapping, utilized by the Lapsus$ extortion group to breach dozens of organizations with a robust safety posture.
Reviewing the group’s operations began in December final 12 months following an extended path of incidents attributed to or claimed by Lapsus$ after leaking proprietary knowledge from alleged victims.
Amongst high-profile corporations impacted by Lapsus$ are Microsoft, Cisco, Okta, Nvidia, T-Cell, Samsung, Uber, Vodafone, Ubisoft, and Globant.
Lapsus$ is described as a loosely-organized group shaped primarily of youngsters, with members within the U.Ok. and Brazil that acted between 2021 and 2022 for notoriety, monetary achieve, or for enjoyable. Nonetheless, additionally they mixed strategies of assorted complexity with “flashes of creativity.”
SIM-swap energy
The Division of Homeland Safety (DHS) Cyber Security Assessment Board (CSRB) finalized its evaluation and describes the group’s ways and strategies in a report that additionally contains suggestions for the trade.
“Lapsus$ employed low-cost strategies, well-known and obtainable to different risk actors, revealing weak factors in our cyber infrastructure that might be susceptible to future assaults” – Division of Homeland Safety Cyber Security Assessment Board.
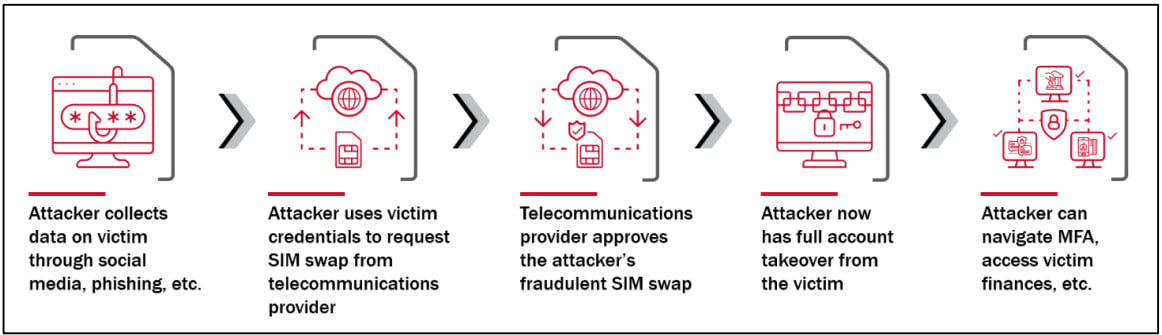
The group used SIM swapping to realize entry to a goal firm’s inner community and steal confidential data like supply code, particulars about proprietary know-how, or enterprise and customer-related paperwork.
In a SIM-swapping assault, the risk actor steals the sufferer’s telephone quantity by porting it to a SIM card owned by the attacker. The trick depends on social engineering or an insider on the sufferer’s cell service.
With management over the sufferer’s telephone quantity, the attacker can obtain SMS-based ephemeral codes for two-factor authentication (2FA) required to log into numerous enterprise companies or breach company networks.
supply: DHS CSRB
Going to the supply
Within the case of Lapsus$, a number of the fraudulent SIM swaps have been carried out straight from the telecommunications supplier’s buyer administration instruments after hijacking accounts belonging to staff and contractors.
To acquire confidential details about their sufferer (identify, telephone quantity, buyer proprietary community data), members of the group generally used fraudulent emergency disclosure requests (EDRs).
An attacker can create a pretend EDR by impersonating a reputable requestor, akin to a regulation enforcement agent, or by making use of official logos to the request.
Lapsus$ additionally relied on insiders at focused corporations, staff, or contractors, to acquire credentials, approve multi-factor authentication (MFA) requests, or use inner entry to assist the risk actor.
“After executing the fraudulent SIM swaps, Lapsus$ took over on-line accounts through sign-in and account restoration workflows that despatched one-time hyperlinks or MFA passcodes through SMS or voice calls” – Division of Homeland Safety Cyber Security Assessment Board.
In a single case, Lapsus$ used their unauthorized entry to a telco supplier to attempt to compromise cell phone accounts related to FBI and Division of Protection personnel.
The try was unsuccessful as a result of further safety carried out for these accounts.
Making and spending cash
Throughout the analysis, CSRB’s findings, the group paid as a lot as $20,000 per week to entry a telecommunications supplier’s platform and carry out SIM swaps.
Though the FBI was not conscious of Lapsus$ promoting the info they stole or discovered proof of victims paying ransoms to the group, CSRB says that some safety consultants “noticed Lapsus$ extorting organizations with some paying ransoms.”
In line with CSRB’s findings the group additionally exploited unpatched vulnerabilities in Microsoft Lively Listing to extend their privileges on the sufferer community.
It’s estimated that Lapsus$ leveraged Lively Listing safety points in as much as 60% of their assaults, exhibiting that members of the group had the technical abilities to maneuver inside a community.
Hitting the brakes
Whereas Lapsus$ was characterised by effectiveness, velocity, creativity, and boldness, the group was not all the time profitable in its assaults. It failed in environments that carried out utility or token-based multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Additionally, strong community intrusion detection programs and flagging suspicious account exercise prevented Lapsus$ assaults. The place incident response procedures have been adopted, the impression was “considerably mitigated,” CSRB says within the report.
Regardless of safety researchers and consultants decrying for years the usage of SMS-based authentication as insecure, DHS’ Cyber Security Assessment Board highlights that “most organizations weren’t ready to stop” the assaults from Lapsus$ or different teams using comparable ways.
The Board’s suggestions to stop different actors from gaining unauthorized entry to an inner community embrace:
- transitioning to a passwordless surroundings with safe id and entry administration options and discarding SMS as a two-step authentication technique
- prioritizing efforts to cut back the effectivity of social engineering via strong authentication capabilities which can be resilient to MFA phishing
- telco suppliers ought to deal with SIM swaps as extremely privileged actions that require robust id verification, and supply account-locking choices for shoppers
- strengthen Federal Communications Fee (FCC) and Federal Commerce Fee (FTC) oversight and enforcement actions
- planning for disruptive cyberattacks and investing in prevention, response, and restoration; adopting a zero-trust mannequin and strengthening authentication practices
- constructing resilience towards social engineering assaults when it comes Emergency Disclosure (Information) Requests
- organizations ought to enhance cooperation with regulation enforcement by reporting incidents promptly; the U.S. Authorities “clear, constant steerage about its cyber incident-related roles and duties”
Lapsus$ fell silent since September 2022, possible as a result of regulation enforcement investigations that led to the arrests of a number of members of the group.
In March final 12 months, the Metropolis of London Police introduced the arrest of seven people linked to Lapsus$. A couple of days later, on April 1, two extra have been apprehended, a 16-year-old and a 17-year-old.
In October, throughout Operation Darkish Cloud, the Brazilian Federal Police arrested a person suspected to be a part of the Lapsus$ extortion group, for breaching the programs of the nation’s Ministry of Well being.
