Stefan Wilhelm, an affiliate professor within the Stephenson Faculty of Biomedical Engineering on the College of Oklahoma, and a number of other college students in his Biomedical Nano-Engineering Lab have just lately revealed an article within the journal Nano Letters that outlines their current essential nanomedicine development.
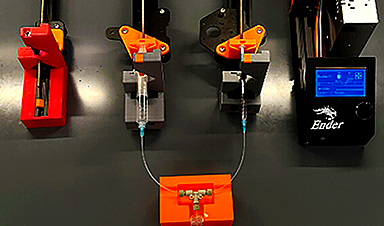
Wilhelm, with pupil researchers comparable to Hamilton Younger, a senior biomedical engineering pupil, and Yuxin He, a biomedical engineering graduate analysis assistant, used 3D printer elements to combine fluid streams collectively containing the constructing blocks of nanomedicines and their payloads in a T-mixer format.
“This mixing gadget is basically a T-shaped piece of tubing that forces two fluid streams to circulate into one another, mixing nanomaterial and payload parts collectively. As soon as blended, the ultimate product would exit by way of the opposite finish,” Wilhelm stated. “This mixing idea is utilized in industrial processes, so we puzzled if we might make these units as cost-efficient as attainable.”
The crew found a publication from a European analysis group that demonstrated that commercially accessible 3D printers could possibly be reassembled into syringe pumps wanted to push the fluids by way of the T-mixer gadget. As soon as constructed, they tried to provide nanomedicines with their 3D-built T-mixer.
“We have been specializing in formulations which are used within the clinic, comparable to mRNA lipid nanoparticles, liposomes, and polymeric nanoparticles. One of many molecules we used was developed by a collaborator at OU Well being Sciences to restrict prostate most cancers cell progress,” Wilhelm stated. “We encapsulated this molecule into our nanomedicine formulations and confirmed that it really stops these prostate most cancers cells from rising.”

Based mostly on this instance, the crew’s analysis has doubtlessly broad implications for novel most cancers therapies and vaccines in opposition to infectious ailments, as mRNA expertise is already being utilized in scientific trials for customized most cancers vaccines.
“All of this mRNA expertise depends on nanotechnology. mRNA molecules degrade too quick within the physique to be efficient with out encapsulating them in nanoparticles,” Wilhelm stated. “This course of might open up a vivid future for nanotechnology in drugs and can hopefully vastly enhance well being care.”
Wilhelm additionally foresees a future the place medical doctors’ places of work and clinics in rural communities with restricted sources might use this expertise to create customized vaccines. His work with B4NANO, a partnership and outreach program with Native American tribes and communities in Oklahoma, conjures up this purpose.
“I might see a future state of affairs the place a affected person walks into a physician’s workplace with an infectious illness —presumably most cancers. After a analysis by the physician, a vaccine is produced on the physician’s workplace in a way much like how a single-serve espresso maker works—you simply put in your capsules, press a button, and get a customized vaccine for that affected person,” Wilhelm stated. “Our purpose is to develop this type of benchtop gadget after which hopefully discover trade companions to commercialize techniques like these.”
One other purpose Wilhelm has is coaching the following technology of biomedical engineers, like Younger and He, to resolve challenges in well being care.
“The challenges we face in biomedical engineering require that we now have a various crew, with folks coming from all completely different sorts of backgrounds. Everyone brings of their distinctive perspective, distinctive ability units,” Wilhelm stated. “My lab locations lots of emphasis on working with undergraduate college students, even highschool college students, and bridging the hole from undergraduates to graduate college students to postdocs. They study from one another and study to mentor one another.”
Extra data: Hamilton Younger et al, Towards the Scalable, Speedy, Reproducible, and Value-Efficient Synthesis of Personalised Nanomedicines on the Level of Care, Nano Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c04171