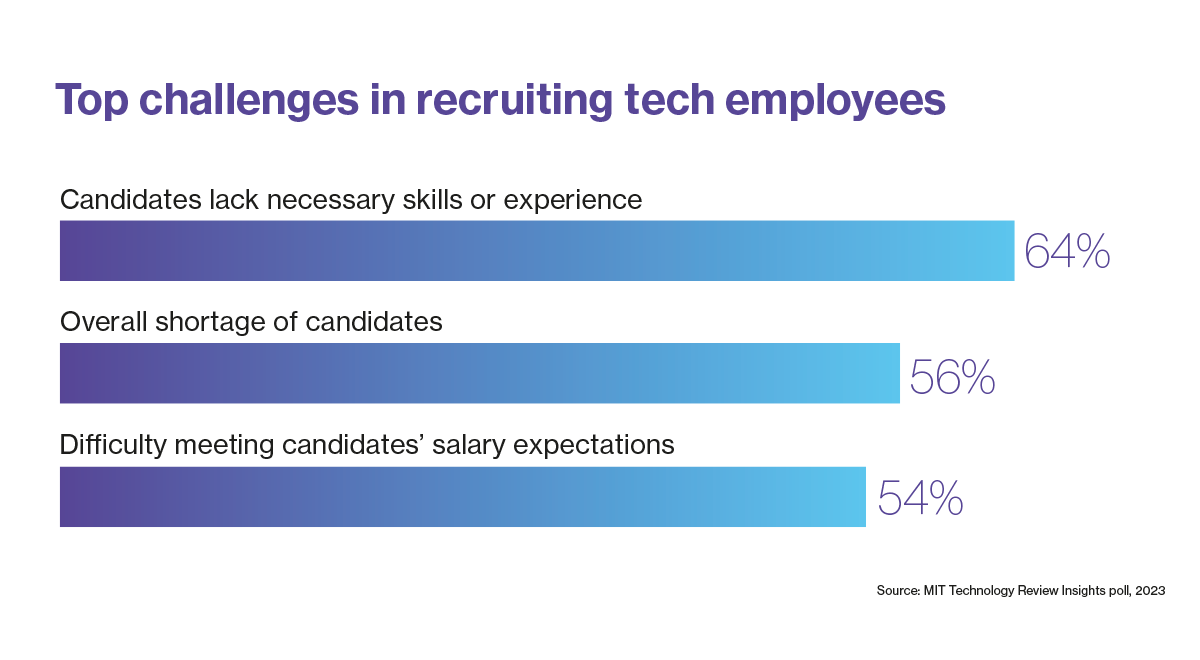
A 2021 Gartner survey of IT executives exhibits {that a} majority — 64% — imagine the continuing tech expertise scarcity is essentially the most important barrier to the adoption of rising applied sciences. By 2030, greater than 85 million jobs may go unfilled, “as a result of there aren’t sufficient expert individuals to take them,” in accordance with Korn Ferry. With out that proficient workforce, corporations may lose out on $8.5 trillion in annual income.
Firms are all searching for methods to handle this expertise scarcity within the quick time period. Because the Nice Resignation has given option to a Nice Reshuffle, with tech workers — together with these affected by the tech layoffs of late 2023 and early 2023 — looking for new roles that meet their wants for flexibility, work-life stability, and profession development, some employers have seen the chance to distinguish themselves with their profession choices. They compete fiercely to supply one of the best salaries, advantages, and dealing circumstances; courtroom freshly minted college graduates in addition to skilled expertise; and produce on contract and momentary employees to bridge the hole.
However tech doesn’t simply want short-term bridges. It wants long-term options. That’s why some corporations are trying earlier within the pipeline — and even constructing their very own pipeline. Modern tech leaders have begun concentrating on much less historically certified candidates, together with those that have simply completed secondary faculty, and they’re cultivating that future potential by new early-career packages.
A brand new strategy to early-career candidates
For many individuals, the normal path from schooling to profession has adopted a linear trajectory: Graduate highschool. Go to school, college, or commerce faculty. Get a job. However that strategy has its dangers — each for college students and for potential future employers.
For college kids, the price of a college diploma might be motive sufficient to pursue a special path. The School Board experiences the common U.S. in-state pupil pays $10,740 per 12 months for tuition at a public, four-year faculty (plus a mean of $11,950 per 12 months for room and board). In line with the identical knowledge, the common pupil will take out $30,000 in loans to earn a bachelor’s diploma.
These prohibitively excessive prices have impacted variety inside the tech business. College students who can’t afford a tech diploma don’t go to high school, after which they don’t be part of the business. Additional down the road, when future college students don’t see tech leaders who come from backgrounds much like their very own, they could go for a special path.
This content material was produced by Insights, the customized content material arm of MIT Expertise Evaluation. It was not written by MIT Expertise Evaluation’s editorial employees

