This unusual course of is extra steadily noticed in neurodegenerative illnesses and will provide insights into illness mechanisms.
In keeping with a brand new research printed in PLOS Biology by Kim Hai-Man Chow and colleagues from the Chinese language College of Hong Kong, neurons within the mind that re-enter the cell cycle after mitosis are susceptible to fast senescence, a course of noticed extra steadily in Alzheimer’s illness. This discovery offers perception into neurodegeneration and means that the strategies used might be utilized to review different distinctive cell populations within the mind.
Most neurons within the mind are post-mitotic, which means they’ve ceased to divide. For a few years, it had been assumed that this post-mitotic state was everlasting. Latest discoveries have proven {that a} small proportion of neurons re-enter the cell cycle, however little is thought about their destiny after they do.
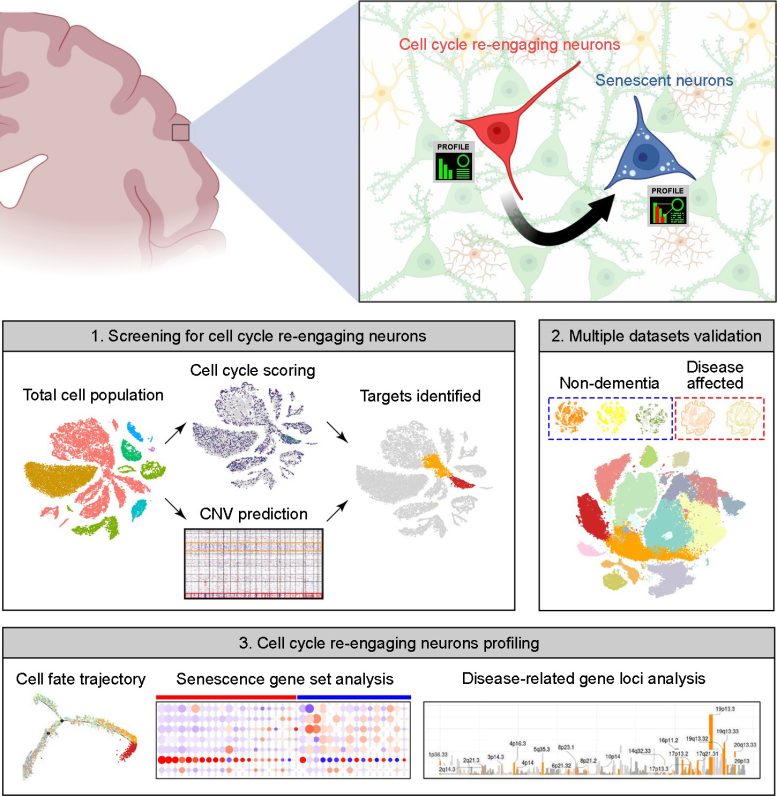
Abstract picture of the article. The higher half highlights neuronal cell cycle re-engagement is a stage continuing neuronal senescence and that their full molecular profiles can now be recognized by the bioinformatics pipeline we reported within the accepted manuscript. The underside half is a simplified model of Determine 1A from the paper. The higher panel is created by the BioRender software. Credit score: Kim Hei-Man Chow (CC-BY 4.0)
To deal with this query, the authors turned to publicly accessible databases of “snRNA-seq” information, through which particular person single nuclei are remoted and their RNA is sequenced, offering a snapshot of what a cell was doing on the time of isolation. The cell cycle proceeds by way of distinct phases, together with progress, DNA synthesis, division-specific progress, and mitosis, and every part is characterised by a particular set of proteins required to hold it out. This allowed the authors to make use of the set of RNAs to inform them which part of the cycle any particular nucleus was in.
Their information included info on over 30,000 nuclei, every of which was assigned a rating based mostly on the extent of expression of a set of about 350 cell cycle-related genes. They discovered that small populations of excitatory neurons had certainly re-entered the cell cycle. These cells didn’t, for probably the most half, proceed efficiently by way of the cell cycle to supply daughter neurons, nonetheless. As an alternative, cells present process re-entry additionally had elevated expression of genes related to senescence; in impact, the cells had reawakened solely to enter senescence.
Implications for Neurodegenerative Illnesses
Intriguingly, the authors discovered that neurons within the brains of Alzheimer’s illness sufferers reentered the cell cycle at the next charge, and that these neurons that had reentered the cell cycle and aged had elevated expression of a number of genes related to the next danger of Alzheimer’s illness, together with those who contribute on to the manufacturing of amyloid, the sticky protein that aggregates within the AD mind. Equally, brains from sufferers with Parkinson’s illness and Lewy physique dementia had a rise within the proportion of re-entering neurons in comparison with wholesome brains.
The neurobiological significance of this heightened re-entry for the diseased mind remains to be unclear, however the analytical method taken right here could provide deeper insights into neuronal subpopulations inside the mind, in addition to shedding mild on illness mechanisms in neurodegenerative illnesses.
“Due to the uncommon existence and random localization of those cells within the mind, their molecular profiles and disease-specific heterogeneities stay unclear,” Chow mentioned. “Whereas experimental validations of those findings in related human samples might be carried out sooner or later, the applicability of this analytical method in numerous illnesses and cross-species settings provides new alternatives and insights to complement mainstay histological-based approaches in learning the roles of those cells in mind getting older and illness pathogenesis.”
The authors add, “This bioinformatics analytical pipeline demonstrated will provide the sphere a brand new software to unbiasedly dissect cell cycle re-engaging and senescent neurons, and to dissect their heterogeneities in wholesome versus disease-affected brains.”
Reference: “Neuronal cell cycle reentry occasions within the getting older mind are extra prevalent in neurodegeneration and result in mobile senescence” by Deng Wu, Jacquelyne Ka-Li Solar and Kim Hei-Man Chow, 23 April 2024, PLOS Biology.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002559
The work was supported, partially, by grants from the next: The Hong Kong Analysis Grants Council (RGC)-Common Analysis Fund (GRF) (PI: ECS24107121, GRF16100219 and GRF16100718) (all to Ok.H-M.C) and the RGC- Collaborative Analysis Fund (CRF) (Co-I: C4033-19EF) (Ok.H-M.C); the Nationwide NaturalScience Basis-Wonderful Younger Scientists Fund 2020 (Ref: 32022087) (Ok.H-M.C); Alzheimer’s Affiliation Analysis Fellowship (PI: AARF-17-531566) (Ok.H-M.C).