Picture by Writer
Within the current century, knowledge is the brand new oil. Optimizing this knowledge storage is at all times important for getting efficiency from it. Choosing appropriate knowledge sorts and making use of the right normalization course of is crucial in deciding its efficiency.
This text will research crucial and generally used datatypes and perceive the normalization course of.
There are primarily two knowledge sorts in SQL: String and Numeric. Apart from this, there are extra knowledge sorts like Boolean, Date and Time, Array, Interval, XML, and many others.
String Knowledge Varieties
These knowledge sorts are used to retailer character strings. The string is commonly carried out as an array knowledge kind and comprises a sequence of parts, sometimes characters.
- CHAR(n):
It’s a fixed-length string that may comprise characters, numbers, and particular characters. n denotes the utmost size of the string in characters it will probably maintain.
Its most vary is from 0 to 255 characters, and the issue with this knowledge kind is that it takes the total area specified, even when the precise size of the string is lower than then. The additional string size is padded with additional reminiscence area.
- VARCHAR(n):
Varchar is just like Char however can assist strings of variable dimension, and there’s no padding. The storage dimension of this knowledge kind is the same as the precise size of the string.
It may retailer as much as a most of 65535 characters. Because of its variable dimension nature, its efficiency is not so good as the CHAR knowledge kind.
- BINARY(n):
It’s just like the CHAR knowledge kind however solely accepts binary strings or binary knowledge. It may be used to retailer photographs, information, or any serialized objects. There may be one other knowledge kind VARBINARY(n) which is analogous to the VARCHAR knowledge kind but additionally accepts solely binary strings or binary knowledge.
- TEXT(n):
This knowledge kind can also be used to retailer the strings however has a most dimension of 65535 bytes.
- BLOB(n): Stands for Binary Giant Object and maintain knowledge as much as 65535 bytes.
Apart from these are different knowledge sorts, like LONGTEXT and LONGBLOB, which might retailer much more characters.
Numeric Knowledge Varieties
- INT():
It may retailer a numeric integer, which is 4 bytes (32bit). Right here n denotes the show width, which could be a most of as much as 255. It specifies the minimal variety of characters used to show the integer values.
Vary:
- a) -2147483648 <= Signed INT <= 2147483647
- b) 0 <= Unsigned INT <= 4294967295
- BIGINT():
It may retailer a big integer of dimension as much as 64 bits.
Vary:
- a) -9223372036854775808 <= Signed BIGINT <= 9223372036854775807
- b) 0 <= Unsigned BIGINT <= 18446744073709551615
- FLOAT():
It may retailer floating level numbers with decimal locations approximated with a sure precision. It has some small rounding errors, so due to this, it’s not appropriate the place precise precision is required.
- DOUBLE():
This knowledge kind represents double-precision floating-point numbers. It may retailer decimal values with the next precision as in comparison with the FLOAT knowledge kind.
- DECIMAL(n, d):
This knowledge kind represents precise decimal numbers with a set precision denoted by d. The parameter d specifies the variety of digits after the decimal level, and the parameter n denotes the scale of the quantity. The utmost worth for d is 30, and its default worth is 0.
Another Knowledge Varieties
- BOOLEAN:
This knowledge kind shops solely two states that are True or False. It’s used to carry out logical operations.
- ENUM:
It stands for Enumeration. It permits you to select one worth from the listing of predefined choices. It additionally ensures that the saved worth is just from the desired choices.
For instance, contemplate an attribute coloration that may solely be 'Pink,' 'Inexperienced,' or 'Blue'. After we put these values in ENUM, then the worth of the coloration can solely be from these specified colours solely.
- XML:
XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language. This knowledge kind is used to retailer XML knowledge which is used for structured knowledge illustration.
- AutoNumber:
It’s an integer that mechanically increments its worth when every document is added. It’s utilized in producing distinctive or sequential numbers.
- Hyperlink:
It may retailer the hyperlinks of information and net pages.
This completes our dialogue on SQL Knowledge Varieties. There are lots of extra knowledge sorts, however the knowledge sorts that we’ve got mentioned are essentially the most generally used ones.
Normalization is the method of eradicating redundancies, inconsistencies, and anomalies from the database. Redundancy means the presence of duplicate values of the identical piece of information, whereas inconsistencies within the database characterize the identical knowledge exists in a number of codecs in a number of tables.
Database anomalies will be outlined as any sudden change or discrepancies within the database that aren’t imagined to exist. These modifications will be attributable to varied causes, equivalent to knowledge corruption, {hardware} failure, software program bugs, and many others. Anomalies can result in extreme penalties, equivalent to knowledge loss or inconsistency, so detecting and fixing them as quickly as doable is crucial. There are primarily three varieties of anomalies. We are going to briefly talk about every however check with this article if you wish to learn extra.
- Insertion Anomaly:
When the newly inserted row creates, inconsistency within the desk results in an insertion anomaly. For instance, we wish to add an worker to a corporation, however his division just isn’t allotted to him. Then we can’t add that worker to the desk, which creates an insertion anomaly.
- Deletion Anomaly:
Deletion anomaly happens after we wish to delete some rows from the desk, and another knowledge is required to be deleted from the database.
- Replace Anomaly:
This anomaly happens after we wish to replace some rows and which results in inconsistency within the database.
The normalization course of comprises a collection of pointers that make the design of the database environment friendly, optimized, and free from redundancies and anomalies. There are a number of varieties of regular kinds like 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, BCNF, and many others.
1. First Regular Kind (1NF)
The primary regular type ensures that the desk comprises no composite or multi-valued attributes. It signifies that just one worth is current in a single attribute. A relation is in first regular type if each attribute is just single-valued.
For Ex-
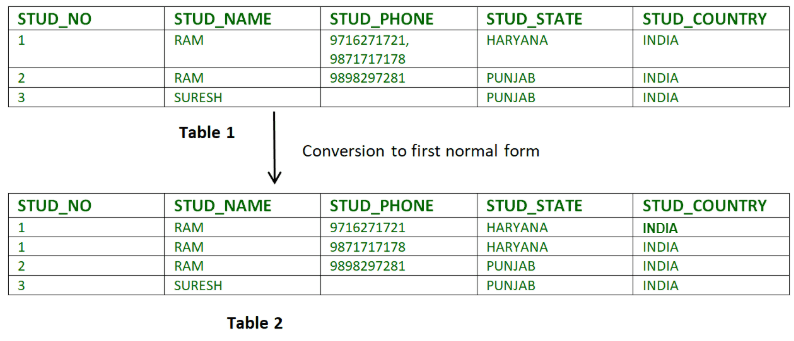
Picture by GeeksForGeeks
In Desk 1, the attribute STUD_PHONE comprises a couple of cellphone quantity. However in Desk 2, this attribute is decomposed into 1st regular type.
2. Second Regular Kind
The desk have to be within the first regular type, and there should not be any partial dependencies within the relations. Partial dependency signifies that the non-prime attribute (attributes which aren’t a part of the candidate key) is partially dependent or relies on any correct subset of the candidate key. For the relations to be within the second regular type, the non-prime attributes have to be totally purposeful and depending on your entire candidate key.
For instance, contemplate a desk named Workers having the next attributes.
EmployeeID (Main Key)
ProjectID (Main Key)
EmployeeName
ProjectName
HoursWorked
Right here the EmployeeID and the ProjectID collectively type the first key. Nonetheless, you may discover a partial dependency between EmployeeName and EmployeeID. It signifies that the EmployeeName relies solely on the a part of the first key (i.e., EmployeeID). For full dependency, the EmployeeName should rely on each EmployeeID and the ProjectID. So, this violates the precept of the second regular type.
To make this relation within the second regular type, we should break up the tables into two separate tables. The primary desk comprises all the worker particulars, and the second comprises all of the mission particulars.
Due to this fact, the Worker desk has the next attributes,
EmployeeID (Main Key)
EmployeeName
And the Mission desk has the next attributes,
Mission ID (Main Key)
Mission Identify
Hours Labored
Now you may see that the partial dependency is eliminated by creating two impartial tables. And the non-prime attributes of each tables rely on the entire set of the first key.
3. Third Regular Kind
After 2NF, nonetheless, the relations can have replace anomalies. It could occur if we replace just one tuple and never the opposite. That might result in inconsistency within the database.
The situation for the third regular type is that the desk must be within the 2NF, and there’s no transitive dependency for the non-prime attributes. Transitive dependency occurs when a non-prime attribute relies on one other non-prime attribute as a substitute of straight relying on the first attribute. Prime attributes are the attributes which can be a part of the candidate key.
Think about a relation R(A, B, C), the place A is the first key and B & C are the non-prime attributes. Let A→B and B→C be two Purposeful Dependencies, then A→C would be the transitive dependency. It signifies that attribute C just isn’t straight decided by A. B acts as a intermediary between them.
If a desk consists of a transitive dependency, then we will carry the desk into 3NF by splitting the desk into separate impartial relations.
4. Boyce-Codd Regular Kind
Though 2NF and 3NF take away many of the redundancies, nonetheless the redundancies aren’t 100% eliminated. Redundancy can happen if the LHS of the purposeful dependency just isn’t a candidate or tremendous key. A Candidate Key kinds from the prime attributes, and the Tremendous Key is a superset of the candidate key. To beat this difficulty, one other kind of purposeful dependency is accessible named Boyce Codd Regular Kind (BCNF).
For a desk to be in BCNF, the left-hand facet of a purposeful dependency have to be a candidate key or a brilliant key. A. For instance, for a purposeful dependency X→Y, X have to be a candidate or tremendous key.
Think about an Worker Desk that comprises the next attributes.
- Worker ID (major key)
- Worker Identify
- Division
- Division Head
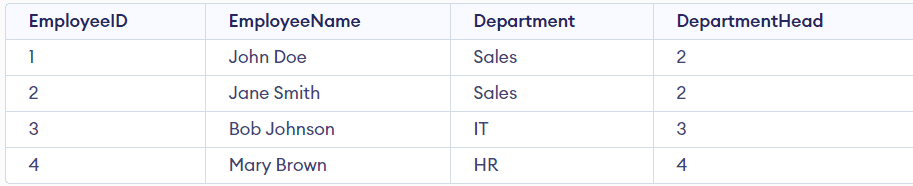
The EmployeeID is the first key that uniquely identifies every row. The Division attribute represents the division of a selected worker, and the Division Head attribute represents the Worker ID of the worker who’s the pinnacle of that particular division.
Now we’ll verify if this desk is within the BCNF. The situation is that the LHS of the purposeful dependency have to be a brilliant key. Under are the 2 purposeful dependencies of that desk.
Purposeful Dependency 1: Worker ID → Worker Identify, Division, Division Head
Purposeful Dependency 2: Division → Division Head
For the FD1, the EmployeeID is the first key, which can also be a brilliant key. However for FD2, Division just isn’t the tremendous key as a result of a number of staff will be in the identical division.
Due to this fact this desk violates the situation of BCNF. To fulfill the property of BCNF, we have to break up that desk into two separate tables: Workers and Departments. The Workers desk comprises the EmployeeID, EmployeeName, and Division, and the Division desk may have the Division and the Division Head.
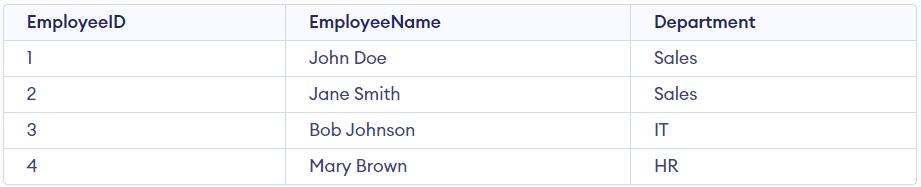
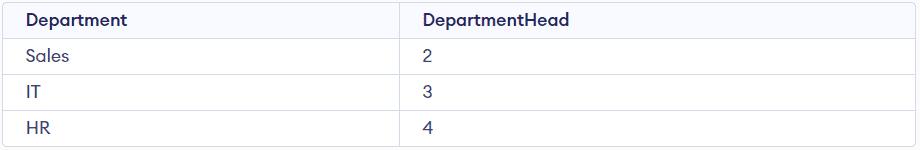
Now we will see in each tables that each one the purposeful dependencies are depending on the first keys, i.e., there are not any non-trivial dependencies.
We have now lined all of the well-known normalization methods, however apart from these, there are two extra regular kinds, specifically 4NF and 5NF. If you wish to learn extra about them, check with this article from GeeksForGeeks.
We have now mentioned essentially the most generally used knowledge sorts in SQL and the numerous Normalization methods in database administration techniques. Whereas designing a database system, we purpose to make it scalable, minimizing redundancy and guaranteeing knowledge integrity.
We are able to create a fragile steadiness between storage, precision, and reminiscence consumption by deciding on acceptable knowledge sorts. Additionally, the normalization course of helps eradicate knowledge anomalies and make the schema extra organized.
It’s all for as we speak. Till then, hold studying and continue learning.
Aryan Garg is a B.Tech. Electrical Engineering scholar, at the moment within the closing yr of his undergrad. His curiosity lies within the subject of Internet Growth and Machine Studying. He have pursued this curiosity and am desperate to work extra in these instructions.
