Analysis groups have efficiently regenerated mouse mind circuits utilizing rat stem cells, showcasing a brand new technique for restoring mind perform and learning interspecies mind growth.
These findings open up prospects for treating neurological ailments and understanding mind evolution, whereas additionally hinting at future scientific functions and moral challenges in utilizing comparable strategies for human organ transplantation.
Scientists Regenerate Neural Pathways in Mice With Cells From Rats
Two impartial analysis teams have efficiently restored mind circuits in mice utilizing neurons derived from rat stem cells. Just lately revealed within the journal Cell, these research present vital insights into mind tissue growth and open up new prospects for rejuvenating mind capabilities misplaced to ailments and getting old.
“This analysis helps to point out the mind’s potential flexibility in utilizing artificial neural circuits to revive mind capabilities,” says Kristin Baldwin, a professor at Columbia College in New York and corresponding creator of one of many two papers. Baldwin’s crew restored mouse olfactory neural circuits, the interconnected neurons within the mind answerable for the sense of scent, and their perform utilizing stem cells from rats.
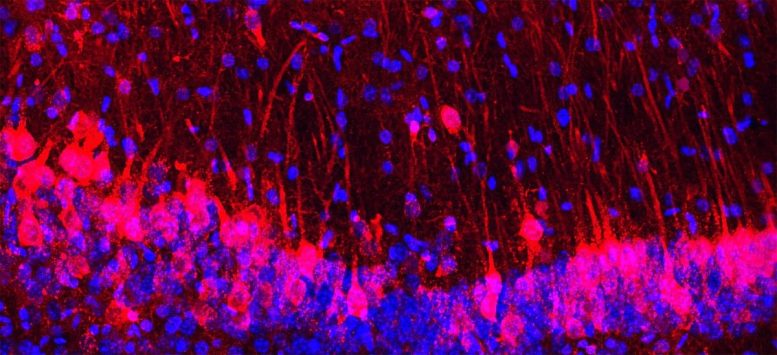
Mouse hippocampus with rat cells (purple) and nuclei of each mouse and rat cells (blue). Credit score: M. Khadeesh Imtiaz, Columbia College Irving Medical Middle
Interspecies Genetic Engineering and Its Implications
“Having the ability to generate mind tissues from one species inside one other may help us perceive mind growth and evolution in several species,” says Jun Wu, an affiliate professor on the College of Texas Southwestern Medical Middle in Dallas and corresponding creator of the opposite paper. Wu’s crew developed a CRISPR-based platform that might effectively establish particular genes that drive the event of particular tissues. They examined the platform by silencing a gene wanted for forebrain growth in mice after which restoring the tissue utilizing rat stem cells.
Mice and rats are two distinct species that developed independently for roughly 20 to 30 million years. In earlier experiments, scientists had been in a position to exchange pancreases in mice utilizing rat stem cells by means of a course of referred to as blastocyst complementation. For this course of to work, researchers inject rat stem cells into mice blastocysts—early-stage embryos—that lack the flexibility to develop a pancreas attributable to genetic mutations. The rat stem cells then developed into the lacking pancreas and complemented its perform.
Breakthroughs in Mind Tissue Regeneration
However, so far, producing mind tissues utilizing stem cells from a special species by means of blastocyst complementation has not been reported. Now, utilizing CRISPR, Wu’s crew examined seven totally different genes and located that knocking out Hesx1 may reliably generate mice that had no forebrain. The crew then injected rat stem cells in blastocysts of Hesx1 knockout mice, and the rat cells stuffed within the area of interest to kind a forebrain in mice. Rats have greater brains than mice, however the rat-origin forebrains developed on the similar tempo and measurement as that of mice. As well as, rat neurons had been in a position to transmit indicators to the neighboring mouse neurons and vice versa.
The researchers didn’t check whether or not the forebrain from rat stem cells modified mice’s behaviors. “There’s a scarcity of fine behavioral assessments to tell apart rats from mice,” Wu says. “However from our experiment, it looks as if these mice with rat forebrain don’t behave out of the odd.”
Superior Purposes and Future Prospects
Within the different research, Baldwin’s crew used particular genes to both kill or silence mouse olfactory sensory neurons used for the sense of scent and injected rat stem cells into the mice embryos. The silencing mannequin mimics what’s seen in neurodevelopmental issues, the place sure neurons can not talk nicely with the mind. The killing mannequin eliminated the neurons totally, simulating degenerative ailments.
They discovered blastocyst complementation restored mouse olfactory neural circuits in another way relying on the mannequin. When mouse neurons had been current however silent, the rat neurons helped kind better-organized mind areas in comparison with the killing mannequin. Nonetheless, when the crew examined these rat-mouse chimeras by coaching them to discover a hidden cookie buried in a cage, rat neurons had been finest at rescuing behaviors within the killing mannequin.
“This actually stunning consequence permits us to have a look at what’s totally different between these two illness fashions and attempt to establish mechanisms that might assist restore capabilities in both sort of mind illness,” Baldwin says. Her crew additionally examined blastocyst complementation in disease-model mice utilizing cells from mice with regular olfactory programs. They confirmed that intraspecies complementation rescued cookie discovering in each fashions.
Exploring the Frontiers of Medical Science
“Proper now, persons are being transplanted with stem cell-derived neurons for Parkinson’s illness and epilepsy in scientific trials. How nicely will that work? And can totally different genetic backgrounds between the affected person and the transplanted cells pose a barrier? This research gives a system by which we are able to consider the chances for similar species mind complementation at a a lot bigger scale than a scientific trial,” Baldwin says.
Blastocyst complementation remains to be removed from scientific utility in people, however each research counsel stem cells from totally different species can synchronize their growth with the host’s mind.
Scientists have additionally been experimenting with rising human organs in different species like pigs utilizing blastocyst complementation. Final yr, scientists generated embryonic kidneys utilizing human stem cells in pigs, providing a possible answer for the many individuals on waitlists for transplants.
“Our aspiration is to complement pig organs with a sure proportion of human cells, with the intention of bettering outcomes for organ recipients. However presently, there are nonetheless many technical and moral challenges that we have to overcome earlier than we are able to check this in scientific trials,” says Wu.
Apart from the research’ implications in medication, the groups are additionally enthusiastic about utilizing this strategy to review the brains of many wild rodents that weren’t accessible within the laboratory setting.
“There are over 2,000 dwelling rodent species on this planet. A lot of them behave in another way from the rodents we generally research within the lab. Interspecies neural blastocyst complementation can doubtlessly open the door to review how the brains from these species develop, evolve, and performance,” Wu says.
For extra on this analysis, see Mice Engineered With Rat Neurons Present Superior Sensory Abilities.
References:
“Practical sensory circuits constructed from neurons of two species” by Benjamin T. Throesch, Muhammad Khadeesh bin Imtiaz, Rodrigo Muñoz-Castañeda, Masahiro Sakurai, Andrea L. Hartzell, Kiely N. James, Alberto R. Rodriguez, Greg Martin, Giordano Lippi, Sergey Kupriyanov, Zhuhao Wu, Pavel Osten, Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte, Jun Wu and Kristin Ok. Baldwin, 25 April 2024, Cell.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.03.042