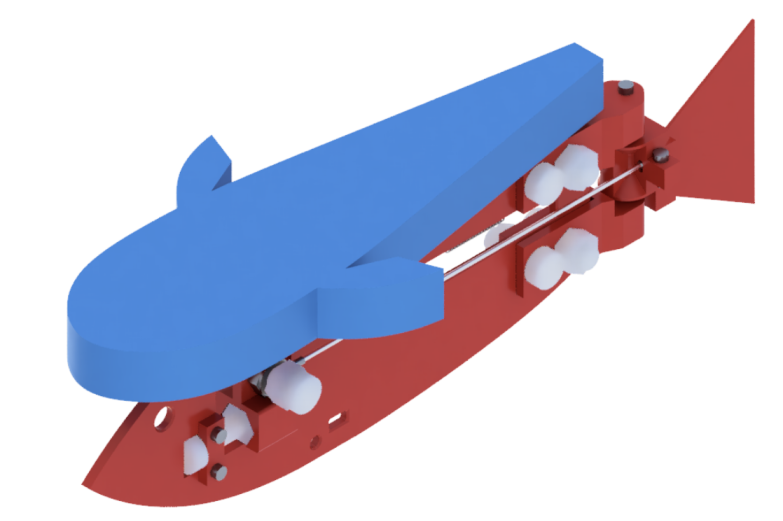
Robotic fish. Picture credit score: Tsam Lung You
The robotic fish was fitted with a twisted and coiled polymer (TCP) to drive it ahead, a lightweight low value gadget that depends on temperature change to generate motion, which additionally limits its velocity.
A TCP works by contracting like muscle tissues when heated, changing the vitality into mechanical movement. The TCP used on this work is warmed by Joule heating – the cross of present by means of {an electrical} conductor produces thermal vitality and heats up the conductor. By minimising the space between the TCP on one aspect of the robotic fish and the spring on the opposite, this prompts the fin on the rear, enabling the robotic fish to achieve new speeds. The undulating flapping of its rear fin was measured at a frequency of 2Hz, two waves per second. The frequency of the electrical present is similar because the frequency of tail flap.
The findings, revealed on the sixth IEEE-RAS Worldwide Convention on Delicate Robotics (RoboSoft 2023), present a brand new path to elevating the actuation – the motion of inflicting a machine or gadget to function – frequency of TCPs by means of thermomechanical design and exhibits the potential of utilizing TCPs at excessive frequency in aqueous environments.
Lead writer Tsam Lung You from Bristol’s Division of Engineering Arithmetic mentioned: “Twisted and coiled polymer (TCP) actuator is a promising novel actuator, exhibiting engaging properties of sunshine weight, low-cost excessive vitality density and easy fabrication course of.
“They are often made out of very simply assessable supplies resembling a fishing line and so they contract and supply linear actuation when heated up. Nevertheless, due to the time wanted for warmth dissipation through the leisure section, this makes them sluggish.”
By optimising the structural design of the TCP-spring antagonistic muscle pair and bringing their anchor factors nearer collectively, it allowed the posterior fin to swing at a bigger angle for a similar quantity of TCP actuation.
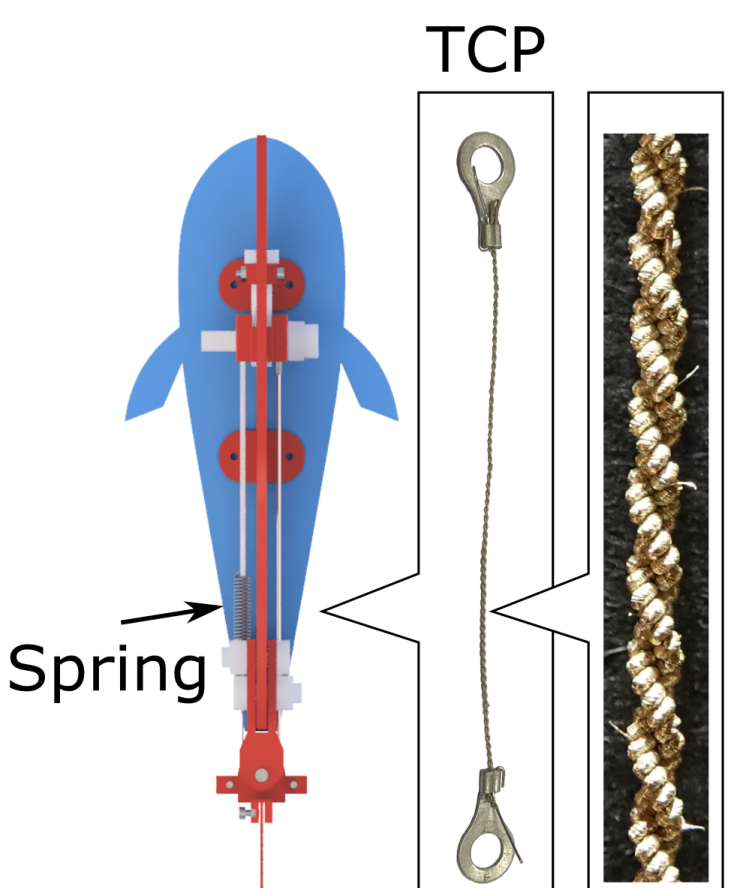
Antagonistic muscle tissues. Picture credit score: Tsam Lung You
Though this requires higher power, TCP is a powerful actuator with excessive work vitality density, and continues to be capable of drive the fin.
Till now, TCPs have been largely used for functions resembling wearable gadgets and robotic arms. This work opens up extra areas of software the place TCP can be utilized, resembling marine robots for underwater exploration and monitoring.
Tsam Lung You added: “Our robotic fish swam on the quickest actuation frequency present in an actual TCP software and in addition the best locomotion velocity of a TCP software up to now.
“That is actually thrilling because it opens up extra alternatives of TCP software in several areas.”
The group now plan to broaden the size and develop a knifefish-inspired TCP-driven ribbon fin robotic that may swim agilely in water.

College of Bristol
is among the hottest and profitable universities within the UK.

