A quantum web would primarily be unhackable. Sooner or later, delicate data—monetary or nationwide safety information, as an example, versus memes and cat photos—would journey via such a community in parallel to a extra conventional web.
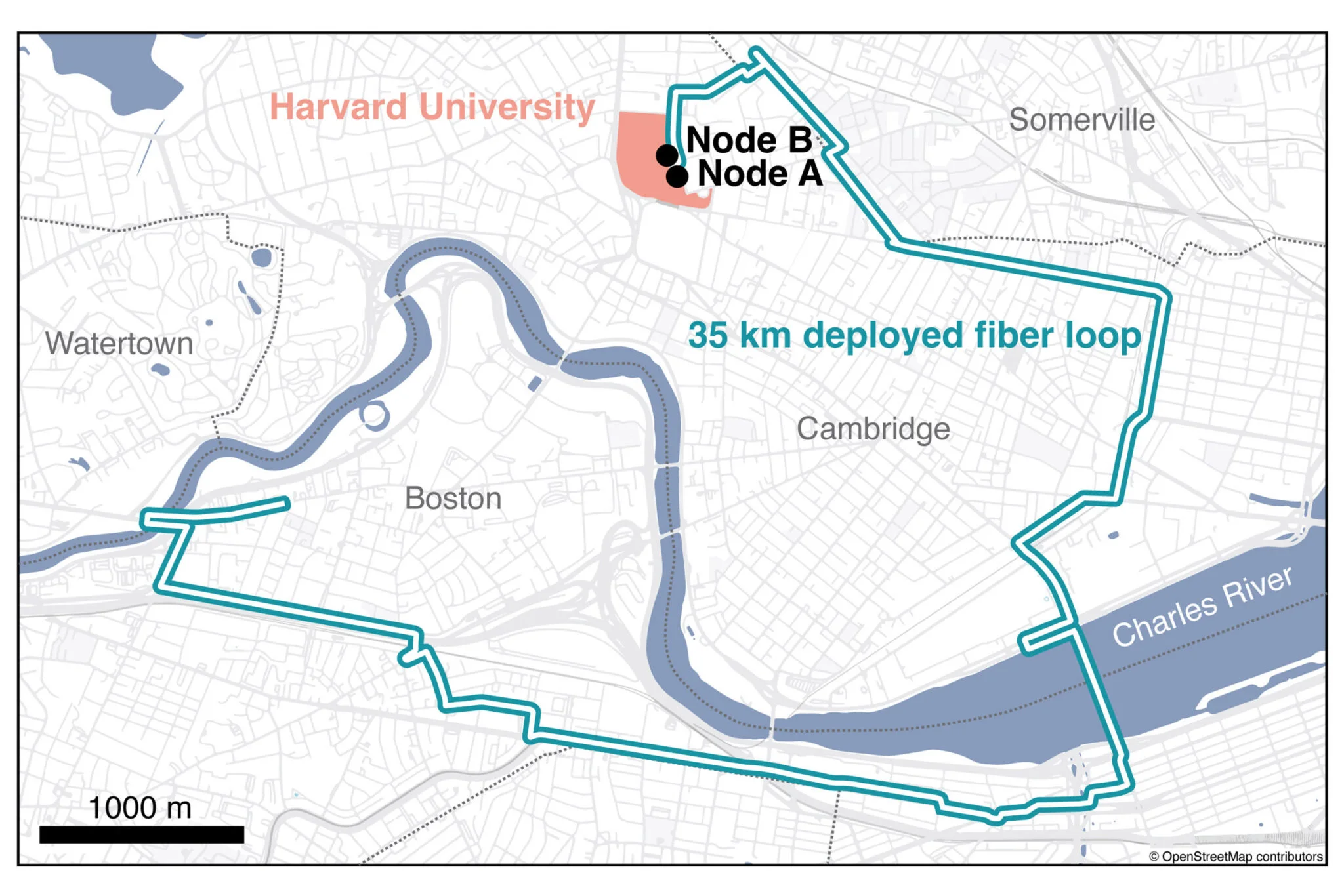
After all, constructing and scaling methods for quantum communications isn’t any simple activity. Scientists have been steadily chipping away on the drawback for years. A Harvard workforce just lately took one other noteworthy step in the proper route. In a paper revealed this week in Nature, the workforce says they’ve despatched entangled photons between two quantum reminiscence nodes 22 miles (35 kilometers) aside on present fiber optic infrastructure below the busy streets of Boston.
“Displaying that quantum community nodes may be entangled within the real-world surroundings of a really busy city space is a vital step towards sensible networking between quantum computer systems,” Mikhail Lukin, who led the venture and is a physics professor at Harvard, stated in a press launch.
A technique a quantum community can transmit data is through the use of entanglement, a quantum property the place two particles, probably photons on this case, are linked so a change within the state of 1 tells us in regards to the state of the opposite. If the sender and receiver of knowledge every have considered one of a pair of entangled photons, they’ll securely transmit information utilizing them. This implies quantum communications will depend on producing huge numbers of entangled photons and reliably sending them to far-off locations.
Scientists have despatched entangled particles lengthy distances over fiber optic cables earlier than, however to make a quantum web work, particles might want to journey tons of or hundreds of miles. As a result of cables have a tendency to soak up photons over such distances, the data will likely be misplaced—until it may be periodically refreshed.
Enter quantum repeaters.
You may consider a repeater as a sort of web fuel station. Info passing via lengthy stretches of fiber optic cables naturally degrades. A repeater refreshes that data at common intervals, strengthening the sign and sustaining its constancy. A quantum repeater is identical factor, solely it additionally preserves entanglement.
That scientists have but to construct a quantum repeater is one purpose we’re nonetheless a methods off from a working quantum web at scale. Which is the place the Harvard examine is available in.
The workforce of researchers from Harvard and Amazon Internet Providers (AWS) have been engaged on quantum reminiscence nodes. Every node homes a chunk of diamond with an atom-sized gap, or silicon-vacancy middle, containing two qubits: one for storage, one for communication. The nodes are principally small quantum computer systems, working at close to absolute zero, that may obtain, file, and transmit quantum data. The Boston experiment, in response to the workforce, is the longest distance anybody has despatched data between such units and an enormous step in the direction of a quantum repeater.
“Our experiment actually put us able the place we’re actually near engaged on a quantum repeater demonstration,” Can Knaut, a Harvard graduate pupil in Lukin’s lab, advised New Scientist.
Subsequent steps embody increasing the system to incorporate a number of nodes.
Alongside these traces, a separate group in China, utilizing a unique approach for quantum reminiscence involving clouds of rubidium atoms, just lately stated they’d linked three nodes 6 miles (10 kilometers) aside. The identical group, led by Xiao-Hui Bao on the College of Science and Know-how of China, had beforehand entangled reminiscence nodes 13.6 miles (22 kilometers) aside.
It’ll take much more work to make the expertise sensible. Researchers want to extend the speed at which their machines entangle photons, for instance. However as every new piece falls into place, the prospect of unhackable communications will get a bit nearer.

