Researchers need to know why cells produce tiny packages known as vesicles — and whether or not these bundles might be used for remedy.
Graça Raposo was a younger postdoc within the Netherlands in 1996 when she found that cells in her laboratory have been sending secret messages to one another.
She was exploring how immune cells react to overseas molecules. Utilizing electron microscopy, she noticed how cells ingested these molecules, which grew to become caught to the floor of tiny intracellular vesicles. The cells then spat out the vesicles, together with the overseas cargo, and Raposo captured them.
Subsequent, she offered them to a different kind of immune cell. It reacted to the package deal simply as it might to a overseas molecule1.
It was an indication that these extracellular vesicles (EVs, also referred to as exosomes) is perhaps transmitting info between cells. “We knew that exosomes existed, however at the moment they have been typically regarded as a means of eliminating a cell’s trash,” says Raposo. “It was thrilling to search out that some may have necessary organic capabilities — even when not everybody believed it at first.”
Simply two years later, collectively together with her colleagues, Raposo, who’s now on the Curie Institute in Paris, discovered that exosomes derived from antitumour immune cells might be enlisted to suppress cancers in mice2.
Different scientists jumped on the idea, and commenced to search out exosomes being spat out from every kind of cell. Curiosity exploded after researchers found that the little packages may include not solely proteins, but additionally nucleic acids. In 2007, as an example, a Swedish crew discovered that the vesicles harboured small RNA molecules3. That implied that exosomes may affect gene expression after they reached their vacation spot cells. The variety of EV-related publications rose steeply, and has tripled previously 5 years.
The form-shifting blobs that shook up cell biology
As the sector has matured, researchers have set out more-stringent guidelines for what counts as an EV and have established pointers for the best way to determine these minuscule bubbles in dwelling techniques. Scientists are studying ever extra about how vesicles transfer out and in of cells and throughout the complicated terrain between them, in addition to in regards to the roles of vesicles in well being and illness. EVs may, for instance, be chargeable for cancers spreading within the physique, or may even be concerned within the ageing course of.
It’s all very a lot a piece in progress, however there’s a robust sense of promise within the discipline. Researchers hope that EVs might be exploited to diagnose, and even deal with, varied illnesses. The variety of patent purposes and registered scientific trials has soared in parallel with the rise in publications.
However there’s additionally a darkish facet. To the priority of regulatory companies, tons of of personal clinics and corporations promoting unproven EV-based therapies have sprung up world wide, providing to deal with something from Alzheimer’s illness to baldness. “The variety of direct-to-consumer corporations peddling EV remedies with out proof of security or efficacy is surprising,” says stem-cell biologist Darius Widera on the College of Studying, UK.
Tiny however mighty
It may be tough sufficient to see entire cells beneath a microscope, not to mention detect the nanoscale particles that they eject. Scientists who’ve embraced this problem have outlined round half a dozen broad lessons of EVs in keeping with the best way through which they’re created and expelled.
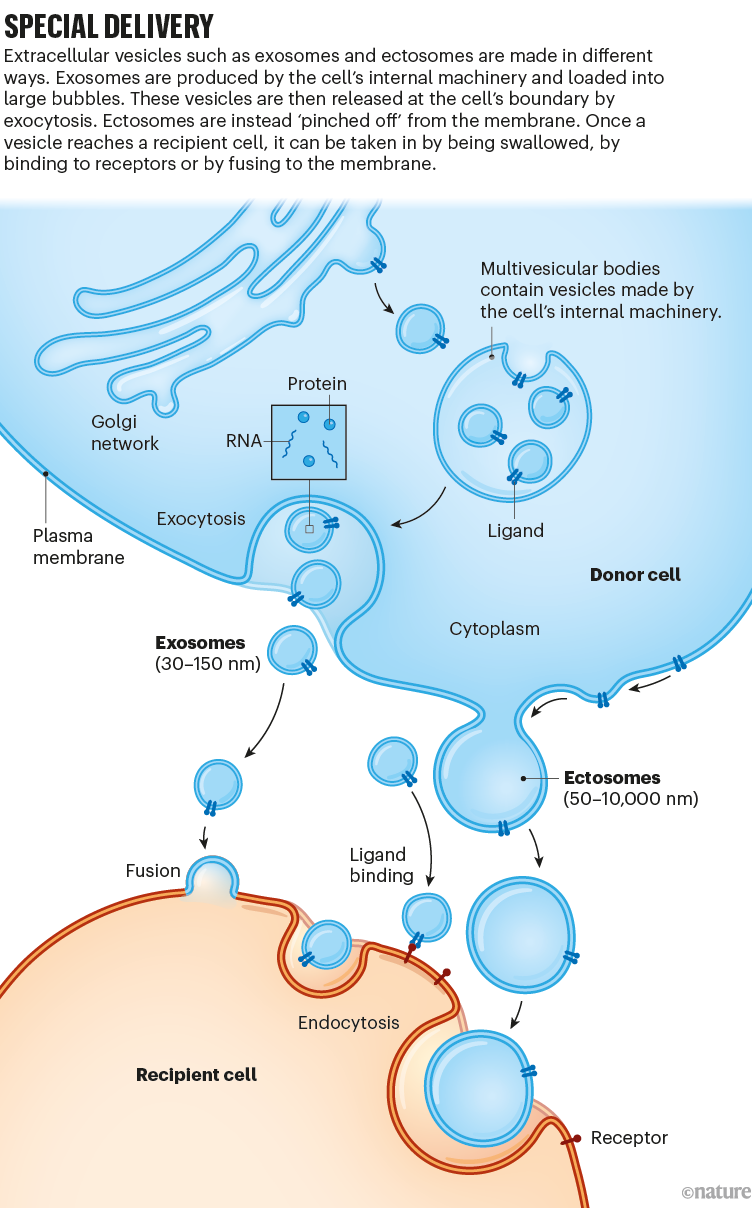
The lessons have overlapping sizes. Exosomes, with a dimension vary of 30–150 nanometres, are the smallest class. They’re produced by equipment contained in the cell that traffics molecules and particles to the place they must be. Exosomes are held in bigger packages, which transfer to the cell membrane, fuse with it and launch the vesicles to the surface. One other class, often known as ectosomes, has the widest dimension vary: 50–10,000 nm. Ectosomes pinch off from the sting of the primary cell membrane (see ‘Particular supply’).
In these lessons, tons of, if not hundreds, of sorts of EV carrying a broad vary of cargo may exist, created by pathways in numerous cells at varied occasions and in numerous states of well being. Practically all sorts of cell (together with these from crops, fungi and micro organism) generate a wealthy number of vesicles. Many varieties overlap by way of dimension and the repertoire of marker molecules on their surfaces, so they’re laborious to distinguish.
What all these vesicles are doing is an enormous open query. Many merely perform the cell’s garbage — by-products and toxins, as an example — and ship a few of it to the liver for breakdown. Others talk with cells in the identical or totally different tissues. Some vesicles do that by way of signalling molecules on the cells’ floor (such because the EVs from Raposo’s immune cells); others achieve this by getting into cells and delivering their cargo internally. But others might be concerned in oblique communication, for instance, by releasing their contents exterior cells to create a supportive setting for themselves.
EVs launched from wholesome cells are recognized to manage a variety of physiological processes, from triggering an immune response to sustaining mobile equilibrium. These from diseased cells may assist to unfold the illness. EVs from tumour cells, for instance, carry cancer-promoting proteins and RNA molecules to different websites within the physique, the place they’ll develop as metastases. In neurodegenerative illnesses, resembling Alzheimer’s, which can be related to misfolded proteins, together with amyloid-β, tau and α-synuclein, scientists suspect that EVs secreted by neurons is perhaps chargeable for spreading these proteins — and due to this fact the illness — throughout the mind.
These discoveries have been hard-won owing to the technical challenges of learning such tiny and terribly assorted particles. In actual fact, a lot of the early work within the discipline has proved tough to interpret due to confusion associated to each nomenclature and claims. “Till not too long ago it was just like the Wild West,” says Rienk Nieuwland on the Amsterdam College Medical Facilities. Measurements of EVs may fluctuate by a number of orders of magnitude, even in customary blood samples, he says, and a few scientists frightened that the uncertainties threatened to undermine the entire discipline.
Over the previous three years, the Worldwide Society for Extracellular Vesicles in Mount Royal, New Jersey, has tried to carry order to the sector by recommending standardized strategies for making ready EVs and for naming them. Nieuwland says that measurements have grow to be a lot much less variable between labs.
Researchers nonetheless have a variety of questions in regards to the biology of EVs. For instance, how precisely do vesicles discover their strategy to their goal cells? And as soon as inside, does their cargo operate as assumed? Maybe the most important take a look at for the sector is whether or not EVs behave in the identical means within the physique as they do in cell tradition. To know for sure, scientists must see how these tiny vesicles act in a complete organism. “I’ve by no means seen conclusive proof that EVs do something in vivo,” says Nieuwland.
Supply service
Nonetheless, researchers say that sufficient is understood about EVs to justify explorations of some areas of scientific potential. Scientists have realized that these cargo carriers may function Trojan horses to enter explicit cells and alter them in helpful methods — for instance, by concentrating on most cancers cells for destruction, or delivering medicine or gene remedy.
Jan Lötvall on the College of Gothenburg in Sweden impressed many drug builders when his crew discovered that exosomes may transport RNA3. The researchers confirmed that the exosomes may cross from one immune cell to a different and that their contents might be translated into biologically lively proteins, no less than in vitro. (Whether or not cargo RNA is able to being translated in recipient cells in vivo is the topic of a lot debate.)
Matthew Wooden on the College of Oxford, UK, instantly noticed the potential for delivering remedy to cells. He had been attempting to develop remedies for inherited genetic issues resembling Duchenne muscular dystrophy for greater than a decade when he learn Lötvall’s paper.
He and others thought EVs might be used within the rising discipline of gene remedy, which was exhibiting promise for changing or modifying faulty genes. “However the problem was at all times to ship the genetic remedy to the precise cells in the precise tissue,” says Wooden. Muscular dystrophy, for instance, impacts all muscle tissue within the physique, together with the center, and in addition impacts the mind, so genetic abnormalities would must be corrected in these locations with out disturbing cells in different, wholesome tissues. That’s an enormous ask, says Wooden.
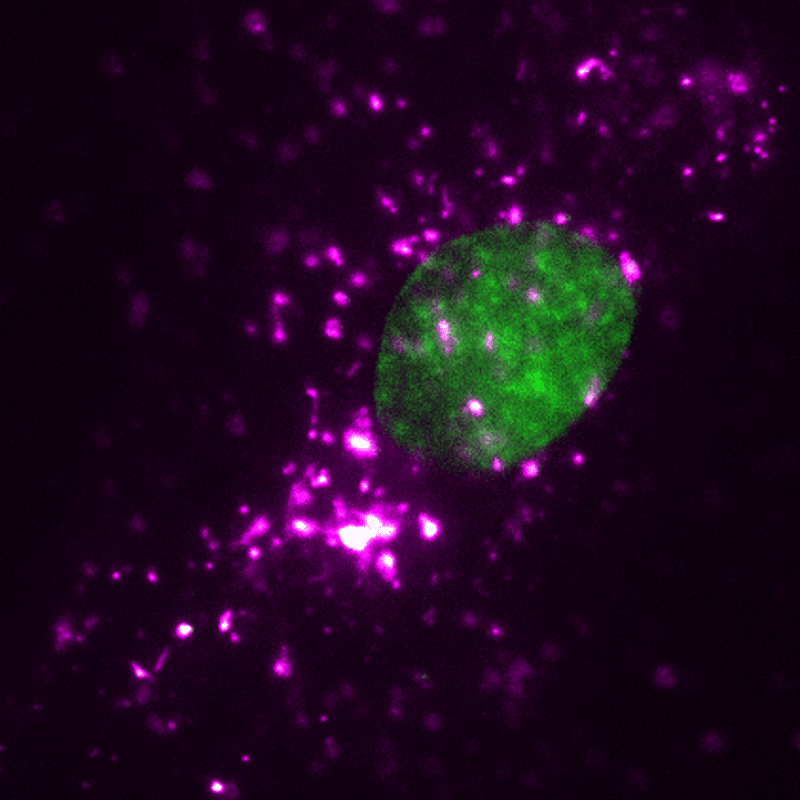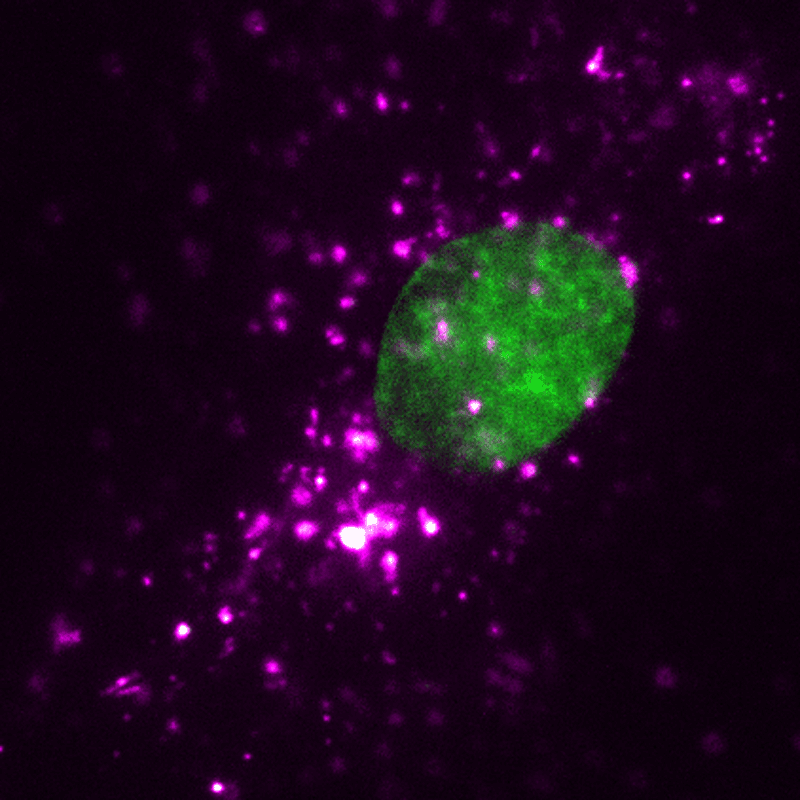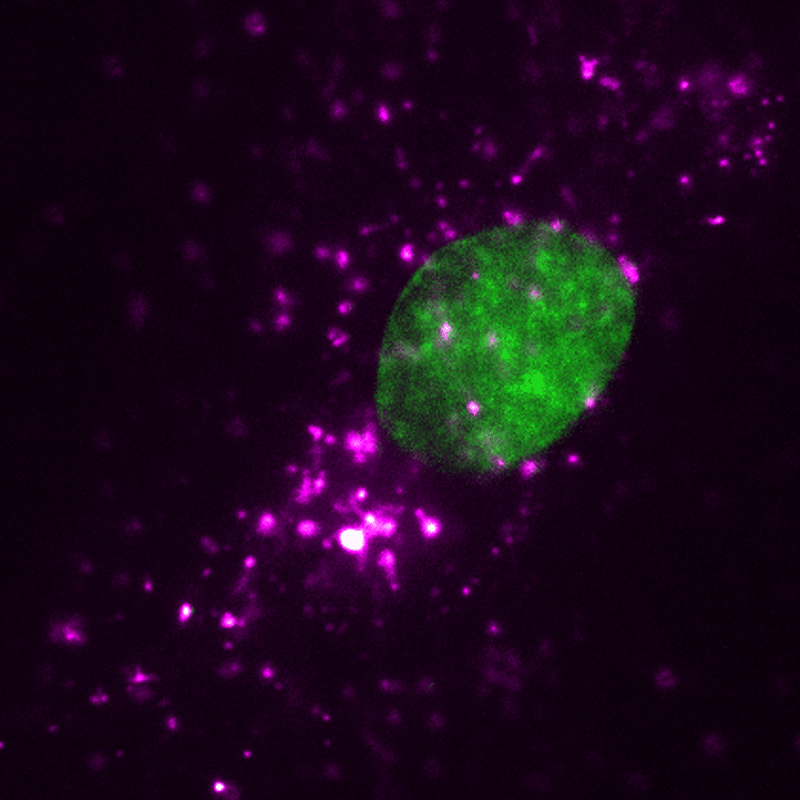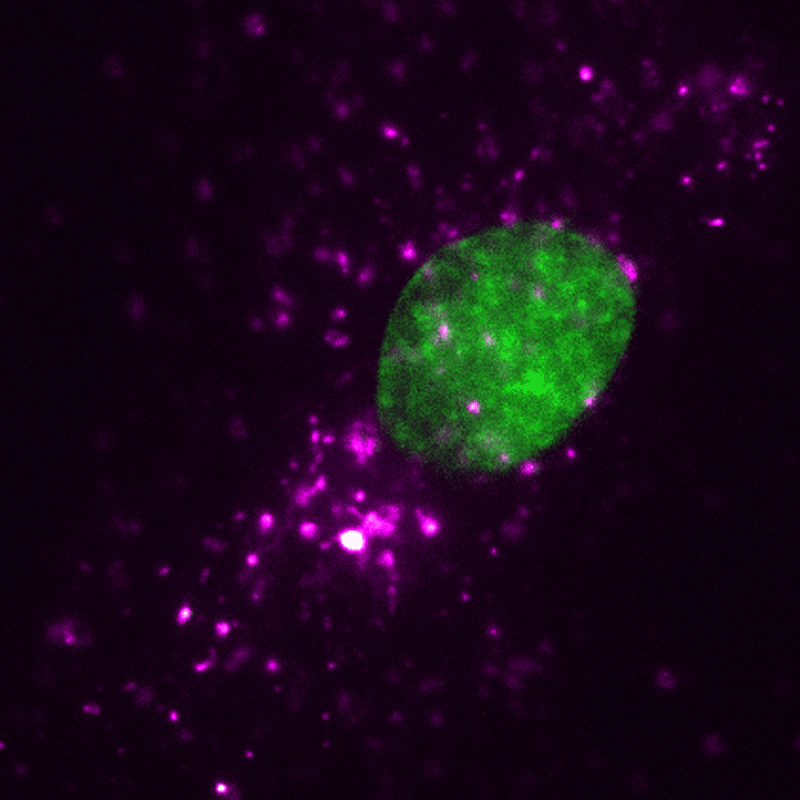
EVs (magenta) may be tracked in a dwelling human cell (nucleus proven in inexperienced) utilizing super-resolution microscopy. Credit score: ONI (Oxford Nanoimaging)/Christopher Gregory (College of Edinburgh Centre for Irritation Analysis)
A technique researchers have been getting genes to cells was inside artificial nanoparticles — the identical methodology now utilized in messenger-RNA vaccines for COVID-19. Wooden questioned whether or not naturally produced EVs might need the potential to make therapies higher tolerated than artificial particles, which might trigger irritation. He was satisfied that, if appropriately engineered, they may make glorious gene-therapy vectors.
It took him 4 years to show the precept that EVs may certainly be designed to ship practical genetic materials to focus on cells. For this take a look at, he labored on the misfolded proteins of Alzheimer’s illness. He remoted EVs from a kind of immune cell in mice, designed them to focus on neurons and obtained them to load up a small RNA that switches off a gene for an enzyme concerned within the illness. When he injected the vesicles into mice, ranges of the enzyme dropped by two-thirds4.
In 2021, he and his colleagues made EVs that may carry and ship helpful proteins, and used them to suppress irritation that contributes to skeletal muscle weak point in a mouse mannequin of Duchenne muscular dystrophy5.
Many corporations, together with Oxford-based Evox Therapeutics, co-founded by Wooden, are actually growing EV techniques to ship gene remedy for varied illnesses. The expertise has grow to be ever extra subtle — EVs may be made to hold varied molecules that permit a tissue to specific new genes, silence them and even edit genes. Up to now, no gene remedy utilizing EVs has been registered for a scientific trial.
Some researchers are whether or not EVs can ship different sorts of molecule. Scientists in China are finishing up early-stage scientific trials through which EVs derived from an individual’s personal tumour cells are loaded with a chemotherapeutic agent, resembling methotrexate or cisplatin6. And small trials utilizing engineered EVs to deal with some cancers are ongoing7.
Some remedies require a selected kind of EV. However for therapies that require EVs merely as a vessel, most researchers make them from a kind of stem cell known as a mesenchymal stem cell. That’s as a result of these cells have been examined, safely and infrequently efficiently, in tons of of scientific trials for cardiovascular, neurological, autoimmune and different issues — though none has but been permitted by the US Meals and Drug Administration (FDA).
Scientists initially thought that the therapeutic energy of mesenchymal stem cells lay of their potential to distinguish into alternative cell sorts. However in 2010, Sai Kiang Lim on the A*STAR Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology in Singapore and her colleagues confirmed8 that the cells’ fascinating properties have been conveyed by a category of significantly small EVs that they secreted. The main target of many scientific trials moved from the cells themselves to their EVs.
EVs have necessary benefits over utilizing entire stem cells for remedy. Cells can replicate, and carry a small danger of engrafting themselves or of differentiating into cells that would trigger immune reactions. EVs keep away from these dangers and are simpler and cheaper to fabricate, retailer and transport. They’re being examined in early-phase scientific trials for a variety of issues through which irritation performs a component in worsening the situation, resembling for stroke or COVID-19.
Their potential in lots of different situations can be being actively studied in animal fashions, together with in myocardial infarction and pores and skin issues. They may even have anti-ageing potential. When previous mice have been handled with EVs secreted from mesenchymal stem cells derived from the fats of younger mice, they lived longer, have been much less frail and had younger biochemical profiles than management animals did9.
Helpful markers
In addition to potential remedies, EVs may function telltale indicators of illness. Completely different EVs, together with these from diseased cells, are inclined to have their very own signature mixture of molecules resembling proteins, RNAs and lipids that may function biomarkers. Many corporations are growing EV-based diagnostic exams for varied issues, significantly these through which early detection can enhance prognosis.
In 2019, the FDA granted entry to an accelerated approval course of for an EV-based diagnostic take a look at for the primary time — a urine take a look at for prostate most cancers made by biotechnology agency Exosome Diagnostics in Waltham, Massachusetts. One other firm, Exosome Sciences in San Diego, California, is growing a take a look at of blood plasma often known as TauSome. This detects tau protein that’s related to EVs to diagnose persistent traumatic encephalopathy, a neurodegenerative mind dysfunction that outcomes from repetitive head trauma. In a preliminary scientific research10, the take a look at recognized larger tau ranges in former US Nationwide Soccer League gamers in contrast with athletes who had participated in non-contact sports activities.
EVs have one other function that makes them enticing for prognosis. As a result of exosomes usually include genetic materials, “that opens the thrilling prospect of growing very delicate diagnostic exams”, says neuroscientist Andrew Hill at Victoria College in Melbourne, Australia, who’s engaged on exams to detect neurodegenerative illnesses, together with Alzheimer’s, based mostly on ranges of microRNAs in EVs within the blood. Other than the diagnostic potential, these exams may additionally assist researchers to grasp extra in regards to the pathogenic mechanisms in these illnesses, they are saying.
Questionable clinics
A shadier market has already developed in parallel, nonetheless. Clinics are sprouting up world wide providing EV remedies for varied situations, from the beauty to the life-threatening. A 2023 evaluation11 discovered that round 110 corporations market such remedies, a number of of which function clinics in a number of nations. “That is all taking place with none proof of security or efficacy,” says Widera, a co-author of the paper. “The entire grey-zone space is poorly regulated.” The Worldwide Society for Extracellular Vesicles has warned in regards to the danger of such unproven therapies, which it says might be contaminated or just ineffective and a waste of cash.
“My fear is just not that the EVs might be intrinsically unhealthy,” says Lim. “The issue is that nobody checks their manufacturing — it is extremely simple to introduce contaminants, like endotoxin or micro organism.” Certainly, in 2019, the FDA put out a press release warning of the risks after a number of individuals in Nebraska had severe opposed unwanted side effects, together with sepsis, following therapy with exosomes. The FDA stated that clinics that provide unregulated merchandise “deceive sufferers with unsubstantiated claims in regards to the potential for these merchandise to stop, deal with or remedy varied illnesses or situations”. Claims by many clinics that they don’t must be regulated are “merely unfaithful”, the company says.
Regardless of issues about EV clinics, scientists who’re within the fundamentals of those carriers are forging forward. They’re attempting to work out precisely how and the place vesicles ship their cargo, and the best way to exploit their potential to distribute messages and mobile elements. The progress from first discoveries to tried medical purposes has been astonishingly fast, says Raposo. “However there’s nonetheless so much we’ve got to grasp.”